NASA Preserves Its Past at Kennedy While Building Future of Space
Current and former employees of NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida gathered recently to celebrate the installation of a Florida Historical Marker cast in bronze at the location of the spaceport’s old headquarters building. The first of its kind inside the center’s secure area, the marker is the latest example of the center’s commitment to […]
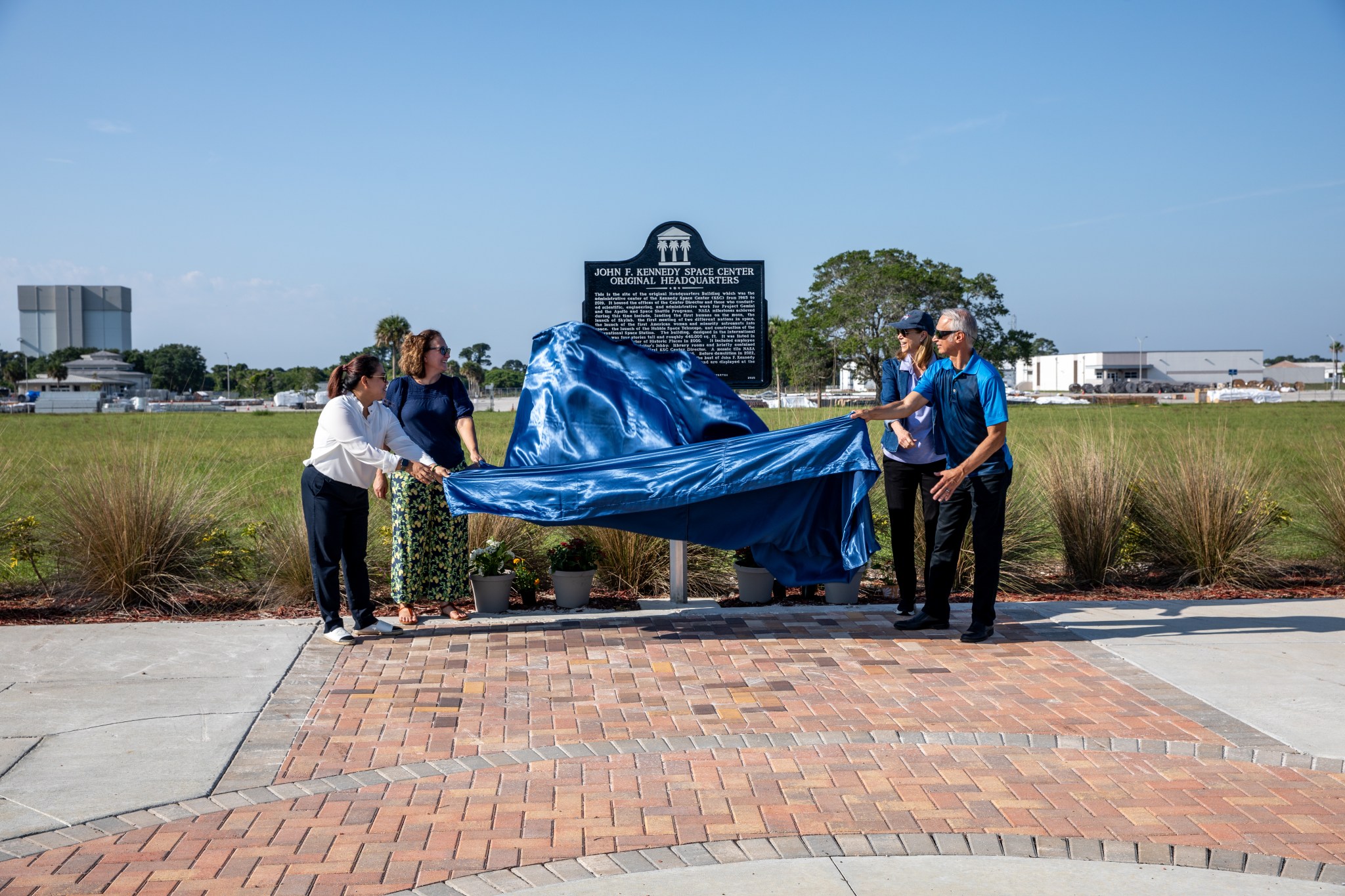


Current and former employees of NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida gathered recently to celebrate the installation of a Florida Historical Marker cast in bronze at the location of the spaceport’s old headquarters building.
The first of its kind inside the center’s secure area, the marker is the latest example of the center’s commitment to remembering its rich history as it continues to launch humanity’s future.
At the forefront of NASA Kennedy’s commitment to preservation is Katherine Zeringue, who serves as cultural resources manager, overseeing the center’s historic resources from buildings to historic districts to archaeological sites.
“Traditional approaches attempt to preserve things to a specific time period, including historic materials,” Zeringue said. “But that’s a challenge here because we still actively use our historic assets, which need to be modified to accommodate new missions and new spacecraft. Therefore, we rely on an adaptive reuse approach, in which the active use of a historic property helps to ensure its preservation.”
Many iconic structures are still in service at NASA Kennedy, like the Beach House where Apollo astronauts congregated with their families, the Vehicle Assembly Building where NASA rockets are still stacked, the Launch Control Center, and Launch Complex 39A. All told, 83 buildings, seven historic districts, and one National Historic Landmark are either listed or are eligible for listing on the National Register of Historic Places.
To conserve these resources, the spaceport follows a variety of federal laws, regulations, and executive orders, including the National Historic Preservation Act of 1966. This includes making a reasonable and good faith effort to identify any historic properties under its care and considering how its decisions affect historic properties.
“The Cultural Resources Management Program aims to balance historic preservation considerations with the agency’s mission and mandate to ensure reliable access to space for government and commercial payloads,” Zeringue said. “Finding that proper balance is challenging in the dynamic environment of our spaceport.”
Perhaps no other location embodies the center’s commitment to the past and the future more than Launch Complex 39A. Created in 1965, the launch complex was initially designed to support the Saturn V rocket, which powered the agency’s Apollo Program as it made numerous trips to the Moon. Outside of launching Skylab in 1973, the pad stood unused following Apollo’s end in 1972 until the agency’s Space Shuttle Program debuted in 1981. The transition from Apollo to space shuttle saw Launch Complex 39A transform from support of a single-use rocket to supporting the nation’s first reusable space launch and landing system.
By the time the program ended in 2011, 135 space shuttle launches had taken place within Kennedy’s boundary, 82 of which were at Launch Complex 39A. Many of those were among the program’s most notable, including the flights of astronauts Sally Ride, NASA’s first woman in space, and Guion Bluford, NASA’s first Black astronaut in space, as well as the first flight to the newly created International Space Station in 1998.
The launch complex began another transformation in 2014 when NASA signed a 20-year lease agreement with SpaceX as part of Kennedy’s transformation into a multi-user spaceport. SpaceX reconfigured Launch Complex 39A to support its Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy rockets, which today launch robotic science missions and other government and commercial payloads, as well as crew and cargo to the space station. Apollo-era infrastructure is incorporated in the SpaceX Crew Launch Tower.
“Launch Complex 39A exemplifies the balance between historic preservation and supporting the mission,” Zeringue noted. “Each chapter of the space program brings change, and those changes become additional chapters in the center’s historical legacy as we continue to build the future in space exploration.”
What's Your Reaction?