55 Years Ago: Five Months Until the Moon Landing
Following the success of the Apollo 8 circumlunar mission, NASA believed that it could achieve a Moon landing by the summer of 1969 and meet President John F. Kennedy’s goal. Much work remained to accomplish that objective. Three crews and their backups trained for the next three Apollo missions while workers at NASA’s Kennedy Space […]

Following the success of the Apollo 8 circumlunar mission, NASA believed that it could achieve a Moon landing by the summer of 1969 and meet President John F. Kennedy’s goal. Much work remained to accomplish that objective. Three crews and their backups trained for the next three Apollo missions while workers at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida prepared the spacecraft and rockets for those flights. With Apollo 9 in the home stretch to test the Lunar Module (LM) in Earth orbit in early March, preparations also continued for Apollo 10 in May, a lunar orbit test of the LM that served as a dress rehearsal for the Moon landing, and for Apollo 11, the landing mission itself planned for July.
Apollo 8
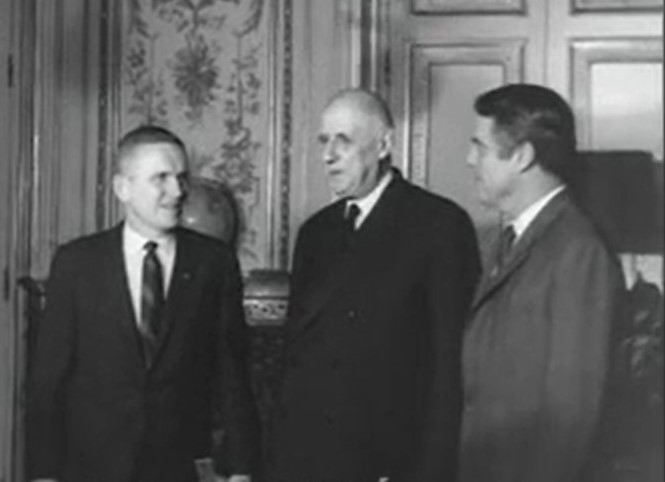



Left: Apollo 8 astronaut Frank Borman and his wife Susan, at left, meet the Royal family at Buckingham Palace during the London stop of their European tour. Middle: Borman, left, meets with French President Charles de Gaulle and U.S. Ambassador to France R. Sargent Shriver during the Paris stop of the tour. Right: In Brussels, Borman, left, presents a model of the Saturn V rocket to Jean Rey, president of the European Commission.
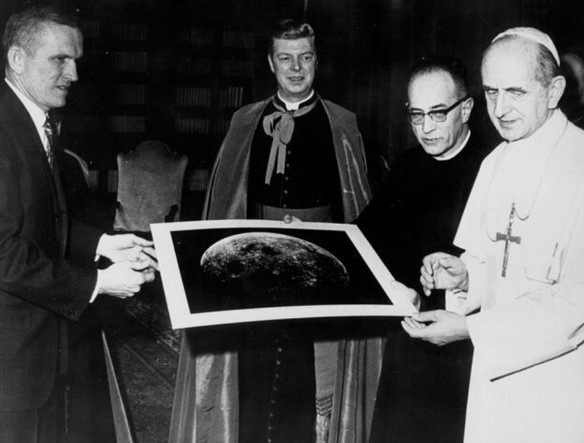
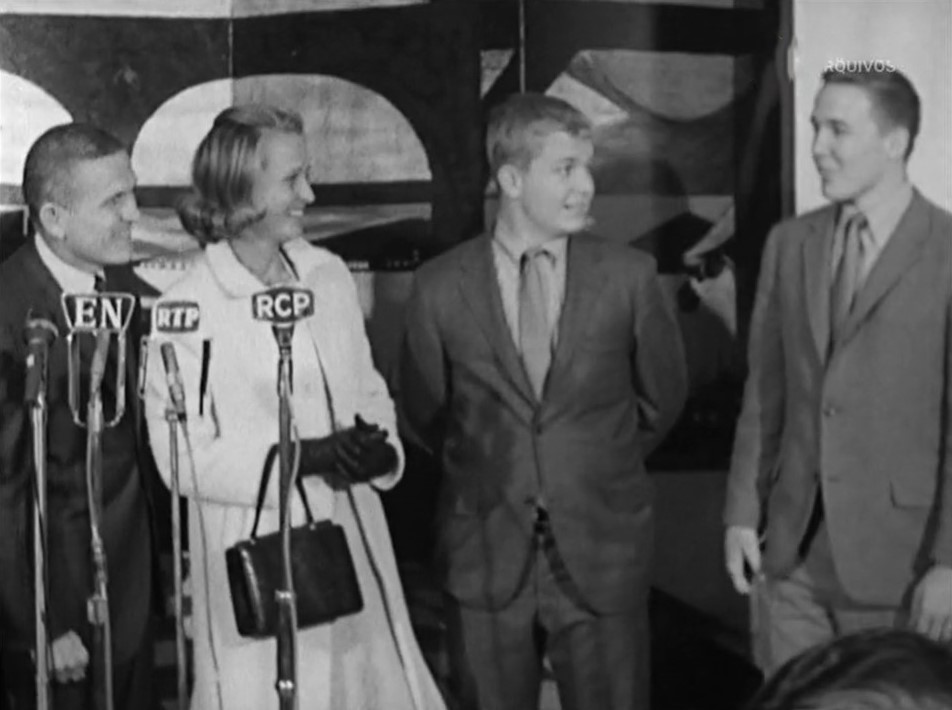



Left: In Den Haag, The Netherlands, Apollo 8 astronaut Borman, right, describes the Lunar Module to Queen Juliana. Middle: At The Vatican, Borman, left, presents a photograph of the Moon from Apollo 8 to Pope Paul VI. Right: The Bormans, Frank, left, Susan, and sons Edwin and Frederick, hold a press conference in Lisbon, the last stop of their European tour.
As President Richard M. Nixon announced on Jan. 30, Apollo 8 astronaut Frank Borman, his wife Susan, and their two children Frederick and Edwin, set off on their European goodwill tour on Feb. 2, flying aboard a presidential Air Force jet. Borman’s Apollo 8 crewmates James A. Lovell and William A. Anders could not participate in the tour because they had already begun training as part of the Apollo 11 backup crew. The Bormans’ 19-day tour took them to London, Paris, Brussels, Den Haag, Bonn, West Berlin, Rome, Madrid, and Lisbon. They met with royalty, politicians, scientists, and Pope Paul VI, gave lectures during which Borman narrated a film from his flight, and held numerous press conferences.
Apollo 9
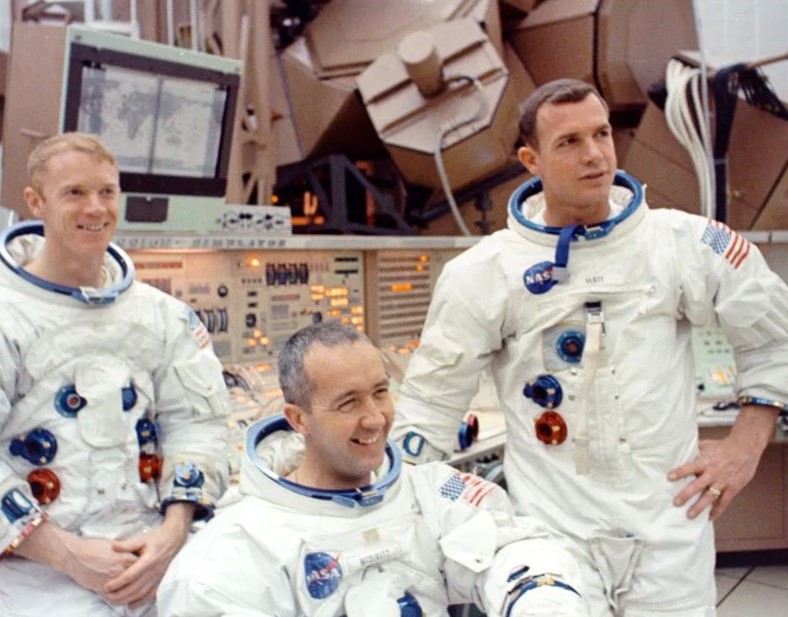
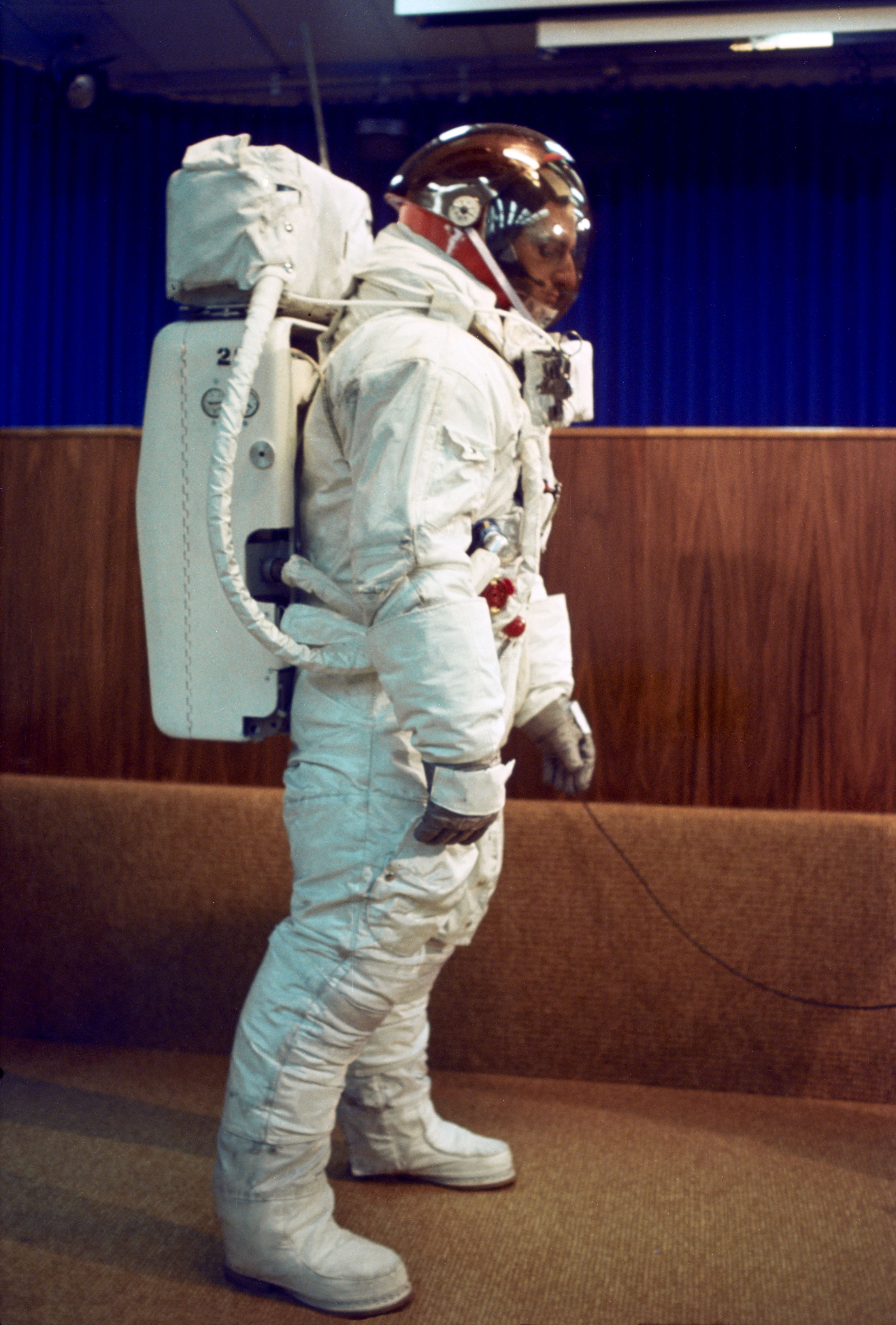



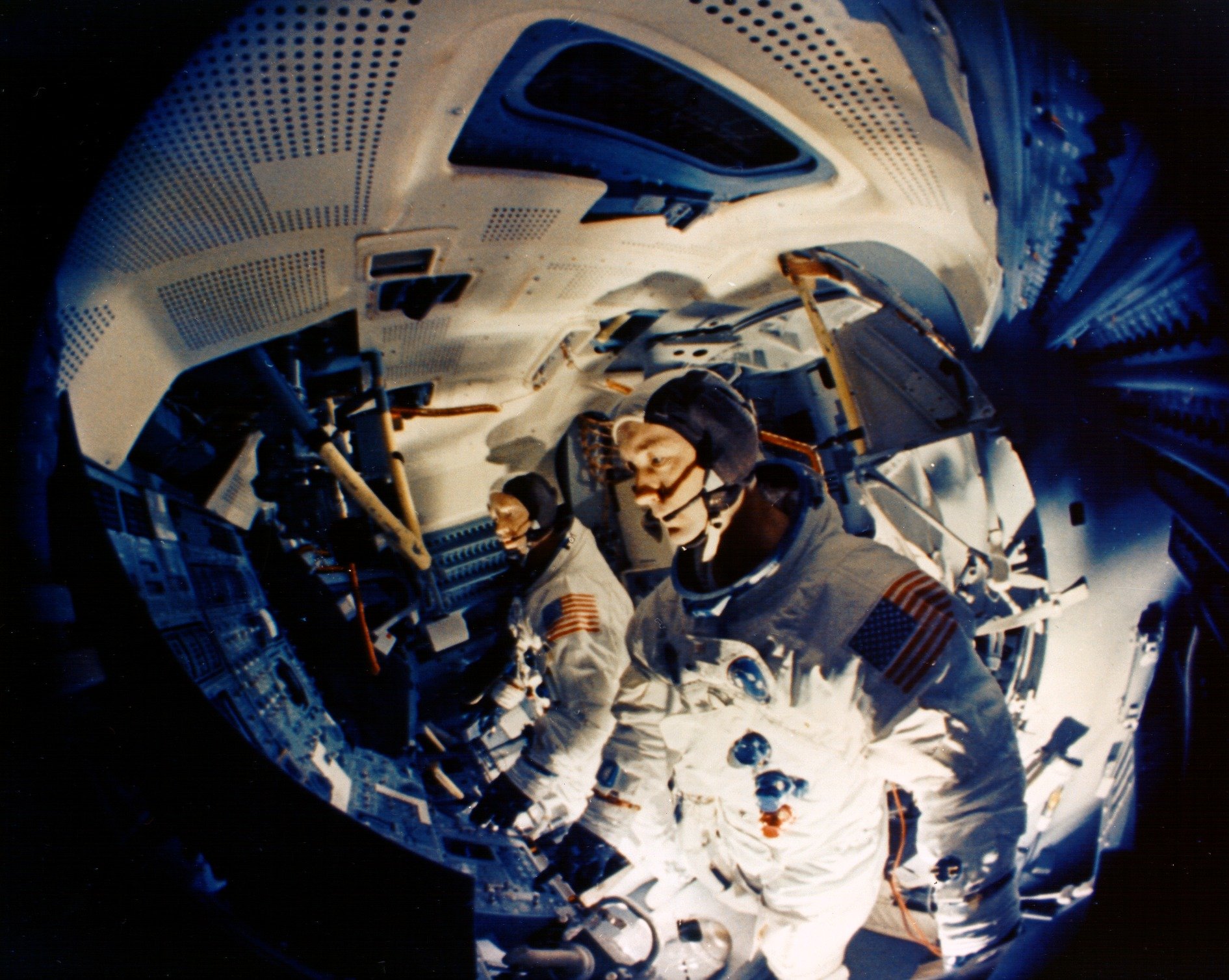
