NASA, Smithsonian Open New Exhibit to Showcase Our Dynamic Earth
NASA Administrator Bill Nelson joined the director of the Smithsonian’s National Museum of Natural History in Washington and agency leadership to unveil the new Earth Information Center exhibit during an early preview on Monday. “NASA has studied Earth and our changing climate for more than 60 years. The Earth Information Center at the Smithsonian Museum […]
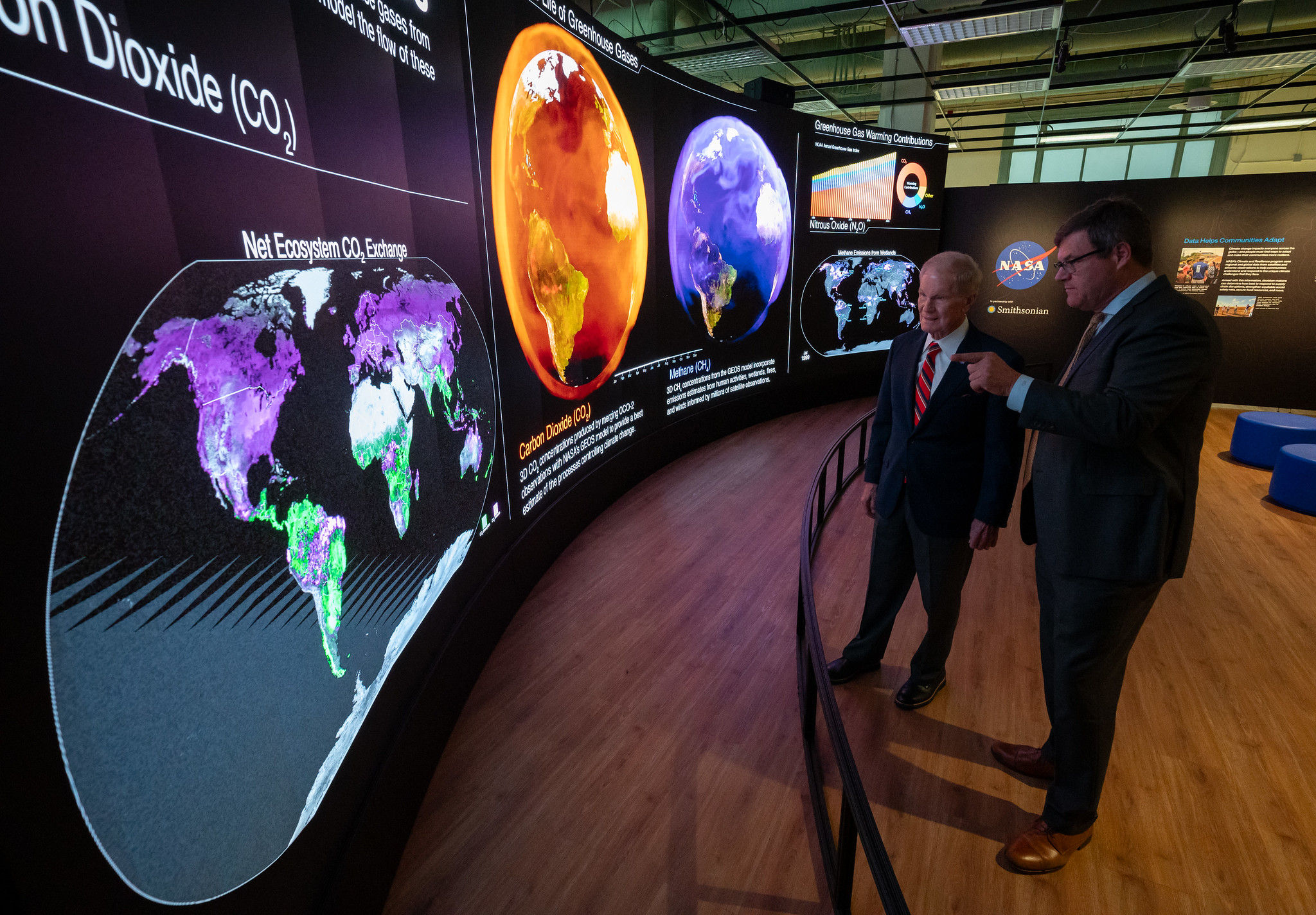
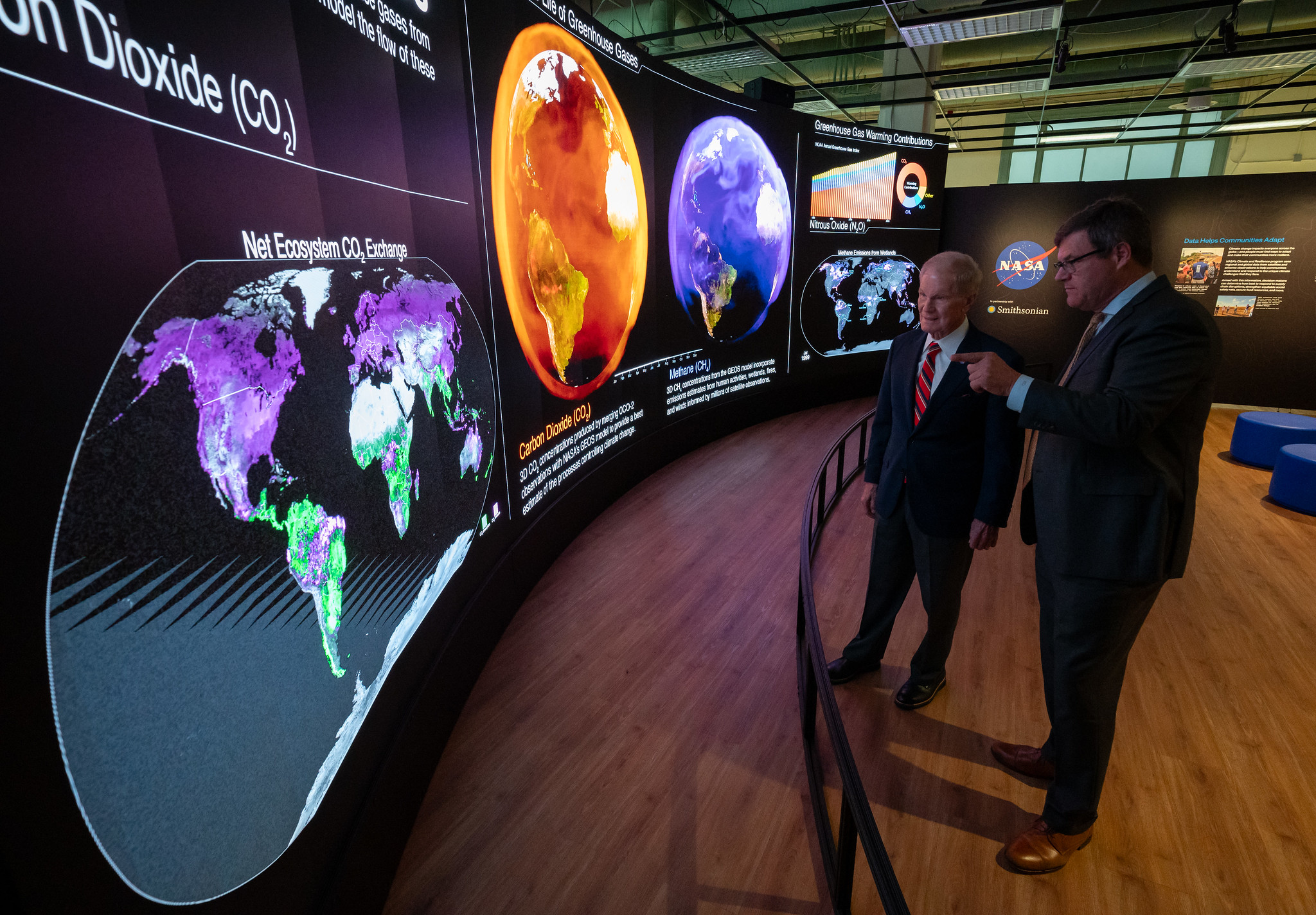


NASA Administrator Bill Nelson joined the director of the Smithsonian’s National Museum of Natural History in Washington and agency leadership to unveil the new Earth Information Center exhibit during an early preview on Monday.
“NASA has studied Earth and our changing climate for more than 60 years. The Earth Information Center at the Smithsonian Museum of Natural History will expand access to NASA’s data and our decades of Earth observation to even more people,” said Nelson. “Together with the Smithsonian, we are providing detailed, usable, and scalable information to enable the public to better understand the climate crisis and take action in their community.”
The exhibit includes a 32-foot-long, 12-foot-high video wall displaying Earth science data visualizations and videos, interpretive panels showing Earth’s connected systems, information on our changing world, and an overview of how NASA and the Smithsonian study our home planet. It opens to the public Tuesday, Oct. 8.
“The new Earth Information Center at the National Museum of Natural History will bring Smithsonian and NASA data on the Earth’s environment and climate to thousands of museum visitors every year,” said Kirk Johnson, the museum’s Sant director. “It is an honor to partner with NASA to bring this dynamic view of Earth to museumgoers and connect people more deeply with their home planet.”
Visitors also can explore Earth observing missions, changes in Earth’s landscape over time, and how climate is expected to change regionally through multiple interactive experiences. The exhibit will remain on display through 2028.
