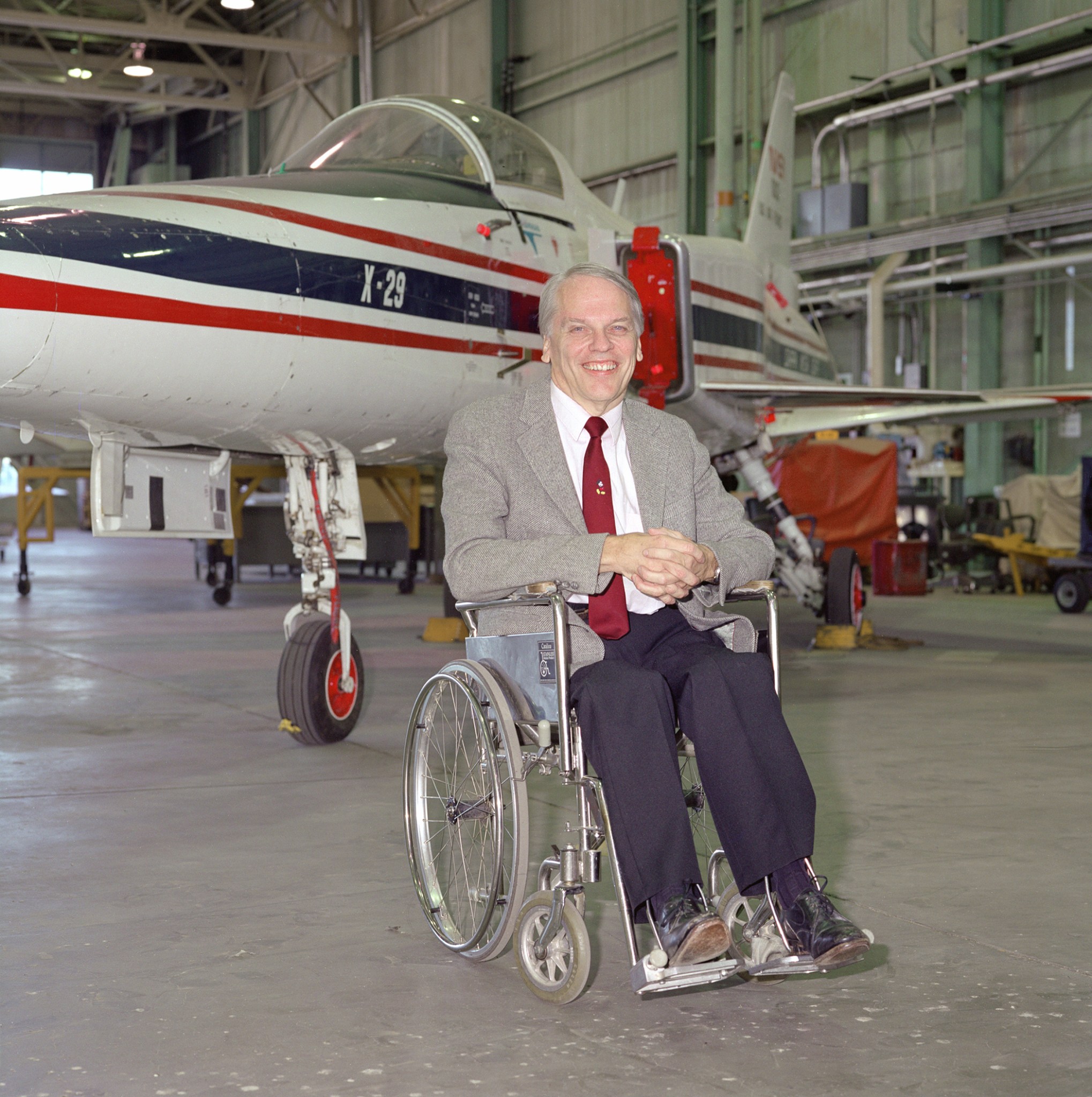
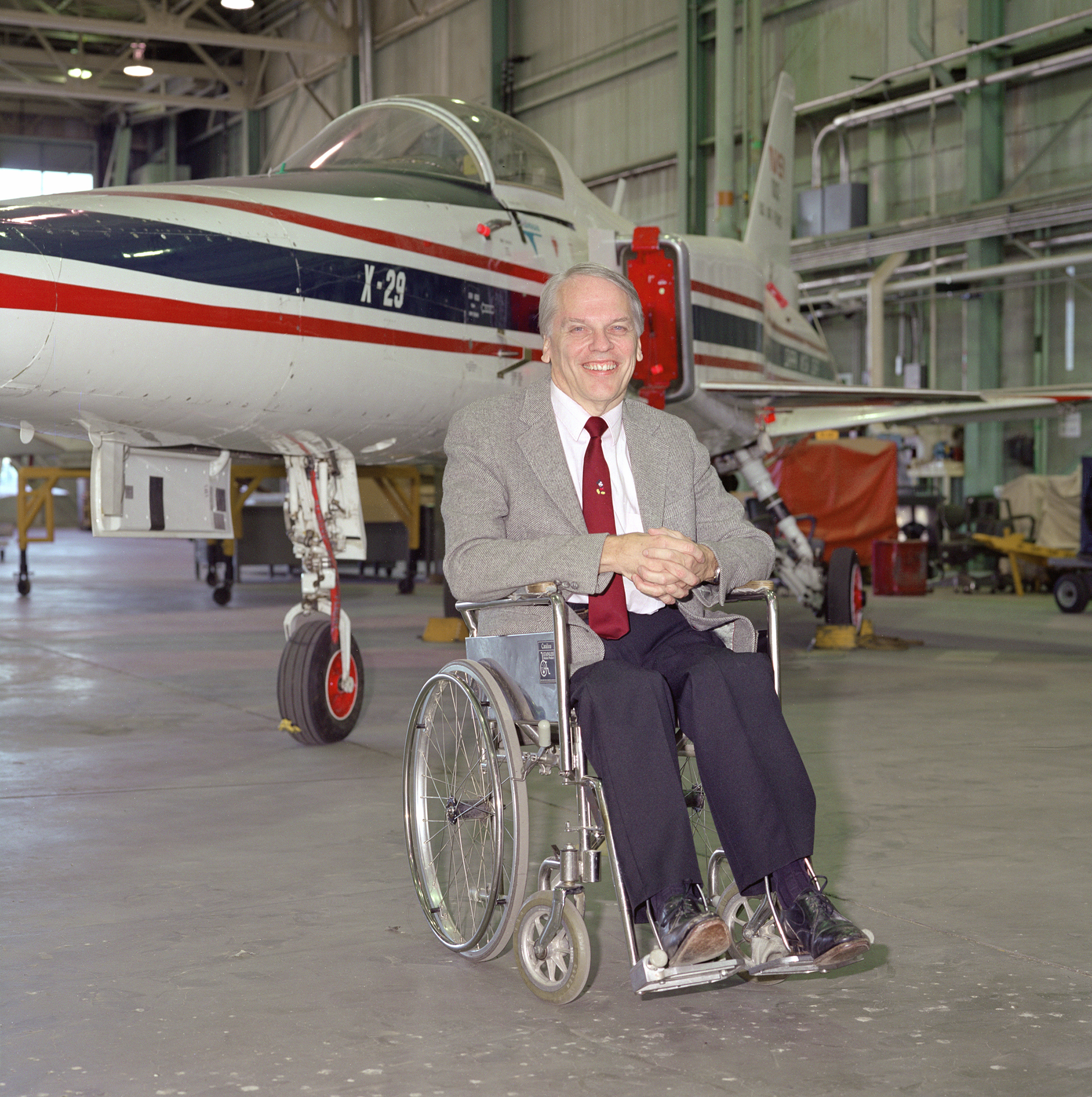
Ken Iliff: Engineering 40 Years of Success
Editor’s note: This article was published May 23, 2003, in NASA Armstrong’s X-Press newsletter. NASA’s Dryden Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, was redesignated Armstrong Flight Research Center on March 1, 2014. Ken Iliff was inducted into the National Hall of Fame for Persons with Disabilities in 1987. He died Jan. 4, 2016. As an […]

10 min read
Preparations for Next Moonwalk Simulations Underway (and Underwater)
Editor’s note: This article was published May 23, 2003, in NASA Armstrong’s X-Press newsletter. NASA’s Dryden Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, was redesignated Armstrong Flight Research Center on March 1, 2014. Ken Iliff was inducted into the National Hall of Fame for Persons with Disabilities in 1987. He died Jan. 4, 2016.
As an Iowa State University engineering student in the early 1960s, Ken Iliff was hard at work on a glider flight simulation.