Left: Apollo 9 astronauts Russell L. Schweickart, left, James A. McDivitt, and David R. Scott pose in front of the control panel for the spacecraft simulators. Middle: Fisheye lens view of Schweickart, left, and McDivitt in the Lunar Module simulator. Right: A technician poses in the Apollo A7L spacesuit, including the Portable Life Support System backpack used for the first time during Apollo 9.
Apollo 9 astronauts James A. McDivitt, David R. Scott, and Russell L. Schweickart planned to conduct the first crewed test of the LM during their 10-day Earth orbital mission. They and their backups Charles “Pete” Conrad, Richard F. Gordon, and Alan L. Bean spent many hours in the spacecraft simulators and training for the spacewalk component of the mission. The planned spacewalk, the first and only one before the Moon landing mission, would not only test the spacesuit and its Portable Life Support System but also demonstrate an external crew transfer should a problem arise with the internal transfer tunnel or hatches. McDivitt, Scott, and Schweickart provided details of their mission to reporters during a press conference on Feb. 8 at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC), now NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. They explained that during the mission phase when the two vehicles fly separately, they will use the call signs Spider for the LM and Gumdrop for the Command Module (CM), lighthearted references to the shapes of the respective spacecraft.
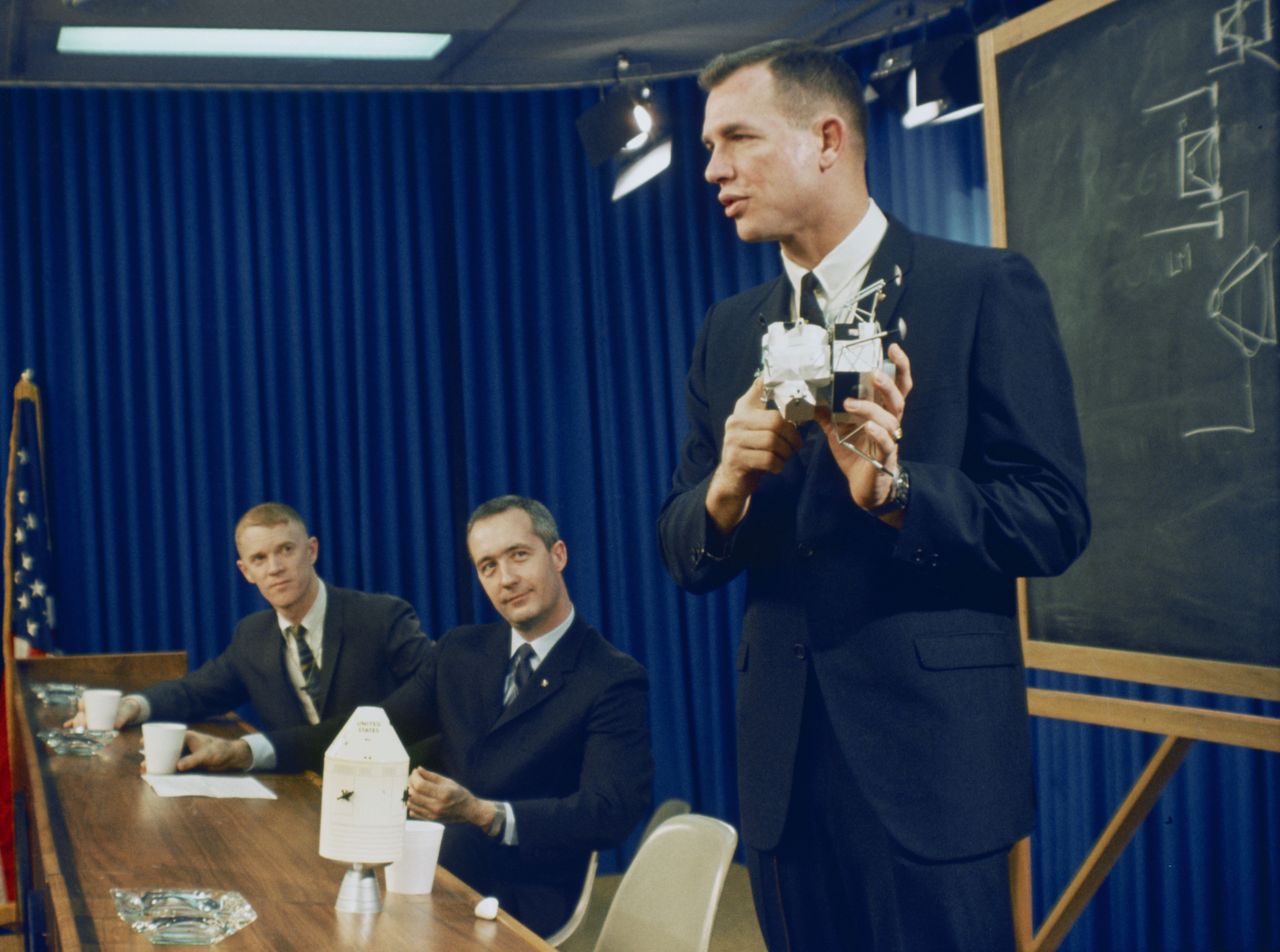


Left: Apollo 9 astronauts Russell L. Schweickart, left, James A. McDivitt, and David R. Scott during the preflight crew press conference at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC), now NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. Right: Senior NASA management assembled for the Apollo 9 Flight Readiness Review at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center (KSC): Associate Administrator for Manned Flight George E. Mueller, left, Apollo Program Director Samuel C. Phillips, KSC Director Kurt H. Debus, MSC Director Robert R. Gilruth, and Marshall Space Flight Center Director Wernher von Braun.
Senior NASA managers met at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida for Apollo 9’s Flight Readiness Review the first week of February. At the end of the meeting, they set the launch date for Feb. 28. The following week, engineers in Firing Room 2 of KSC’s Launch Control Center conducted the Countdown Demonstration Test (CDDT), essentially a dress rehearsal for the actual countdown. On Feb. 12, McDivitt, Scott, and Schweickart participated in the final portion of the CDDT, as they would on launch day, by donning their spacesuits and climbing aboard their spacecraft for the final two hours of the test. Engineers began the countdown to launch on Feb. 26 but had to halt it the next day when the astronauts developed head colds. Managers reset the launch date to March 3, and the countdown restarted on March 1.
