Chandrayaan-3: India's Successful Mission to the Lunar Surface
Chandrayaan-3: India's Successful Mission to the Lunar Surface

Chandrayaan-3: Onboard video
Chandrayaan-3, the highly anticipated follow-on mission to Chandrayaan-2, has achieved a significant milestone in India's space exploration journey. This ambitious mission, comprising a Lander and Rover configuration, aims to demonstrate India's end-to-end capabilities in safe landing and roving on the lunar surface. Let's delve into the details of this successful lunar mission.
Launch and Lunar Orbit
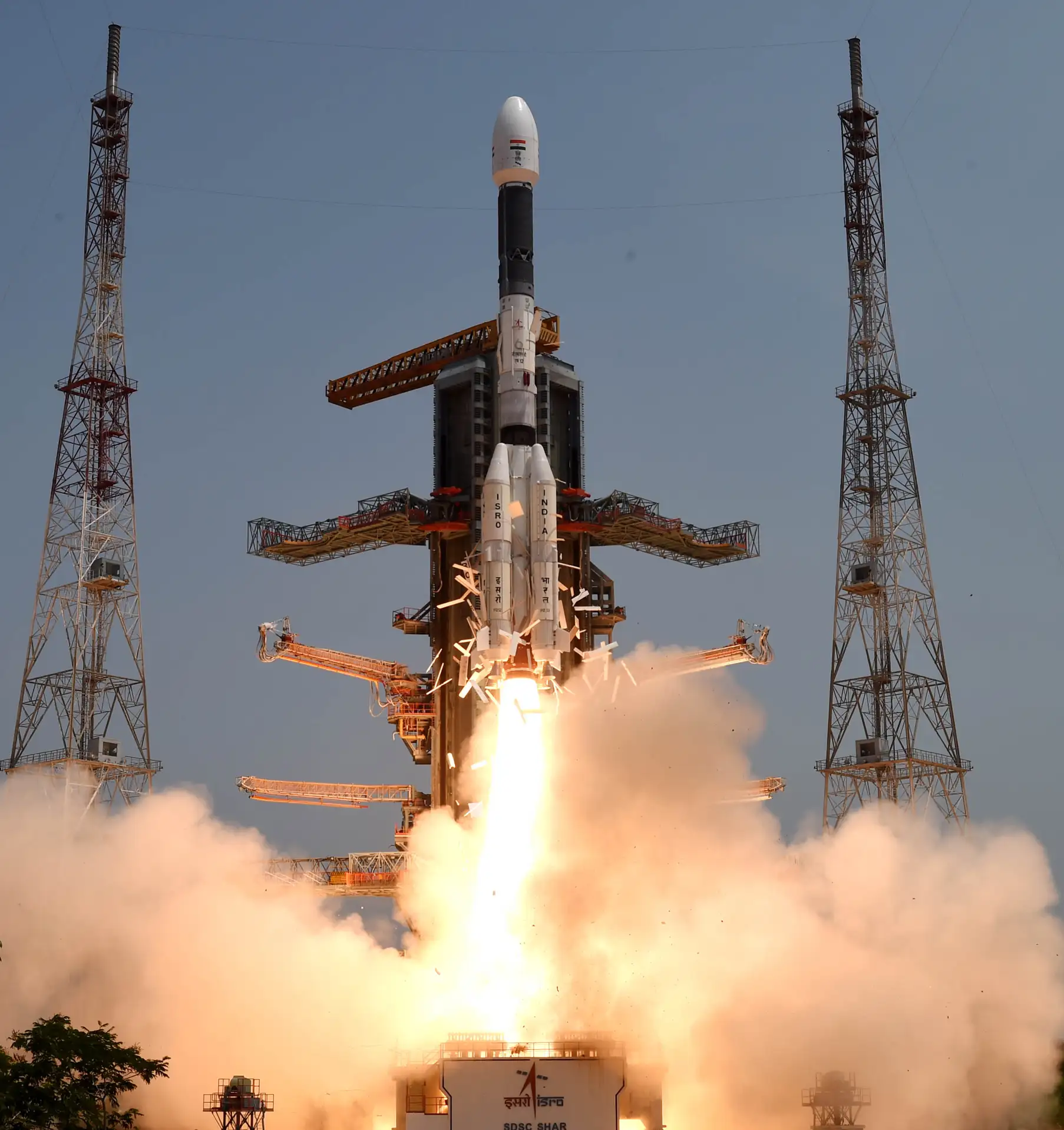
Chandrayaan-3 was launched into space by the powerful LVM3 (Launcher Vehicle Mark 3) from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) SHAR in Sriharikota, India. The propulsion module of the spacecraft carried the Lander and Rover configuration to a lunar orbit of 100 kilometers. Notably, the propulsion module also carried the Spectro-polarimetry of Habitable Planet Earth (SHAPE) payload, enabling the study of spectral and polarimetric measurements of Earth from the lunar orbit.
