NASA Science Payload to Study Sticky Lunar Dust Challenge
The Moon may look like barren rock, but it’s actually covered in a layer of gravel, pebbles, and dust collectively known as “lunar regolith.” During the Apollo Moon missions, astronauts learned firsthand that the fine, powdery dust – electromagnetically charged due to constant bombardment by solar and cosmic particles – is extremely abrasive and clings […]
3 min read
Preparations for Next Moonwalk Simulations Underway (and Underwater)

The Moon may look like barren rock, but it’s actually covered in a layer of gravel, pebbles, and dust collectively known as “lunar regolith.” During the Apollo Moon missions, astronauts learned firsthand that the fine, powdery dust – electromagnetically charged due to constant bombardment by solar and cosmic particles – is extremely abrasive and clings to everything: gloves, boots, vehicles, and mechanical equipment. What challenges does that dust pose to future Artemis-era missions to establish long-term outposts on the lunar surface?
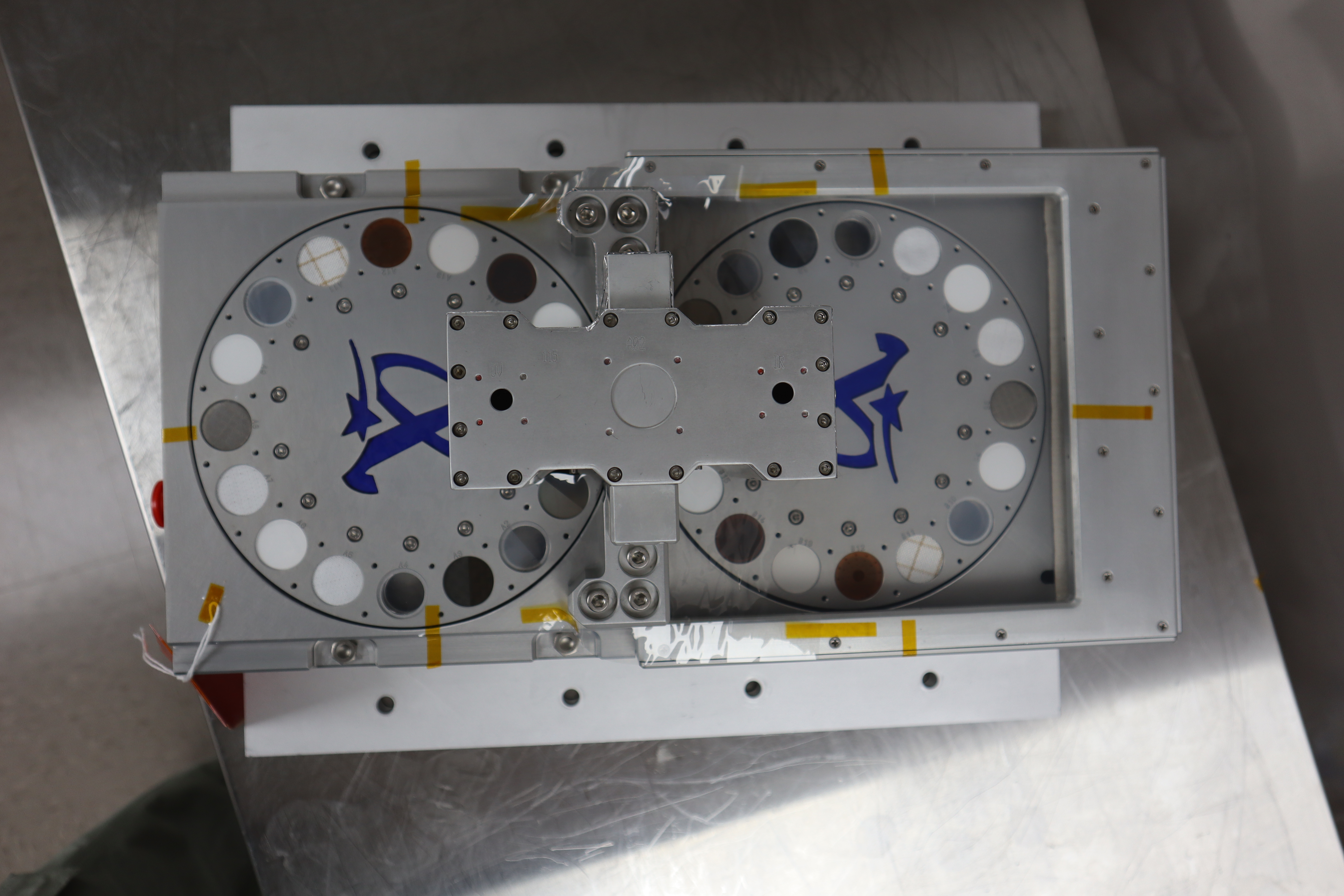
That’s the task of an innovative science instrument called RAC-1 (Regolith Adherence Characterization), one of 10 NASA payloads flying aboard the next delivery for the agency’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and set to be carried to the surface by Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander.
Developed by Aegis Aerospace of Webster, Texas, RAC will expose 15 sample materials – fabrics, paint coatings, optical systems, sensors, solar cells, and more – to the lunar environment to determine how tenaciously the lunar dust sticks to each one. The instrument will measure accumulation rates during landing and subsequent routine lander operations, aiding identification of those materials which best repel or shed dust. The data will help NASA and its industry partners more effectively test, upgrade, and protect spacecraft, spacesuits, habitats, and equipment in preparation for continued exploration of the Moon under the Artemis campaign.
“Lunar regolith is a sticky challenge for long-duration expeditions to the surface,” said Dennis Harris, who manages the RAC payload for NASA’s CLPS initiative at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. “Dust gets into gears, sticks to spacesuits, and can block optical properties. RAC will help determine the best materials and fabrics with which to build, delivering more robust, durable hardware, products, and equipment.”
Under the CLPS model, NASA is investing in commercial delivery services to the Moon to enable industry growth and support long-term lunar exploration. As a primary customer for CLPS deliveries, NASA aims to be one of many customers on future flights. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development of seven of the 10 CLPS payloads carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.
Learn more about. CLPS and Artemis at:
Alise Fisher
Headquarters, Washington
202-358-2546
Alise.m.fisher@nasa.gov
Headquarters, Washington
202-358-2546
Corinne Beckinger
Marshall Space Flight Center, Huntsville, Ala.
256-544-0034
corinne.m.beckinger@nasa.gov
Share
Details
Related Terms
What's Your Reaction?