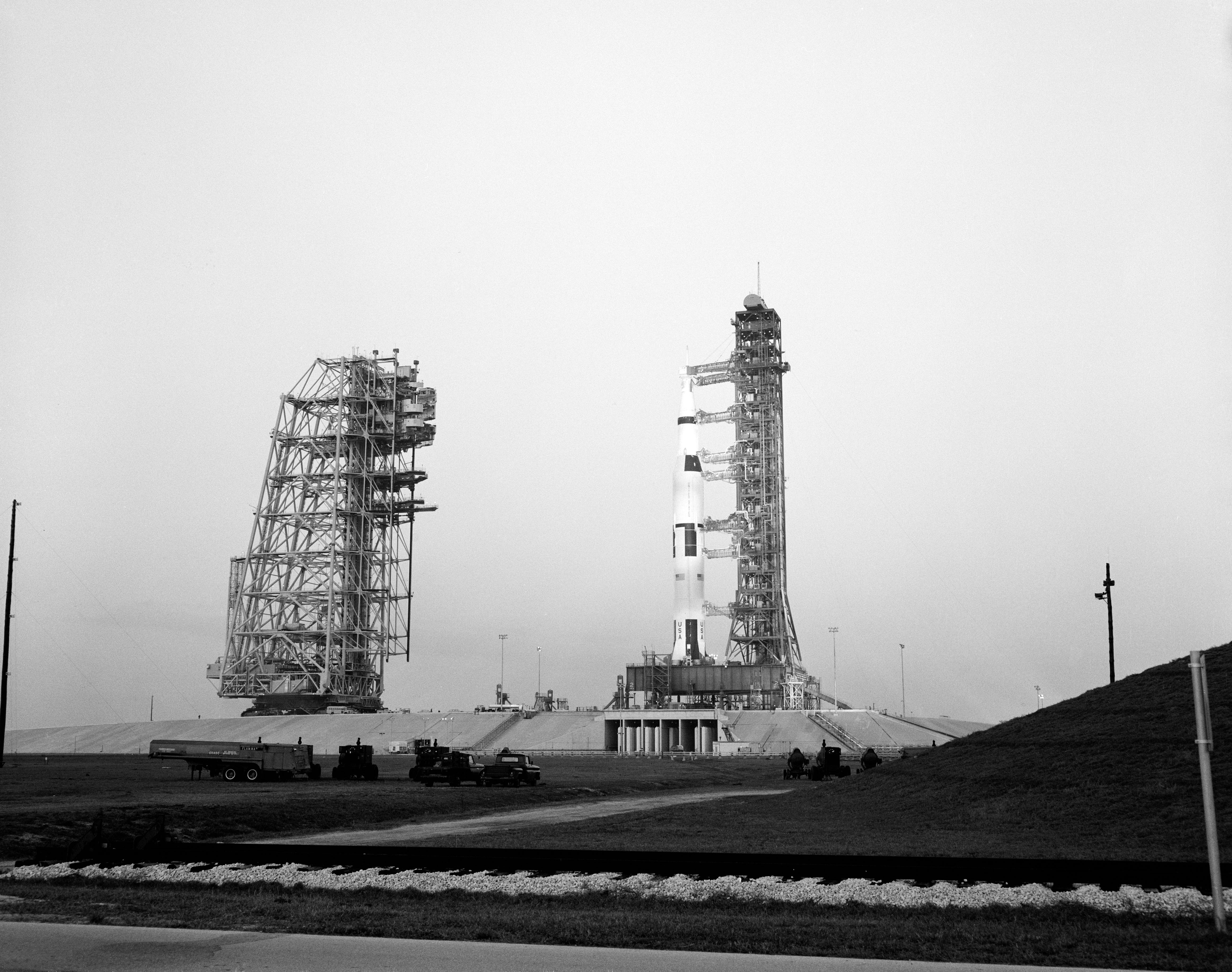
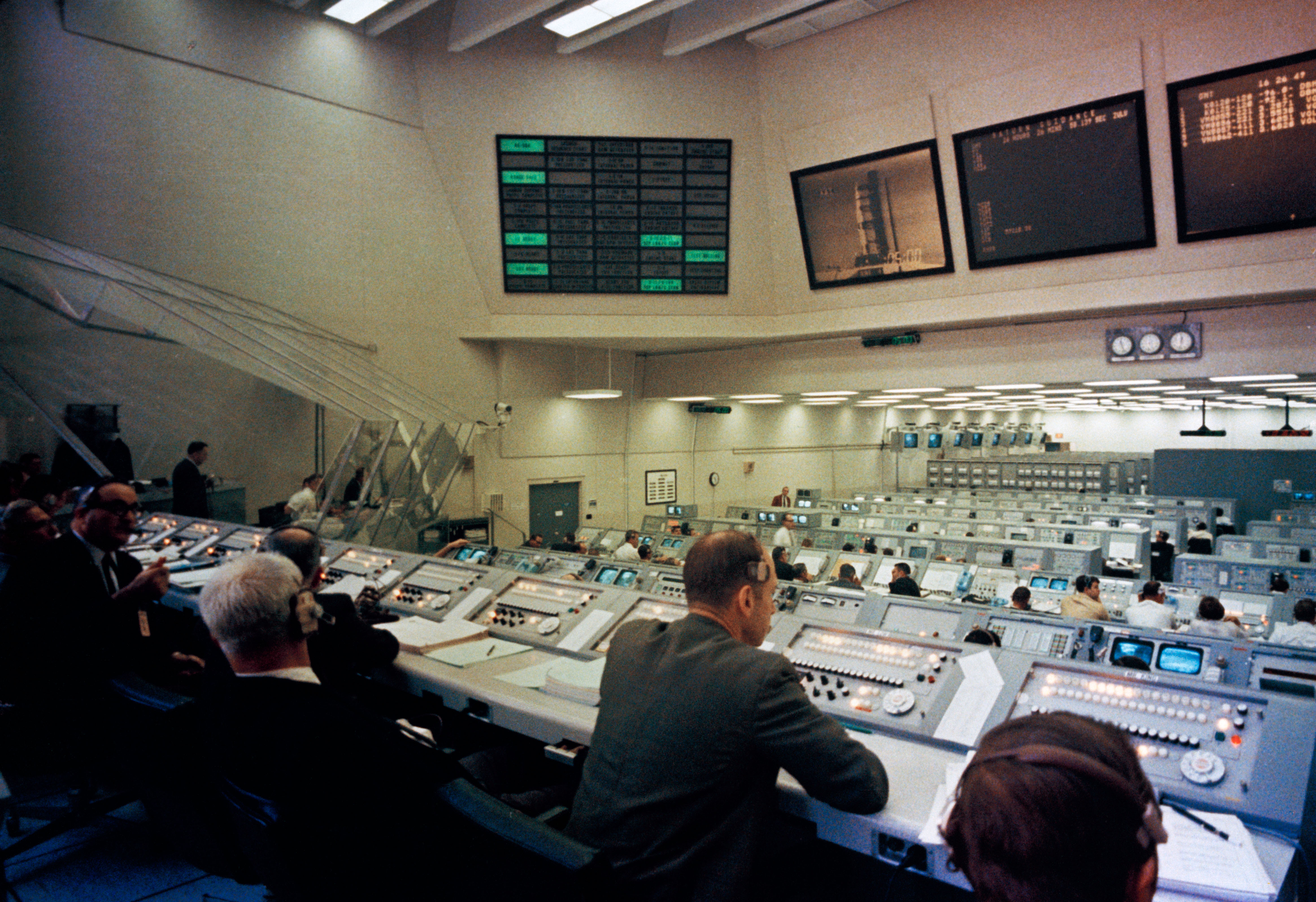
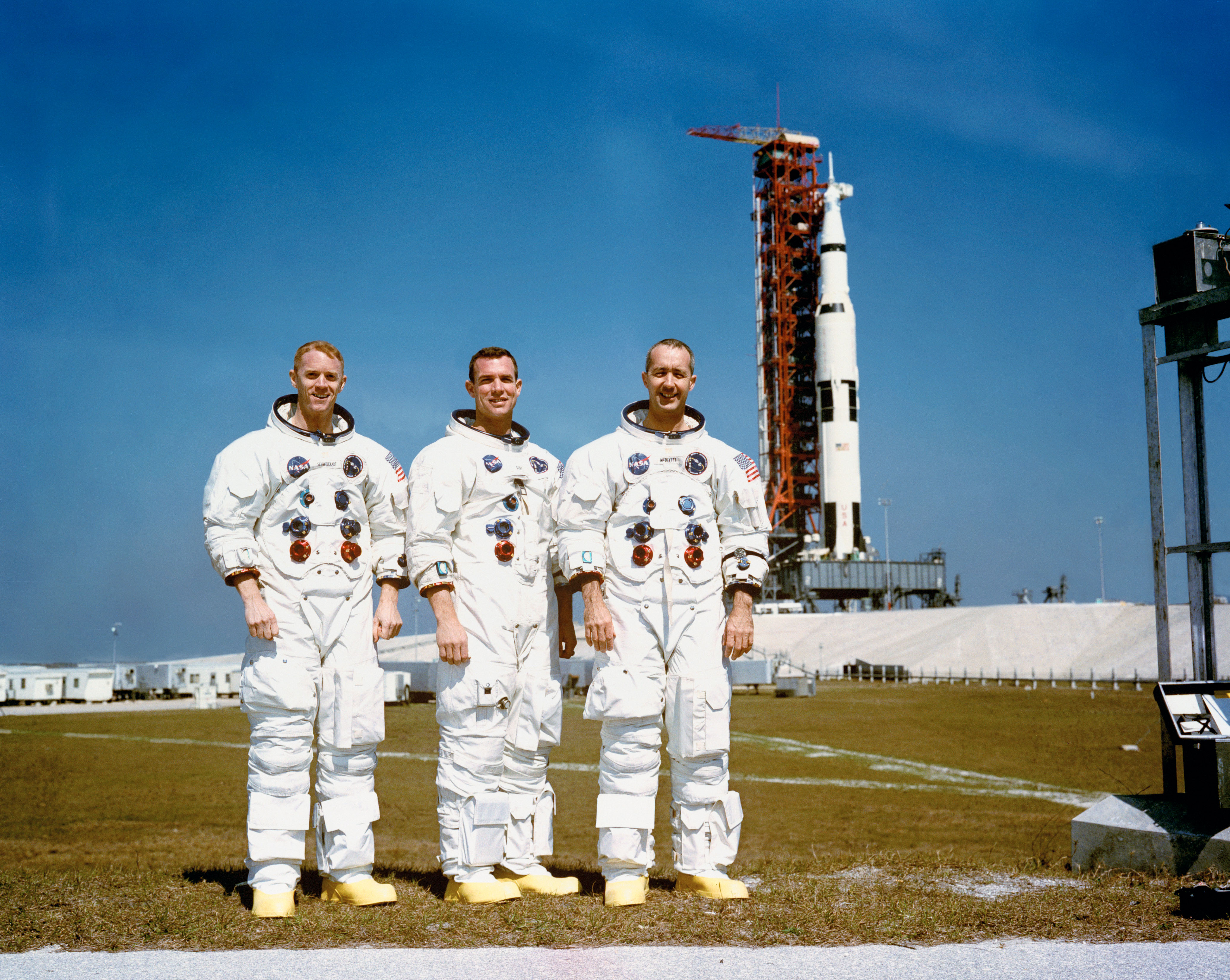



Left: The Apollo 9 Saturn V at Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during the Countdown Demonstration Test (CDDT). Middle: Engineers in the Launch Control Center’s Firing Room 2 monitor the rocket and spacecraft during the CDDT. Right: Apollo 9 astronauts Russell L. Schweickart, left, David R. Scott, and James A. McDivitt pose in front of their Saturn V following the CDDT.