Upon examining the final results – which, in those early days of the computer revolution, were viewed on a long paper printout – he noticed one glaring imperfection: the way he had programmed it, his doomed glider would determinedly accelerate as it headed for the ground.
The culprit was a single keystroke. At the time, programming was based on data that had been painstakingly entered into the computer by hand, on punch cards and piece by piece. Somewhere, Iliff had entered a plus sign instead of a minus sign.
The seemingly minor incident was to foreshadow great things to come in Iliff’s career.
Not long after graduation, the West Union, Iowa, native found himself at what was then called simply the NASA Flight Research Center located on Edwards Air Force Base.
“I just knew I didn’t want to be sitting somewhere in a big room full of engineers who were all doing the same thing,” Iliff said of choosing Dryden over other jobs and other NASA centers. “It was a small center doing important things, and it was in California. I knew I wanted to be there.”
Once at Dryden, the issue of data tidbits was central to the new hire’s workday. Iliff’s post called for him and many of his colleagues to spend much of their time “reading up” data – a laborious process of measuring data from film using a single reference line and a ruler. Measurements were made every tenth of a second; for a ten-second maneuver, a total of one hundred “traces” were taken for every quantity being recorded.
“I watched talented people spending entire days analyzing data,” he recalled. “And then, maybe two people would arrive at two entirely different conclusions” from the same data sets.
As has happened so often at the birth of revolutionary ideas, then, one day Iliff had a single, simple thought about the time-intensive and maddeningly inexact data analysis process:
“There just has to be a better way to do this.”
The remedy he devised was to result in a sea change at Dryden, and would reverberate throughout the world of computer-based scientific research.
Iliff’s work spanned the decades that encompassed some of Dryden’s greatest achievements, from the X-15 through the XB-70 and the tentative beginnings of the shuttle program. The solution he created to the problem of inaccuracy in data analysis focused on aerodynamic performance – how to formulate questions about an aircraft’s performance once answers about it are already known, how to determine the “why?” when the “what happens?” has already happened.
The work is known as “parameter estimation,” and is used in aerospace applications to extract precise definitions of aerodynamic, structural and performance parameters from flight data.
His methodology – cemented in computer coding Iliff developed using Fortran’s lumbering binary forerunner, machine code – allowed researchers to determine precisely the type of information previously derived only as best-estimate guesses through analysis of data collected in wind tunnels and other flight-condition simulators. In addition to aerospace science, parameter estimation is also used today in a wide array of research applications, including those involving submarines, economic models, and biomedicine.
With characteristic deference, Iliff now brushes off any suggestion of his discovery’s significance. Instead, he credits other factors for his successes, such as a Midwestern work ethic and Iowa State University’s early commitment to giving its engineering students good access to the new and emerging computer technology.
To hear him tell it, “all good engineers are a little bit lazy. We know how to innovate – how to find an easier way.
“I’d been trained well, and given the right tools – I was just in the right place at the right time.”
But however modestly he might choose to see it characterized, it’s fair to number Iliff’s among the longest and most distinguished careers to take root in the ranks of Dryden research engineers. Though his groundbreaking work will live forever in research science, when Iliff retired in December he brought to a close his official role in some of the most important chapters in Dryden history.
His pioneering work with parameter estimation carried through years of aerodynamic assessment and data analysis involving lifting-body and wing-body aircraft, from the X-15 through the M2-F1, M2-F2 and M2-F3 projects, the HL-10, the X-24B and NASA’s entire fleet of space shuttles. His contributions aided in flight research on the forward-swept-wing X-29 and the F/A-18 High Angle of Attack program, on F-15 spin research vehicles, on thrust vectoring and supermaneuverability.
Iliff began work on the space shuttle program when it was little more than a speculative “what’s next?” chapter in manned spaceflight, long before it reached officially sanctioned program status. Together with a group spearheaded by the late NASA research pilot and long-time Dryden Chief Engineer Milt Thompson – who Iliff describes unflinchingly as “my hero” – Iliff helped explore the vast range of possibilities for a new orbiting craft that would push NASA to its next frontier after landing on the moon.
In an environment much more informal than today’s, when there were few designations of “program manager” or “task monitor” or “deputy director” among NASA engineers like Iliff and Thompson, a handful of creative, disciplined minds were at work dreaming up a reusable aircraft that would launch, orbit the Earth and return. Iliff’s role was to offer up the rigor of comparison in size, speed and performance among potential aircraft designs; Thompson and Iliff’s group was responsible, for example, for the decision to abandon the notion of jet engines on the orbiter, decreeing them too heavy, too risky and too inefficient.