Lander Payloads
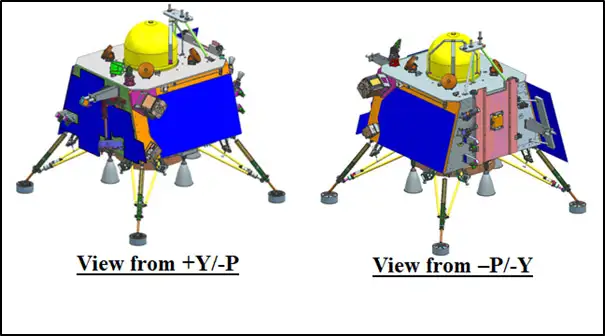
Chandrayaan-3 Lander Module -Views
The Lander module of Chandrayaan-3 was equipped with various scientific payloads to carry out experiments on the lunar surface. These payloads included Chandra's Surface Thermophysical Experiment (ChaSTE), which measured thermal conductivity and temperature. Another crucial payload was the Instrument for Lunar Seismic Activity (ILSA), designed to measure seismicity around the landing site. Additionally, the Lander carried the Langmuir Probe (LP), which estimated plasma density and its variations. Notably, a passive Laser Retroreflector Array from NASA was also accommodated for lunar laser ranging studies.
Rover Payloads
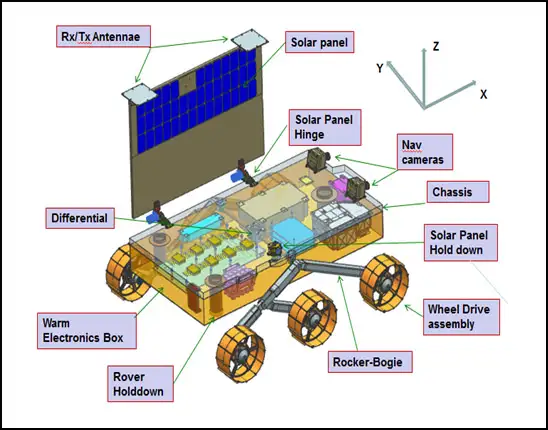
Chandrayaan-3 Rover
The Rover module of Chandrayaan-3 was equipped with advanced scientific instruments to conduct in-situ chemical analysis of the lunar surface. Two essential payloads on the Rover were the Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) and the Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscope (LIBS). These instruments enabled the derivation of the elemental composition in the vicinity of the landing site, providing valuable insights into the lunar surface.
Mission Objectives
Chandrayaan-3 had three primary mission objectives. The first objective was to demonstrate safe and soft landing on the lunar surface, building upon the lessons learned from the previous Chandrayaan-2 mission. The second objective was to showcase the capabilities of the Rover in roving on the Moon's surface, enabling mobility and exploration. Lastly, the mission aimed to conduct in-situ scientific experiments to further our understanding of the lunar environment.
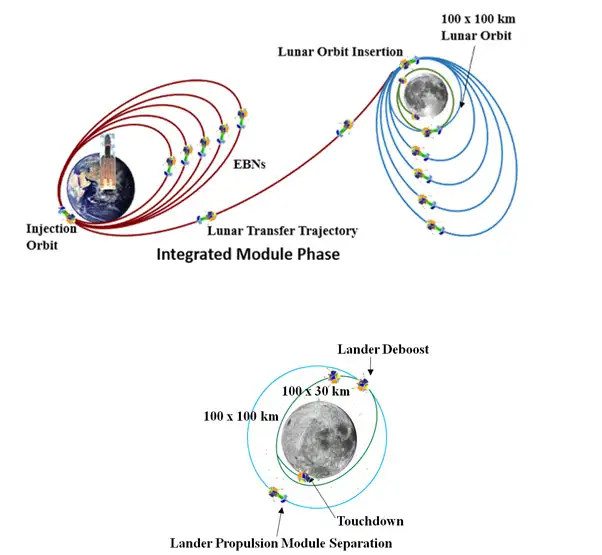
Chandrayaan-3 – Mission Profile
Advanced Technologies and Tests
To achieve its mission objectives, Chandrayaan-3 incorporated several advanced technologies in its Lander module. These technologies included laser and RF-based altimeters for precise altitude measurement, laser Doppler velocimeters, and a Lander Horizontal Velocity Camera for accurate velocity measurements. The propulsion system consisted of 800N throttleable liquid engines, 58N attitude thrusters, and throttleable engine control electronics.
Navigation, Guidance & Control (NGC) systems played a crucial role in ensuring a successful mission. Chandrayaan-3 utilized powered descent trajectory design and associated software elements to enable precise control during landing. Furthermore, hazard detection and avoidance mechanisms, such as the Lander Hazard Detection & Avoidance Camera and Processing Algorithm, were incorporated to ensure a safe landing. The Lander was also equipped with a robust landing leg mechanism for stability and touchdown in various conditions.
Validation and Testing
Before its launch, Chandrayaan-3 underwent rigorous testing and validation processes. The spacecraft and its advanced technologies were subjected to various special tests to ensure their performance and reliability. These tests included the Integrated Cold Test, which demonstrated the integrated sensors and navigation performance using a helicopter as a test platform. The Integrated Hot Test showcased closed-loop performance with sensors, actuators, and NGC using a tower crane as a test platform. Additionally, the Lander Leg mechanism performance test was conducted on a lunar simulant test bed, simulating different touchdown conditions.
Chandrayaan-3 marks a significant achievement for the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) in its pursuit of space exploration. With its successful launch and deployment, the mission is set to accomplish its objectives of safe landing, rover mobility, and in-situ scientific experiments on the lunar surface. Equipped with advanced technologies and scientific payloads, Chandrayaan-3 will contribute significantly to our understanding of the Moon and pave the way for future interplanetary missions. India's remarkable accomplishment in space exploration inspires hope and curiosity, as we eagerly await the discoveries and advancements that Chandrayaan-3 will bring.
Questions or comments on this article? E-mail us at news@sciencex.in
Source:
Image Credit:
What's Your Reaction?