Apollo 10
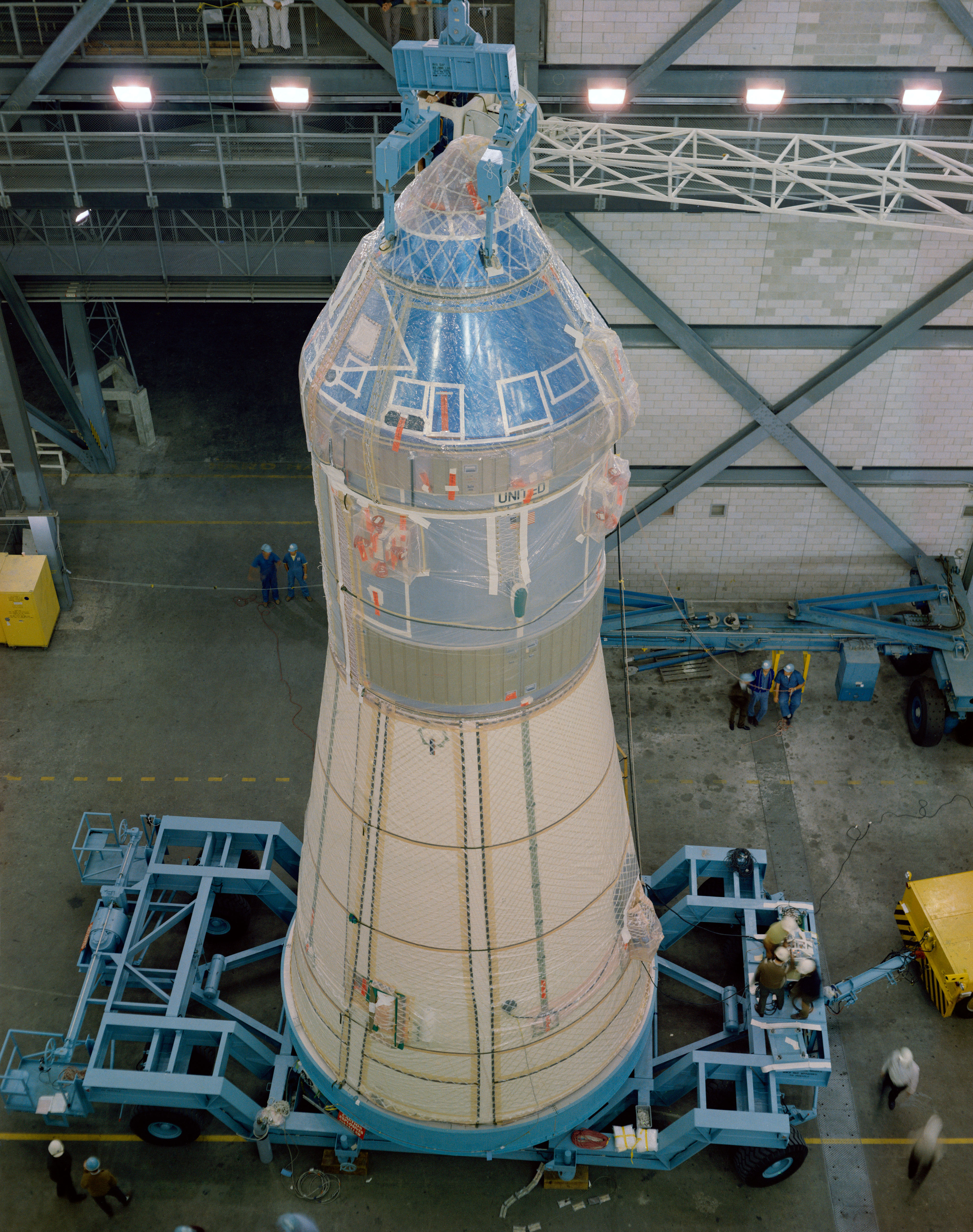
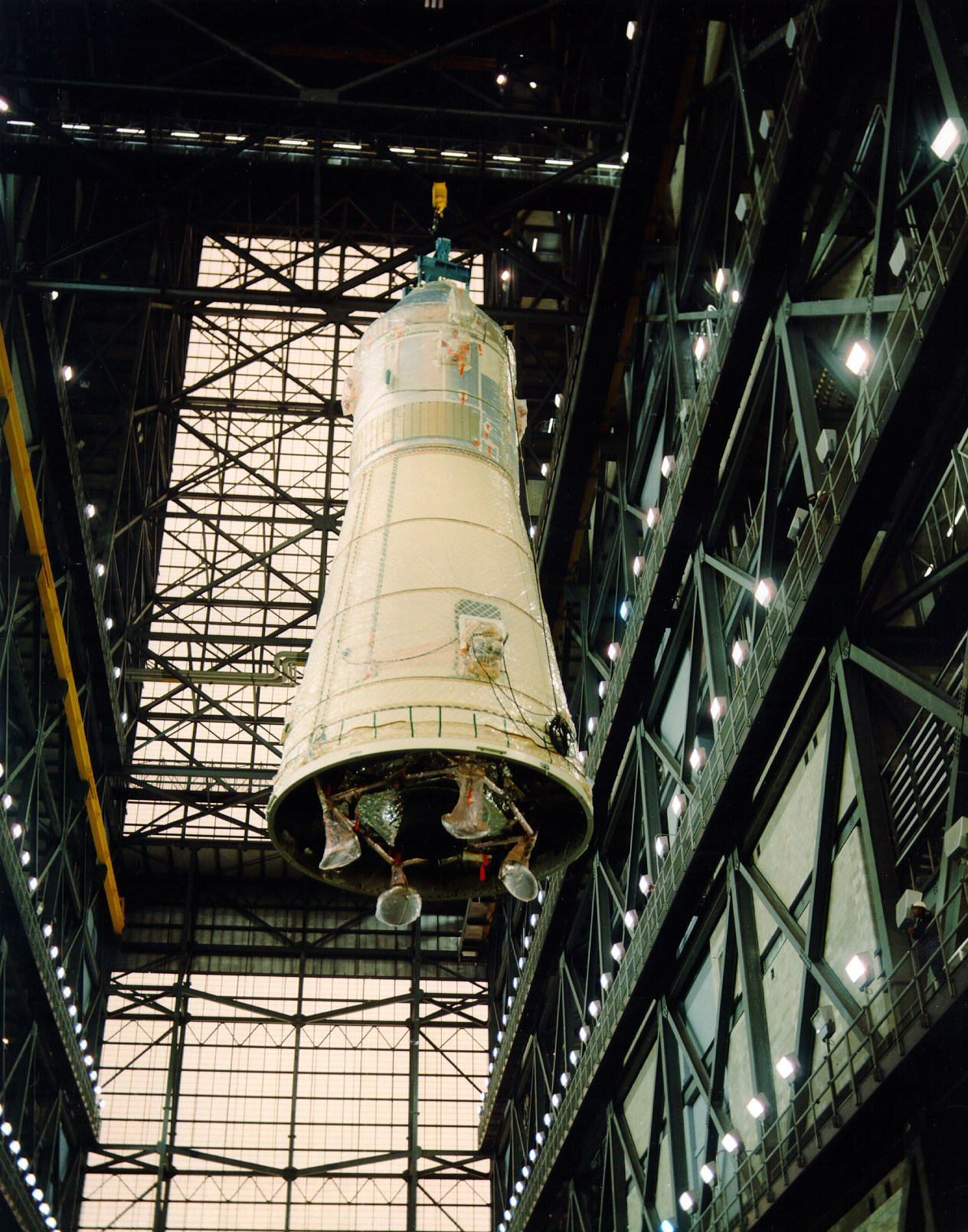
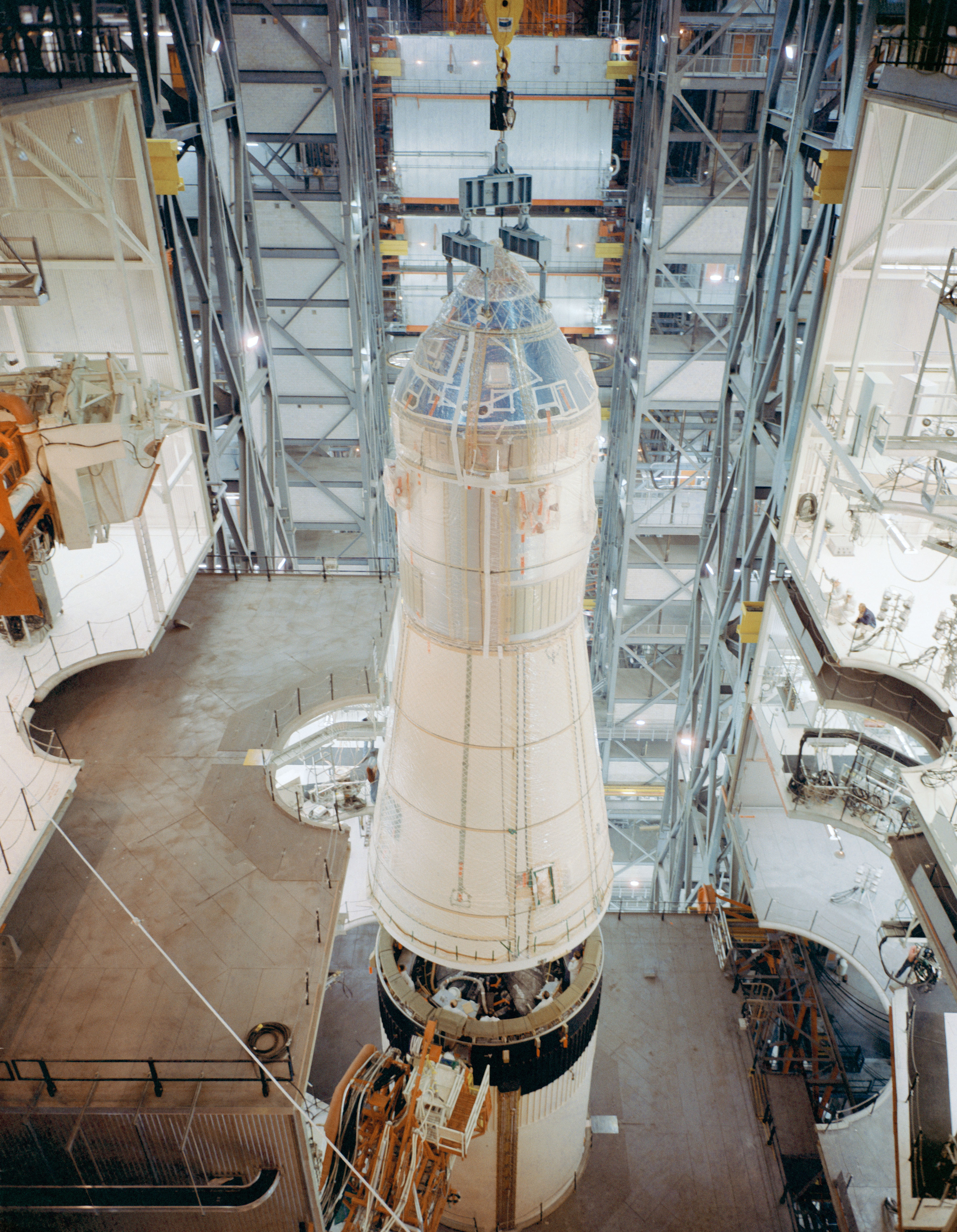




Stacking of the Apollo 10 vehicle in High Bay 2 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Left: The three stages of the Saturn V stacked on Mobile Launcher-3. Middle left: The Apollo 10 spacecraft, the Command and Service Modules and the Lunar Module (LM) encased in the Spacecraft LM Adapter, arrives from the Manned Spacecraft Operations Building. Middle right: Workers lift the spacecraft for stacking onto the rocket, the footpads of the LM’s folded landing gear visible. Right: Workers lower the spacecraft onto the Saturn V rocket’s third stage.
