Deimos Before Dawn
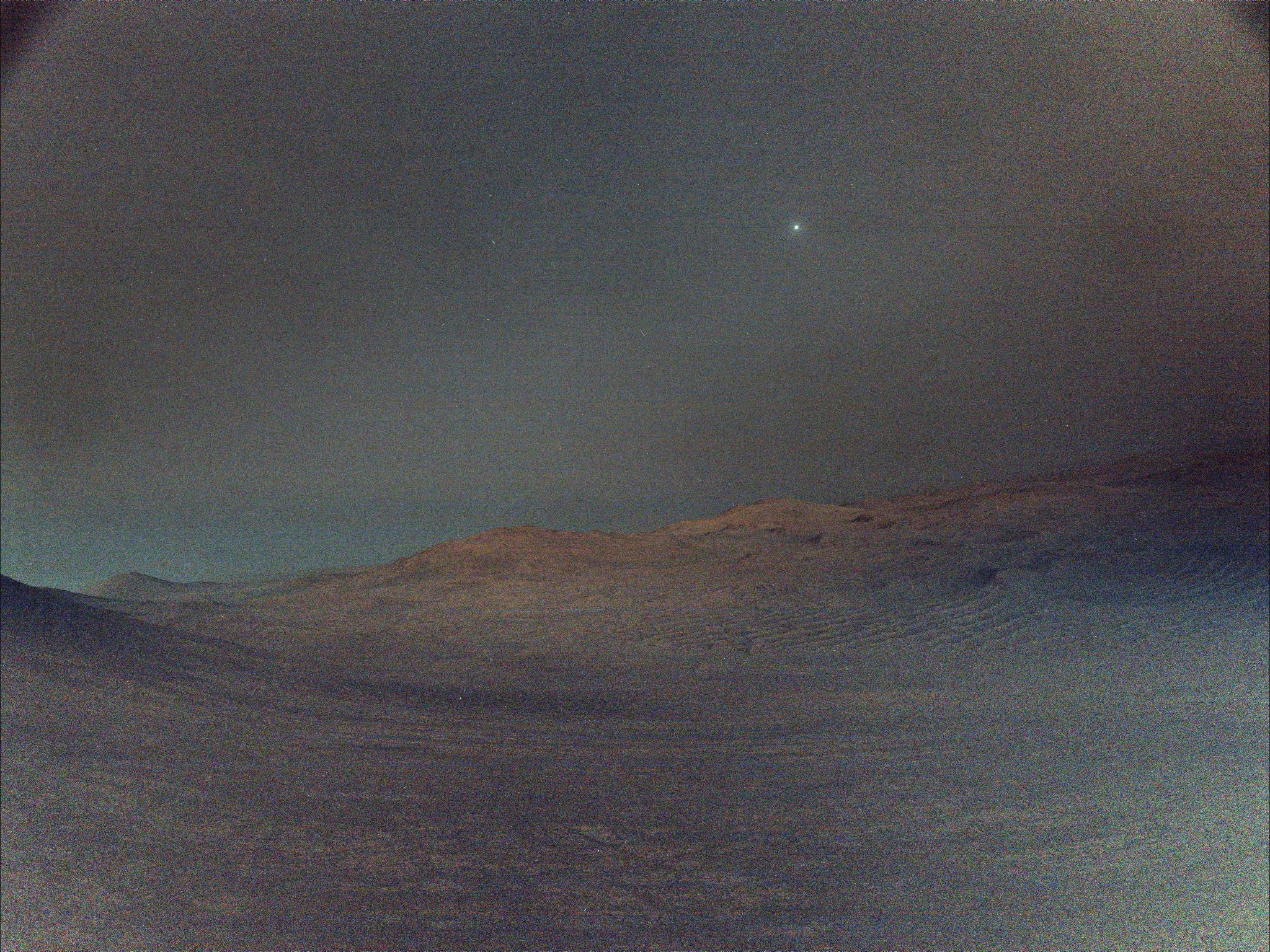
NASA’s Perseverance rover captured this view of Deimos, the smaller of Mars’ two moons, shining in the sky at 4:27 a.m. local time on March 1, 2025, the 1,433rd Martian day, or sol, of the mission. In the dark before dawn, the rover’s left navigation camera used its maximum long-exposure time of 3.28 seconds for […]

NASA’s Perseverance rover captured this view of Deimos, the smaller of Mars’ two moons, shining in the sky at 4:27 a.m. local time on March 1, 2025, the 1,433rd Martian day, or sol, of the mission. In the dark before dawn, the rover’s left navigation camera used its maximum long-exposure time of 3.28 seconds for each of 16 individual shots, all of which were combined onboard the camera into a single image that was later sent to Earth. In total, the image represents an exposure time of about 52 seconds.
The low light and long exposures add digital noise, making the image hazy. Many of the white specks seen in the sky are likely noise; some may be cosmic rays. Two of the brighter white specks are Regulus and Algieba, stars that are part of the constellation Leo.
Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
What's Your Reaction?