NASA Goddard Lidar Team Receives Center Innovation Award for Advancements
NASA researchers Guan Yang, Jeff Chen, and their team received the 2024 Innovator of The Year Award at the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, for their exemplary work on a lidar system enhanced with artificial intelligence and other technologies. Like a laser-based version of sonar, lidar and its use in space exploration […]
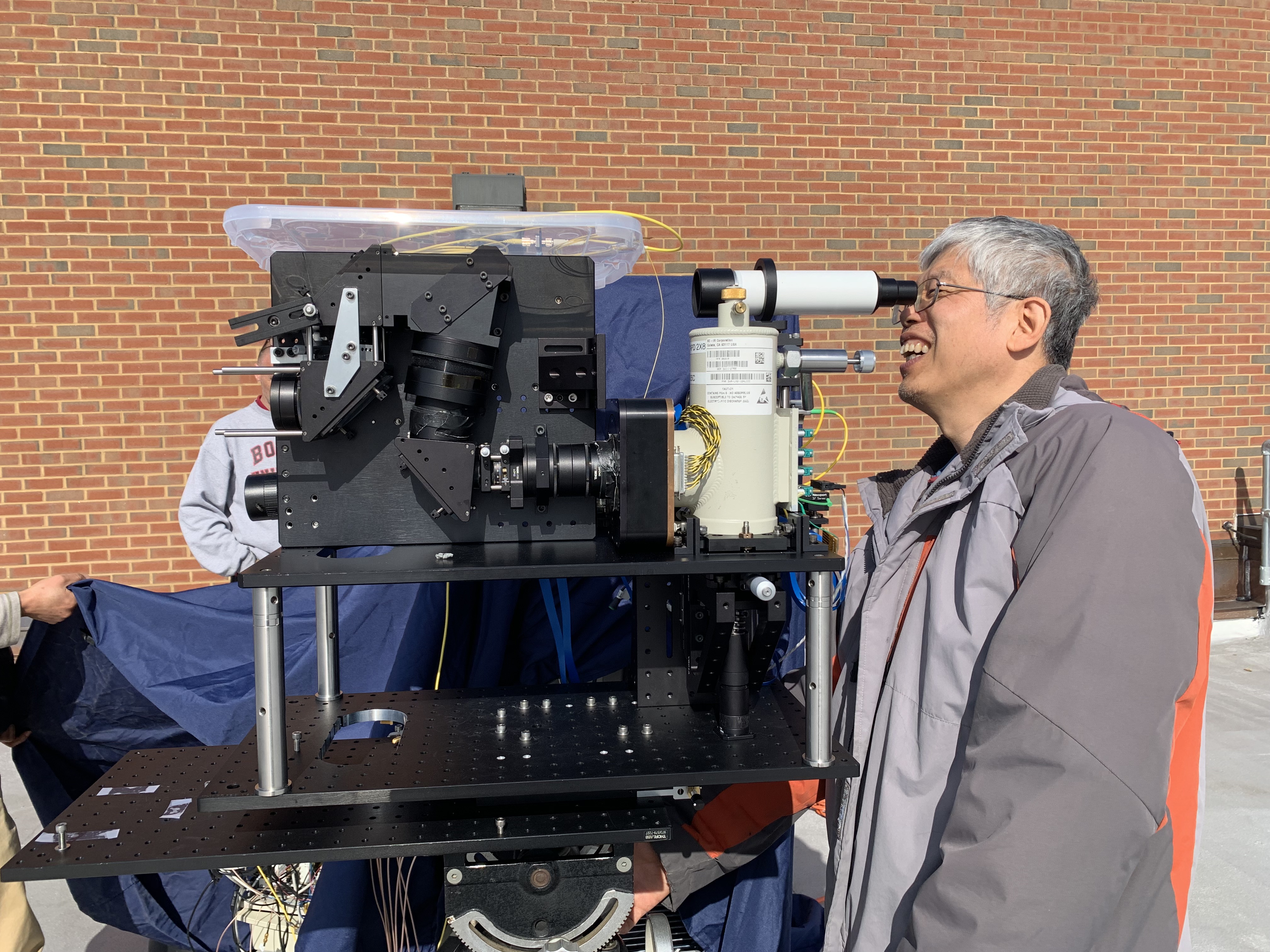
NASA researchers Guan Yang, Jeff Chen, and their team received the 2024 Innovator of The Year Award at the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, for their exemplary work on a lidar system enhanced with artificial intelligence and other technologies.
Like a laser-based version of sonar, lidar and its use in space exploration is not new. But the lidar system Yang and Chen’s team have developed — formally the Concurrent Artificially-intelligent Spectrometry and Adaptive Lidar System (CASALS) — can produce higher resolution data within a smaller space, significantly increasing efficiency compared to current models.
The true revolution in CASALS is a unique combination of related technologies, such as highly efficient laser and receiver designs, wavelength-based, non-mechanical beam steering, multispectral imaging, and the incorporation of artificial intelligence to allow the instrument to make its own decisions while in orbit, instead of waiting for direction from human controllers on the ground.
“Existing 3D-imaging lidars struggle to provide the 2-inch resolution needed by guidance, navigation and control technologies to ensure precise and safe landings essential for future robotic and human exploration missions,” team engineer Jeffrey Chen said in an earlier interview. “Such a system requires 3D hazard-detection lidar and a navigation doppler lidar, and no existing system can perform both functions.”
The CASALS lidar is being developed to study land and ice topography, coastline changes, and other Earth science topics. Future applications in solar system science beyond our planet are already in the works, including space navigation improvements and high-resolution lunar mapping for NASA’s Artemis campaign to return astronauts to the Moon.
An effective and compact lidar system like CASALS could also map rocky planets like Venus or Mars.
NASA leveraged contributions from external Small Business Innovation Research companies such as Axsun Technologies, Freedom Photonics, and Left Hand for laser and optical technology to help make CASALS a reality.
The Internal Research and Development (IRAD) Innovator of The Year award is presented by Goddard’s Office of the Chief Technologist to a person or team within the program with a notable contribution to cutting-edge technology. The CASALS team was presented their award at a technology poster session on Nov. 6, 2024, at NASA Goddard.
By Avery Truman
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.
Share
Details
Related Terms
What's Your Reaction?