With Apollo 9 on Launch Pad 39A and almost ready to launch, workers in High Bay 2 of KSC’s Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) completed stacking of the Apollo 10 launch vehicle. The spacecraft, consisting of the Command and Service Modules atop the LM encased in the Spacecraft LM Adapter, arrived from the Manned Spacecraft Operations Building (MSOB) on Feb. 6 and VAB workers stacked it on the Saturn V rocket the same day. Engineers began to conduct integrated tests on the launch vehicle in preparation for rollout to Launch Pad 39B in mid-March. Apollo 10 astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, John W. Young, and Eugene A. Cernan and their backups L. Gordon Cooper, Donn F. Eisele, and Edgar D. Mitchell spent much time in spacecraft simulators and testing their spacesuits in vacuum chambers.
Apollo 11
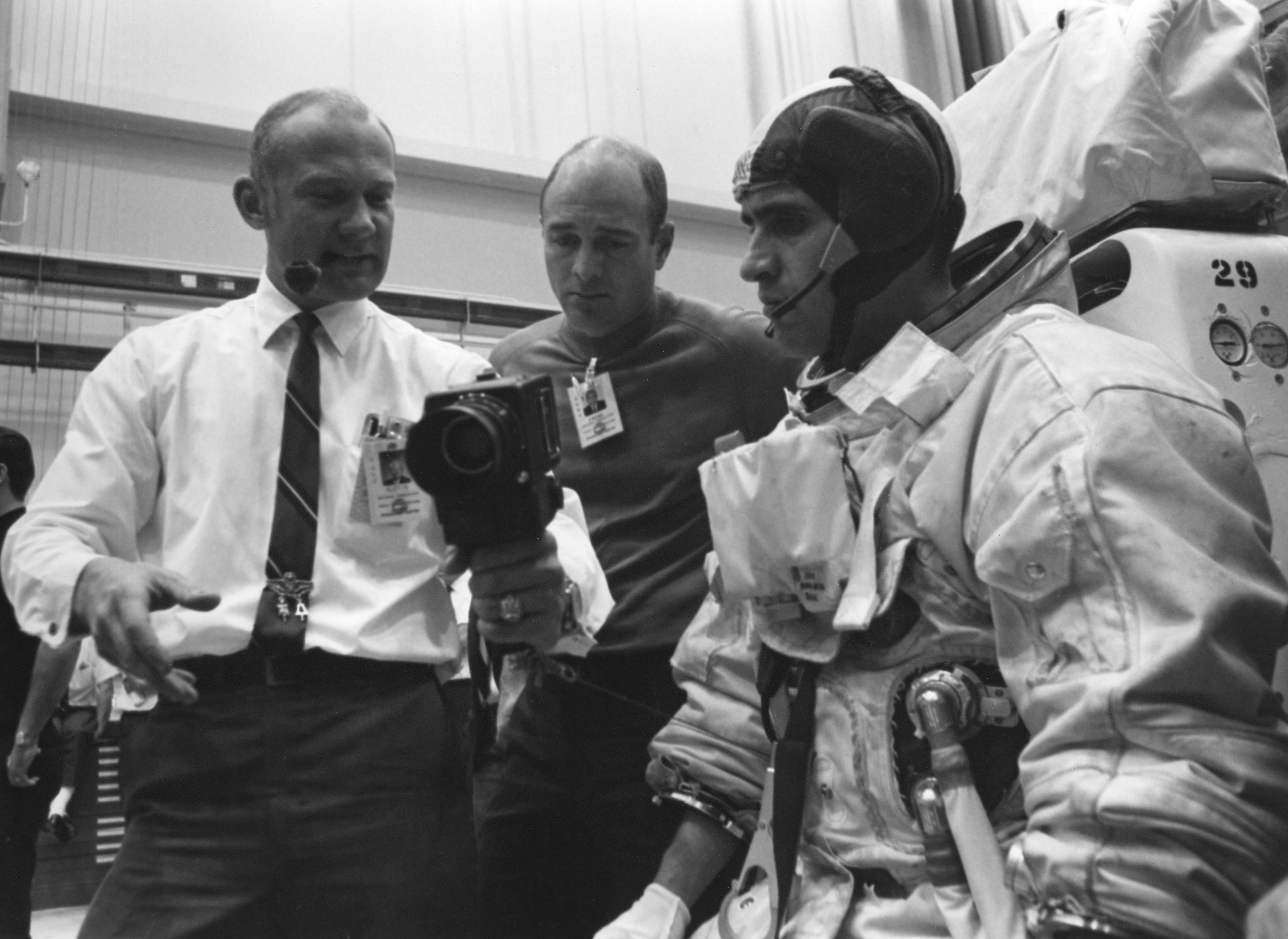
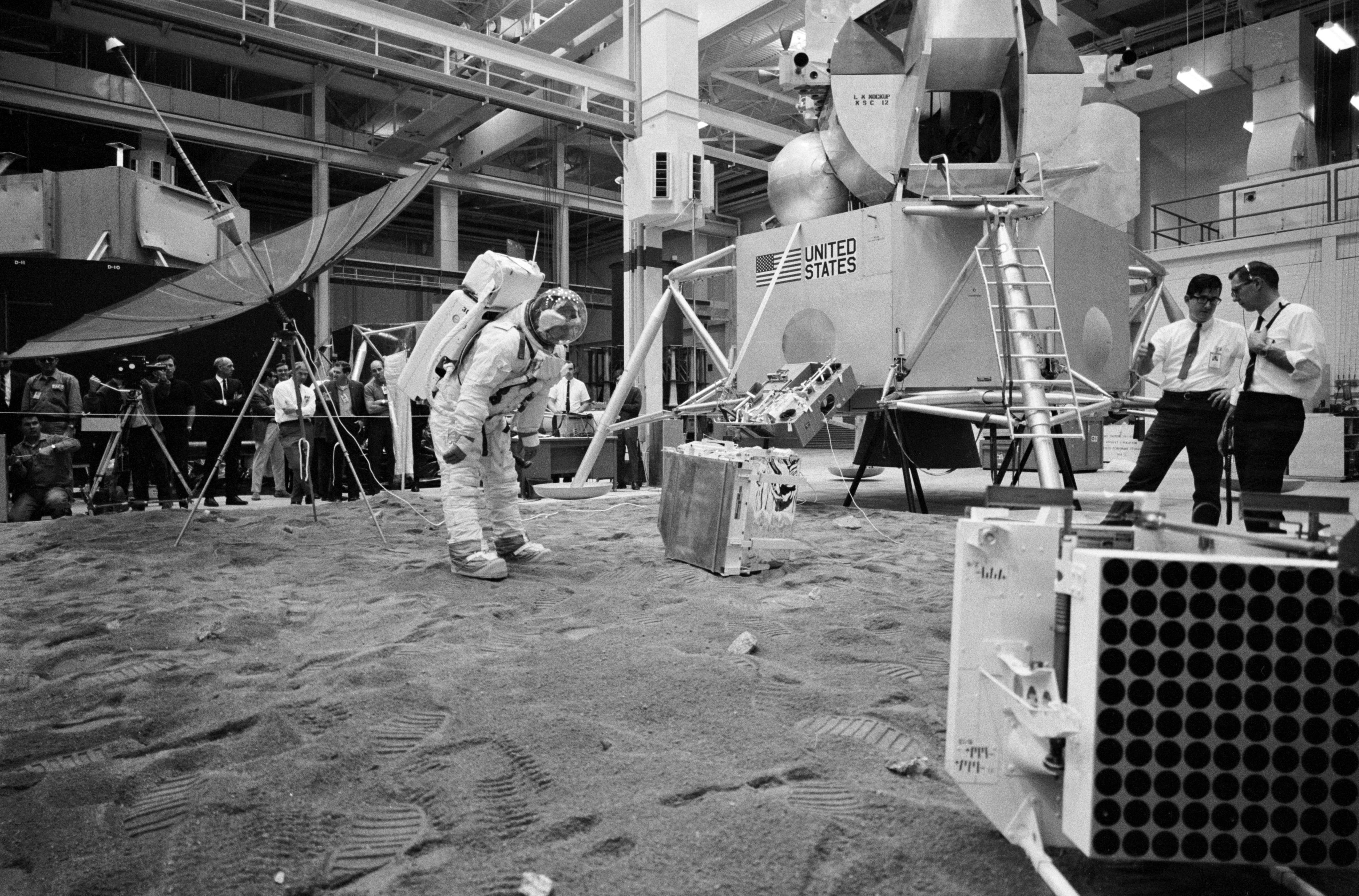


Left: Apollo 11 astronaut Edwin E. “Buzz” Aldrin, left, confers with support astronauts Ronald E. Evans and Harrison H. “Jack” Schmitt, the only geologist in the astronaut corps at the time, during training for deployment of the Early Apollo Science Experiment Package (EASEP). Right: Astronaut Don L. Lind, suited, practices deploying the EASEP instruments as Aldrin, in white shirt behind the dish antenna, oberves.
With their historic mission only five months away, the Apollo 11 prime crew of Neil A. Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Edwin E. “Buzz” Aldrin and their backups James A. Lovell, William A. Anders, and Fred W. Haise busied themselves training for the Moon landing. Although the primary goal of the first Moon landing mission centered on demonstrating that the Apollo spacecraft systems could safely land two astronauts on the surface and return them safely to Earth, the surface operations also included collecting lunar samples and deploying experiments. During their two-and-a-half-hour surface excursion, Armstrong and Aldrin planned to deploy three instruments comprising the Early Apollo Surface Experiment Package (EASEP) – a passive seismometer, a laser ranging retro-reflector, and a solar wind composition experiment. On Jan. 21, 1969, astronauts Harrison H. “Jack” Schmitt, the only geologist in the astronaut corps, and Don L. Lind conducted a simulation of the EASEP deployment in MSC’s Building 9. Aldrin observed the simulation, obviously with great interest.