Month in and month out, Iliff and his colleagues painstakingly researched and developed the myriad design details that eventually materialized into the shuttle fleet. There was, in Iliff’s words, “a love affair between the shuttle and the engineers.”
And in a display typifying the charged environment of creative collaboration that governed the effort – an effort many observe wryly that it would be difficult to replicate at NASA, today or anytime – the body of research was compiled into the now-legendary aero-data book, a living document that records in minute detail every scrap of design and performance data recorded about the shuttles’ flight activity.
Usually with more than a touch of irony, the compiling of the aero-data book has been described with phrases like “a remarkably democratic process,” involving as it did the need for a hundred independent minds and strong personalities to agree on indisputable facts about heat, air flow, turbulence, drag, stability and a dozen other aerodynamic principles. But Iliff says the success of the mammoth project, last updated in 1996, was ultimately enabled by a shared commitment to a culture that was unique to Dryden, one that made the Center great.
“Well, big, complicated things don’t always come out like you think they will,” Iliff said.
“But we understood completely the idea of ‘informed risk.’ We had a thorough understanding of risks before taking them – nobody ever did anything on the shuttle that they thought was dangerous, or likely to fail.
“The truly great thing (about that era at Dryden) was that they mentored us, and let us take those risks, and helped us get good right away. That was how we were able to do what we did.”
It was an era that Iliff says he was thrilled to be a part of, and which he admits was difficult to leave. It was also, he adds with a note of uncharacteristic nostalgia, a time that would be hard to reinvent today after the intrusion of so many bureaucratic tentacles into the hot zone that spawned Dryden’s greatest achievements.
A man not much given to dwelling on the past, however, Iliff has moved on to a retirement he is making the most of. Together with his wife, Mary Shafer, also retired from her career as a Dryden engineer, he plans to dedicate time to cataloging the couple’s extensive travel experiences with new video and graphics software, and adding to the travel library with footage from new trips. Iraq ranks high on the short list.
During his 40-year tenure, Iliff held the post of senior staff scientist of Dryden’s research division from 1988 to 1994, when he became the Center’s chief scientist. Among numerous awards he received were the prestigious Kelly Johnson Award from the Society of Flight Test Engineers (1989), an award permanently housed in the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum, and NASA’s highest scientific honor, the NASA Exceptional Scientific Achievement Award (1976).
He was inducted into the National Hall of Fame for Persons with Disabilities in 1987, and served on many national aeronautic and aerospace committees throughout his career. He is a Fellow in the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA) and is the author of more than 100 technical papers and reports. He has given eleven invited lectures for NATO and AGARD (Advisory Group for Aerospace Research and Development), and served on four international panels as an expert in aircraft and spacecraft dynamics. Recently, he retired from his position as an adjunct professor of electrical engineering at the University of California, Los Angeles.
Iliff holds dual bachelor of science degrees in mathematics and aerospace engineering from Iowa State University; a master of science in mechanical engineering from the University of Southern California; a master of engineering degree in engineering management and a Ph.D. in electrical engineering, both from UCLA.
Iliff’s is the kind of legacy shared by a select group of American engineers, and to read the papers these days, there’s the suggestion that his is a vanishing breed. NASA and other science-based organizations are often depicted as scrambling for new engineering talent – particularly of the sort personified by Iliff and his pioneering achievements.
But, typical of the visionary approach he applies to life in general as well as to science, Iliff takes a wider view.
“I remember, after the X-1 – people figured all the good things had been done,” he said, with a smile in his voice. “And of course, they had not.
“If I was starting out now, I’d be starting in work with DNA, or biomedicine – improving lives with drug research. There are so many exciting things to be discovered there. They might not be as showy as lighting off a rocket, but they’re there.
“I’ve seen cycles. We’re at a low spot right now – but military, or space, will eventually be at the center again.”
And when that day comes, Iliff says he hopes officials in the flight research world will heed the example of Dryden’s early years, and give its engineers every opportunity to succeed unfettered – as he had been.
“Beware the ‘Chicken Littles’ out there,” he said. “I hope the government will be strong enough to resist them.”
Sarah Merlin
Former X-Press newsletter assistant editor
Former Dryden historian Curtis Peebles contributed to this article.
Share
Related Terms
What's Your Reaction?