“The Earth Information Center allows people to see our planet as we at NASA see it – an awe-inspiring and complex system of oceans, land, ice, atmosphere, and the life they support,” said Karen St. Germain, division director, Earth Sciences Division at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “We are thrilled that this collaboration puts NASA’s Earth science at the fingertips of Smithsonian visitors for the benefit of all.”
With more than two dozen missions in orbit, NASA observes our planet’s oceans, land, ice, and atmosphere, and measure how a change in one drives change in others. NASA develops new ways to build long-term data records of how our planet evolves. The agency freely shares this unique knowledge and works with institutions around the world.
As part of NASA’s ongoing mission to better understand our home planet, NASA created the Earth Information Center which draws insights from across all NASA centers and its federal partners – the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, U.S. Geological Survey, U.S. Department of Agriculture, U.S. Agency for International Development, Environmental Protection Agency, and Federal Emergency Management Administration. It allows viewers to see how our home planet is changing and gives decision makers information to develop the tools they need to mitigate, adapt, and respond to those changes.
NASA’s Earth Information Center is a virtual and physical space designed to aid people to make informed decisions on Earth’s environment and climate. It provides easily accessible Earth information, enabling global understanding of our changing planet.
The expansion of the physical Earth Information Center at the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History makes it the second location in the Washington area. The first is located at NASA Headquarters in Washington at 300 E St., SW.
To learn more about the Earth Information Center, visit:
-end-
Meira Bernstein / Elizabeth Vlock
Headquarters, Washington
202-358-1600
meira.b.bernstein@nasa.gov / elizabeth.a.vlock@nasa.gov
What's Your Reaction?