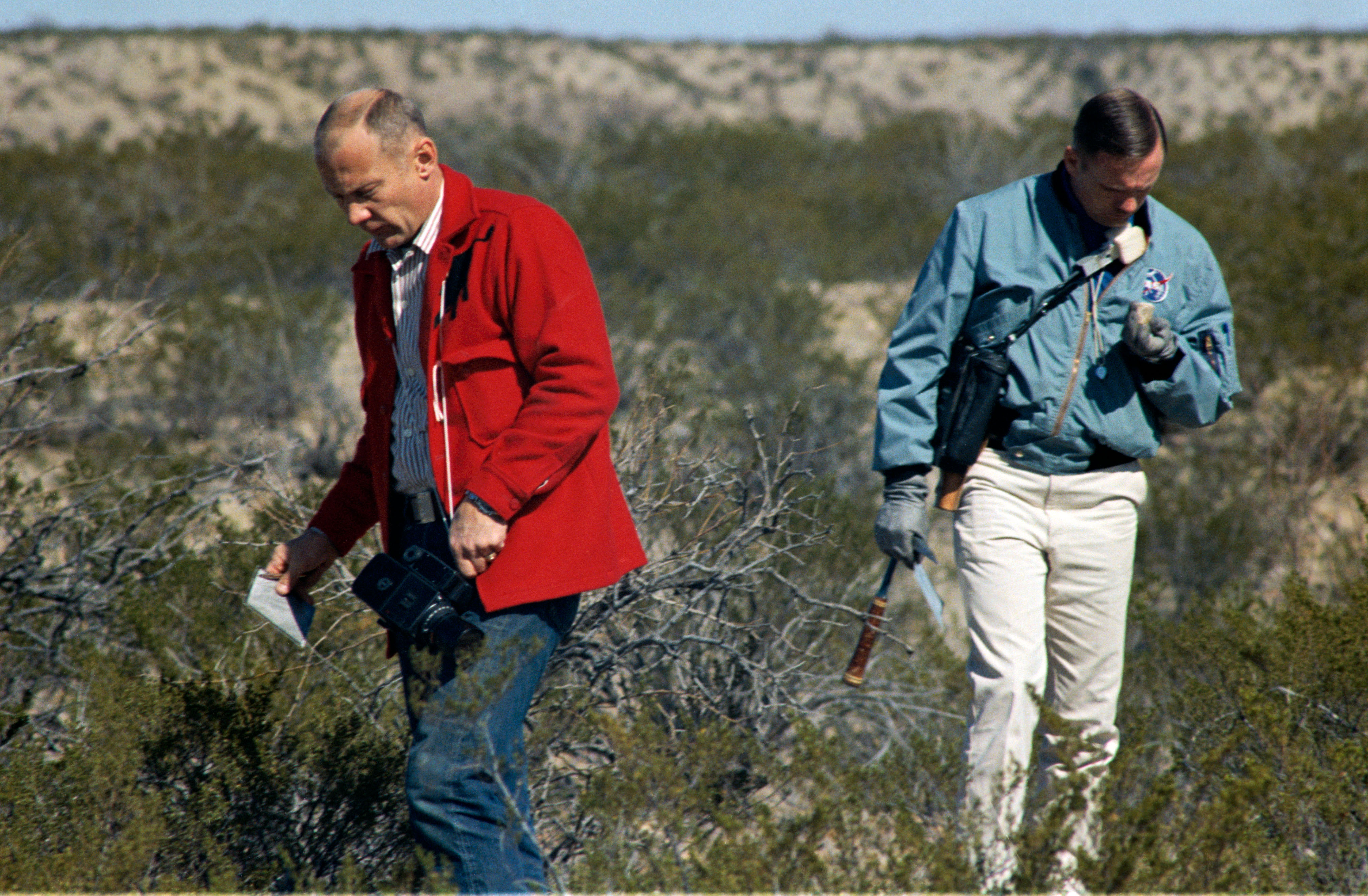
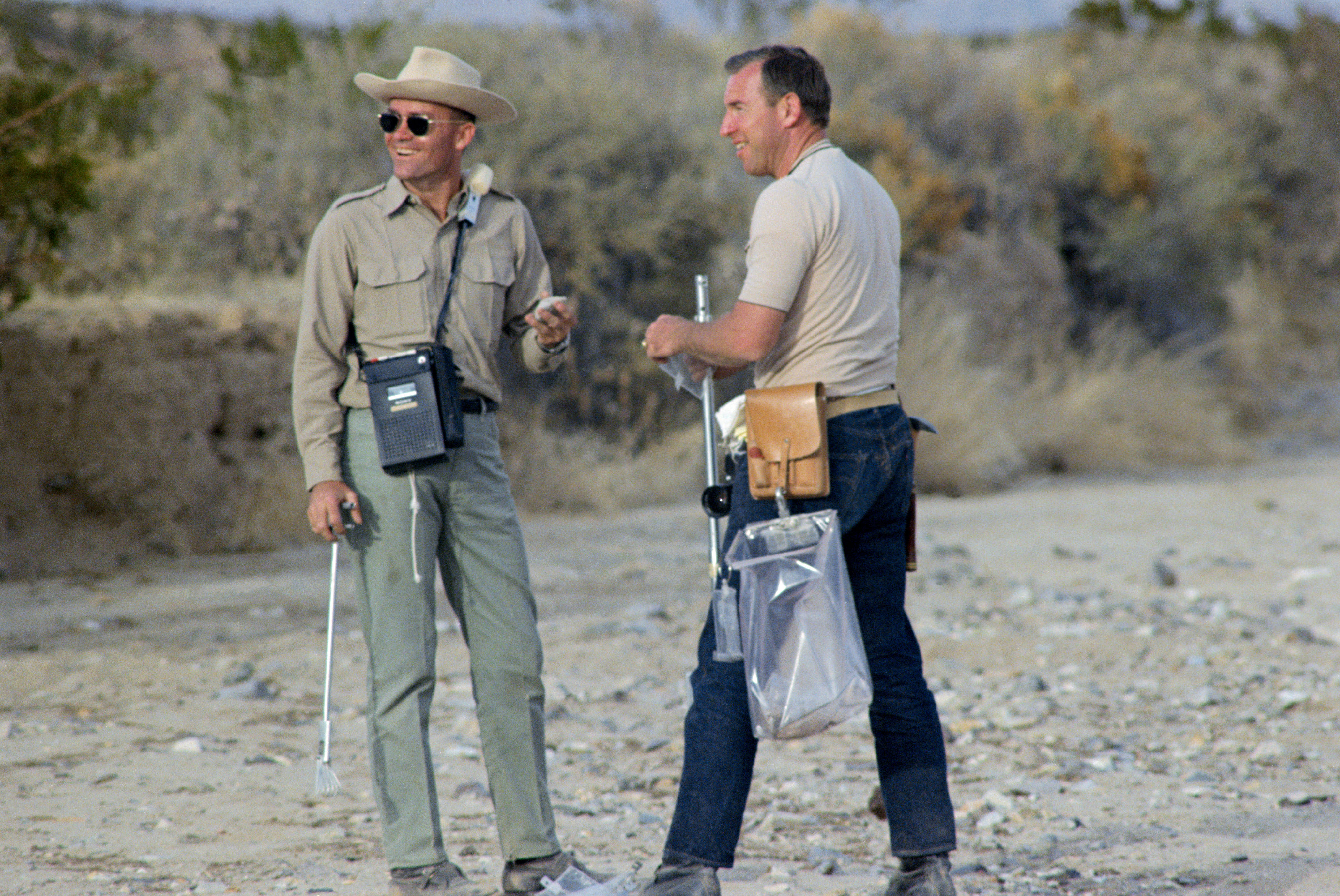


Left: Apollo 11 astronauts Edwin E. “Buzz” Aldrin, left, and Neil A. Armstrong during geology training at Sierra Blanco, Texas. Right: Apollo 11 backup astronauts Fred W. Haise, left, and James A. Lovell at the Sierra Blanco geology training session.
Generic instruction in geology, including classroom work and field trips, became part of overall NASA astronaut training beginning in 1964. Once assigned to a crew that had a very good chance of actually walking on the lunar surface and collecting rock and soil samples, those astronauts received specialized instruction in geology. On Feb. 24, 1969, the two prime moonwalkers Armstrong and Aldrin, along with their backups Lovell and Haise, participated in their only trip specifically dedicated to geology training. The field exercise in west Texas took place near Sierra Blanca and the ruins of Fort Quitman, about 90 miles southeast of El Paso. Accompanied by a team from MSC’s Geology Branch, the astronauts practiced sampling the variety of rocks present at the site to obtain a representative collection, skills needed to choose the best sample candidates during their brief excursion on the lunar surface.
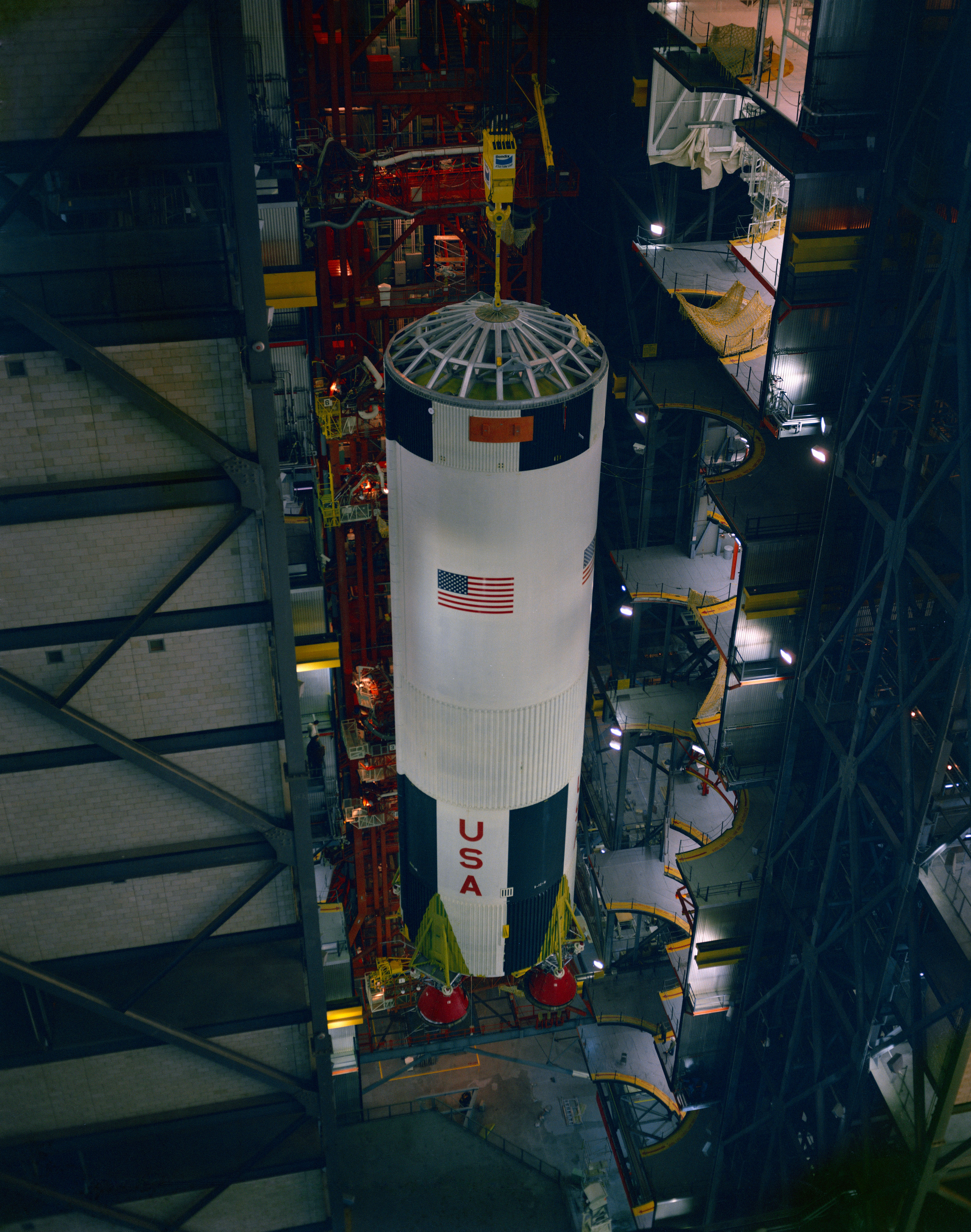
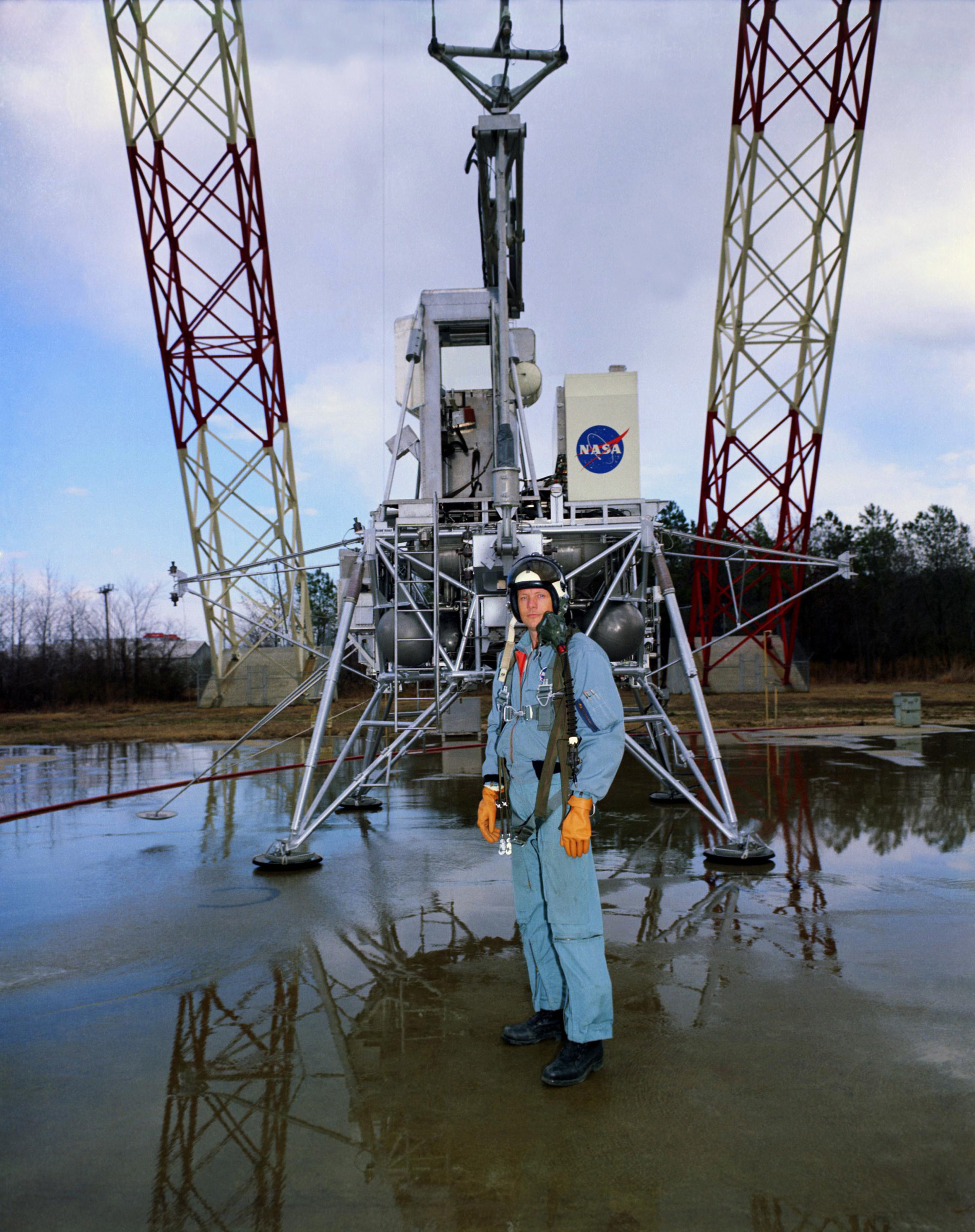
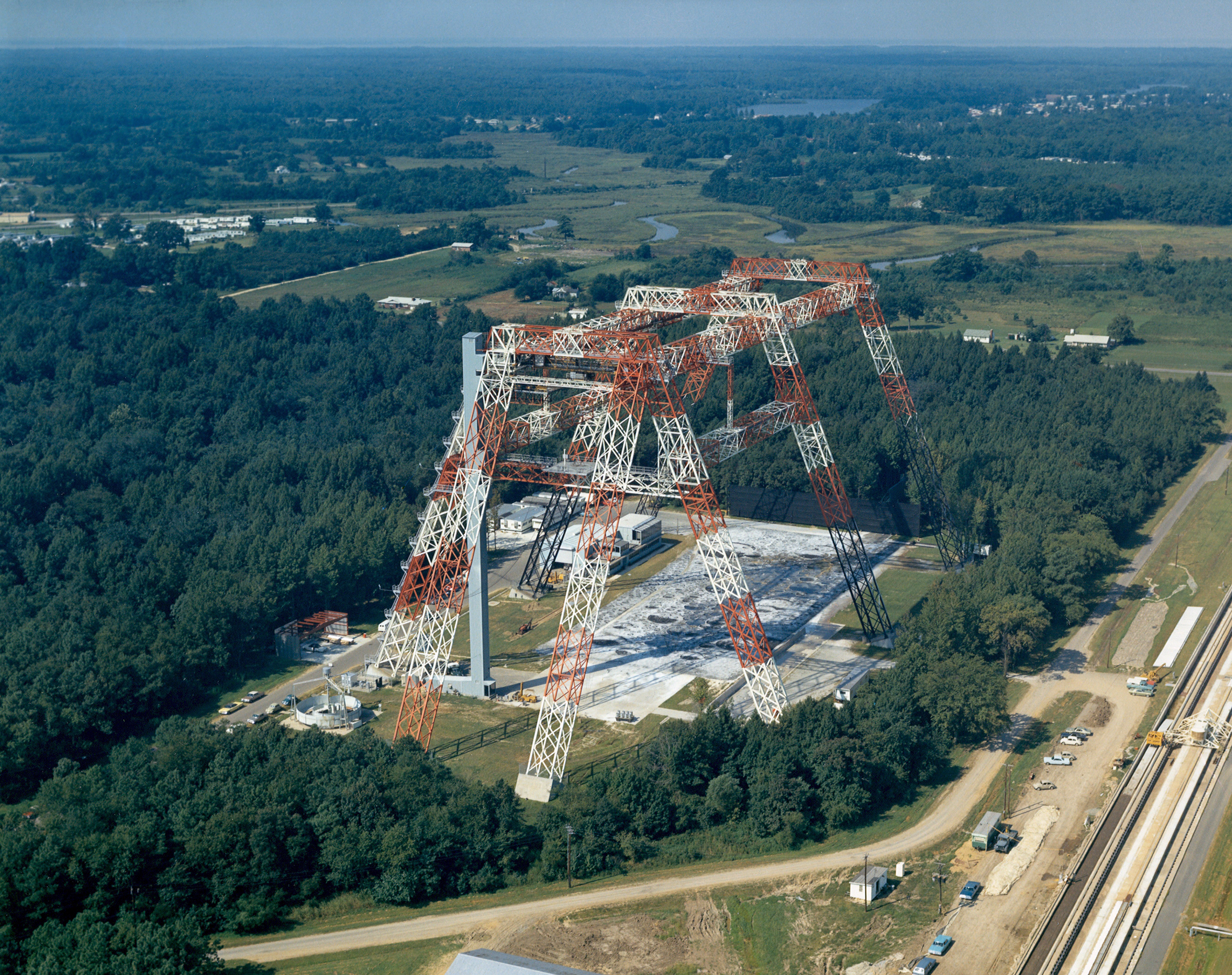



Left: Workers mount the S-IC first stage on its Mobile Launcher in the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Middle: Neil A. Armstrong stands in front of the Lunar Module simulator at the Lunar Landing Research Facility (LLRF) at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia. Right: Aerial view of the LLRF at Langley.
By mid-February, all three stages of the Apollo 11 Saturn V had arrived in the VAB, and on Feb. 21, workers stacked the S-IC first stage on its Mobile Launcher in High Bay 1. They finished assembling the rocket in March. In an altitude chamber in the nearby MSOB, on Feb. 10, engineers conducted a docking test between the CM and the LM. Five days later, they mated the ascent and descent stages of the LM for further testing. With the Lunar Landing Training Vehicle (LLTV) still grounded following its December 1968 crash, the Lunar Landing Research Facility (LLRF) at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, remained as the only high-fidelity trainer for the descent and landing of the LM on the Moon. Armstrong practiced landings in the LLRF on Feb 12.
Lunar Receiving Laboratory and Mobile Quarantine Facility
To minimize the risk of back contamination of the Earth with any possible lunar microorganisms, NASA designed and built the 83,000-square-foot Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL), residing in MSC’s Building 37. The facility isolated the astronauts, their spacecraft, and lunar samples to prevent any Moon germs from escaping into the environment, and also maintained the lunar samples in as pristine a condition as possible. The Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) provided isolation for the returning astronauts from shortly after splashdown until their delivery to the LRL, an activity that required transport of the MQF on a cargo jet aircraft. On Feb. 6, following its return from sea trials, workers placed the MQF inside Chamber A of MSC’s Space Environment Simulation Facility. The test in the large vacuum chamber checked out the MQF’s emergency oxygen supply during a simulated aircraft pressure loss. Three test subjects successfully completed the test.
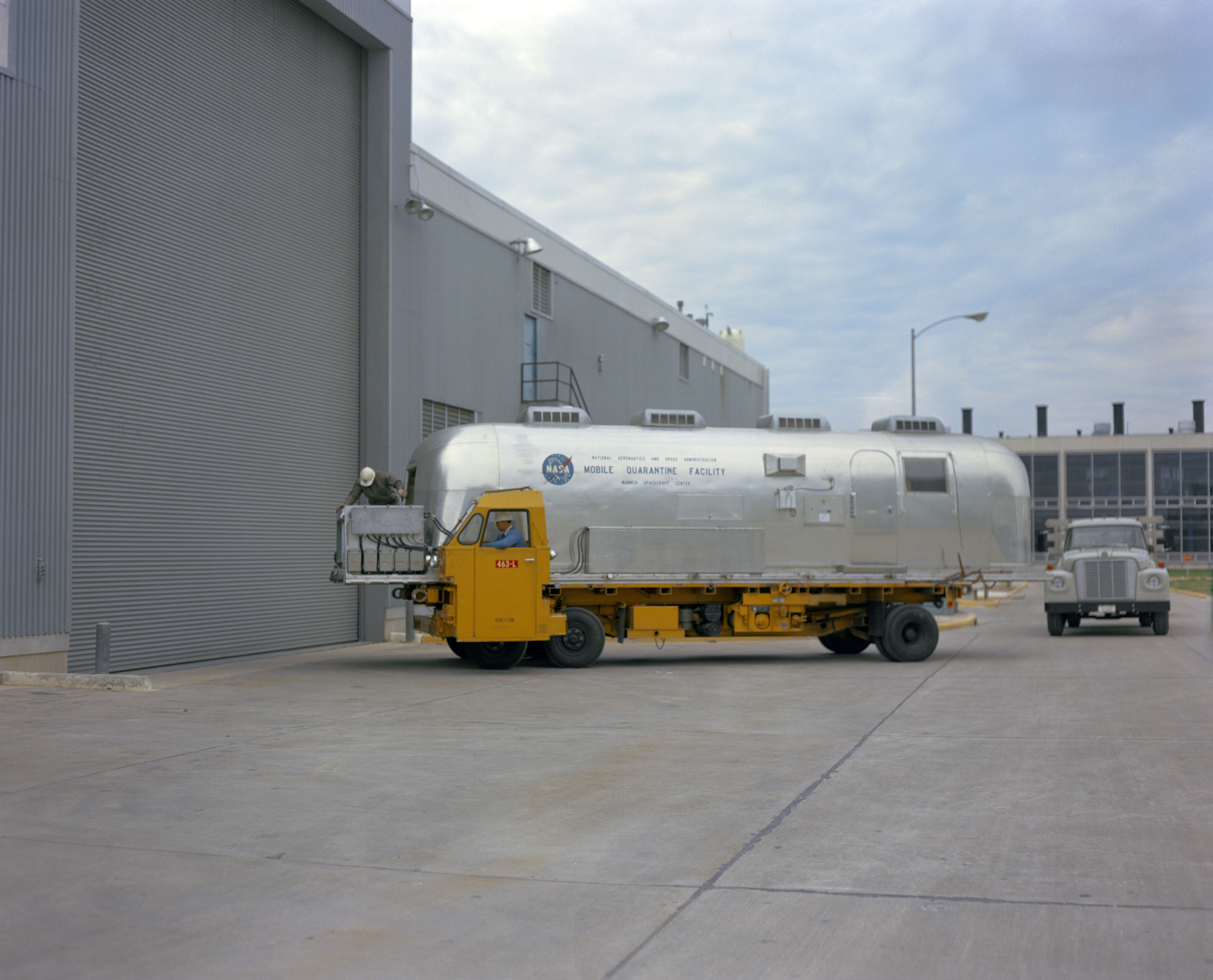
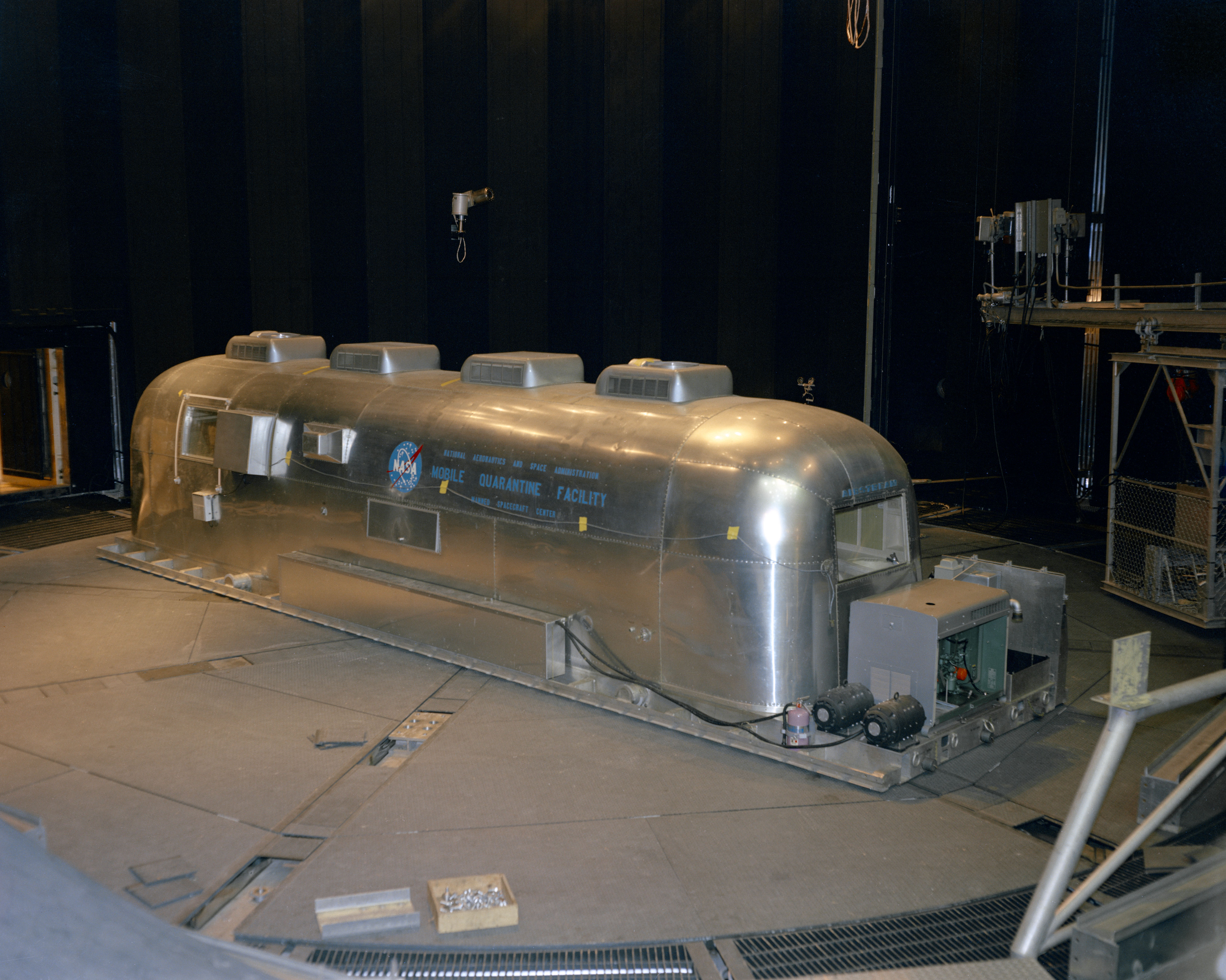
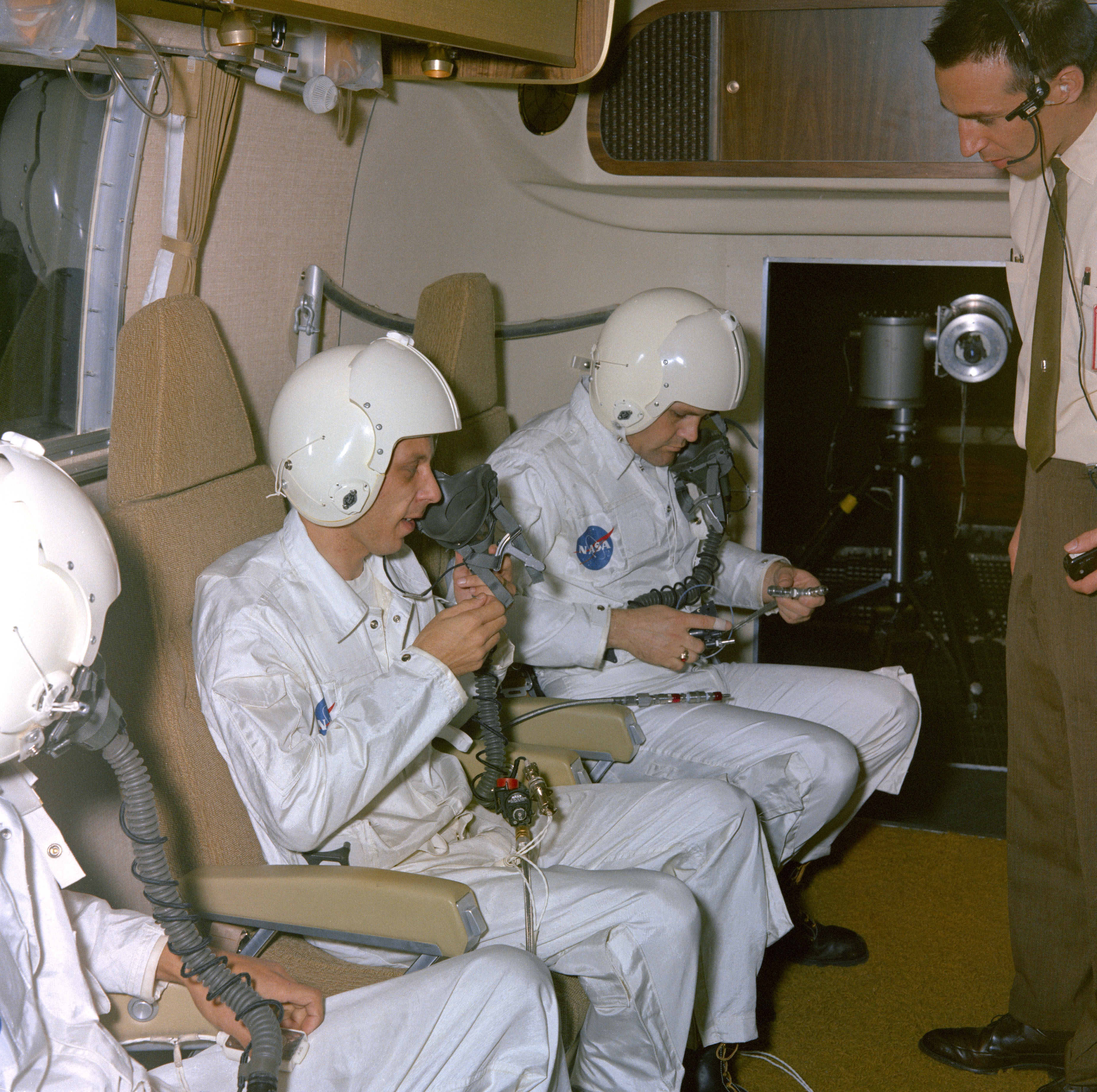



Left: Workers truck the Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) into the Space Environment Simulation Laboratory (SESL) at the Manned Spacecraft Center, now NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. Middle: Workers install the MQF in Chamber A of the SESL for a test of the emergency oxygen system. Right: Test subjects inside the MQF prepare for the emergency oxygen system test in the SESL.
To be continued …
News from around the world in February 1969:
Feb. 3 – Ibuprofen launched in the United Kingdom as a prescription anti-inflammatory analgesic.
Feb. 5 – The population of the United States reaches 200 million.
Feb. 7 – British band The Who record their song “Pinball Wizard.”
Feb. 7 – Diane Krump becomes the first woman jockey at a major U.S. racetrack (Hialeah, Florida).
Feb. 8 – The Allende meteorite weighing nearly two tons explodes in mid-air and fragments fall on Pueblito de Allende, Chihuahua, Mexico.
Feb. 9 – First flight of the Boeing 747 Jumbo Jet from Everett, Washington.
Feb. 21 – First launch of U.S.S.R.’s N-1 Moon rocket, not successful.
Feb. 24 – U.S. launches Mariner 6 to fly-by Mars.
Share
Details
Related Terms
What's Your Reaction?