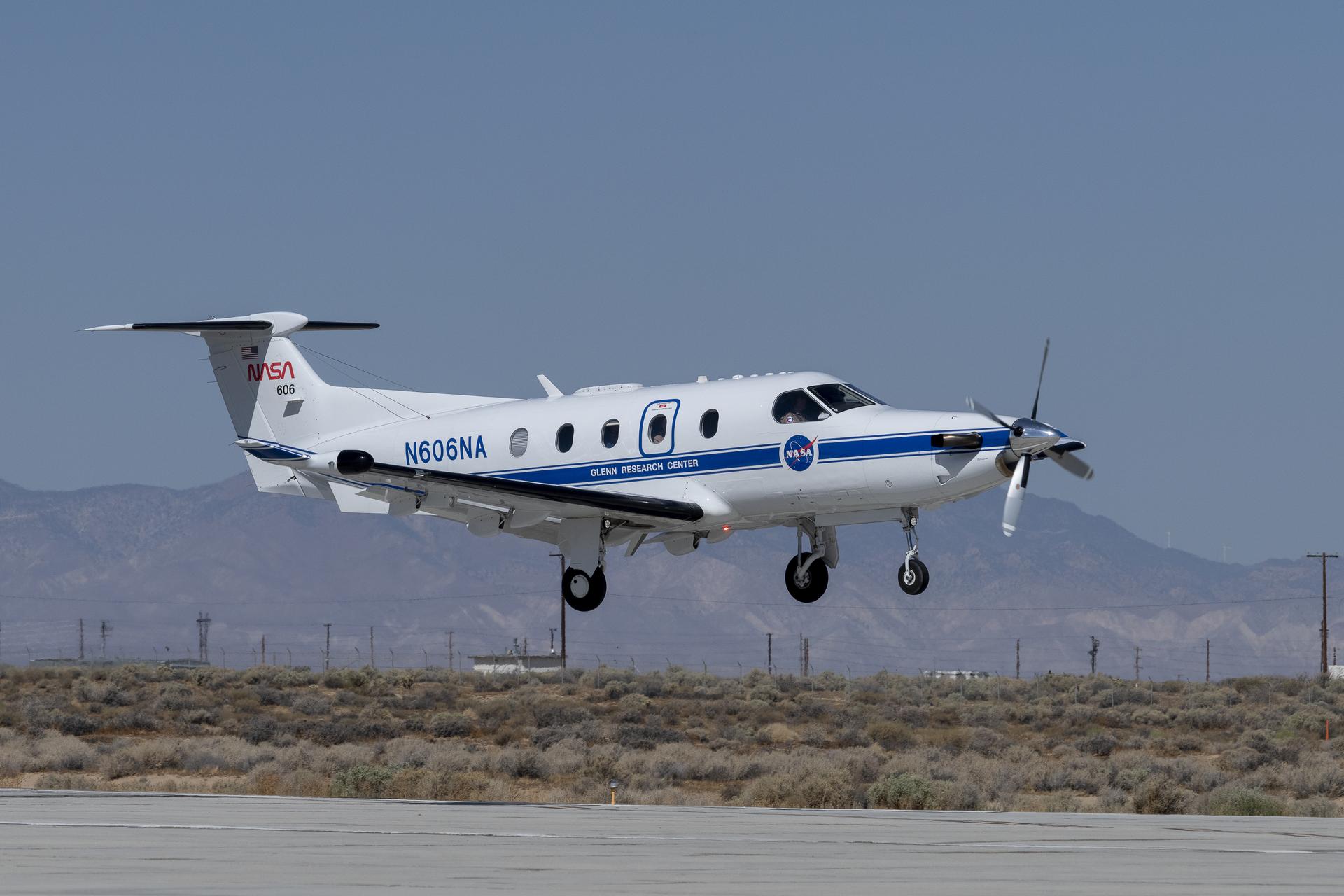
NASA Tests Air Traffic Surveillance Technology Using Its Pilatus PC-12 Aircraft
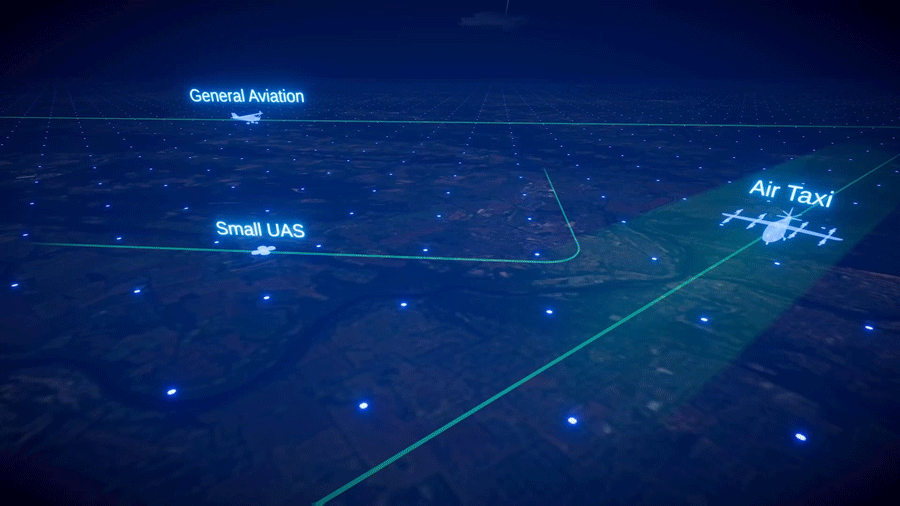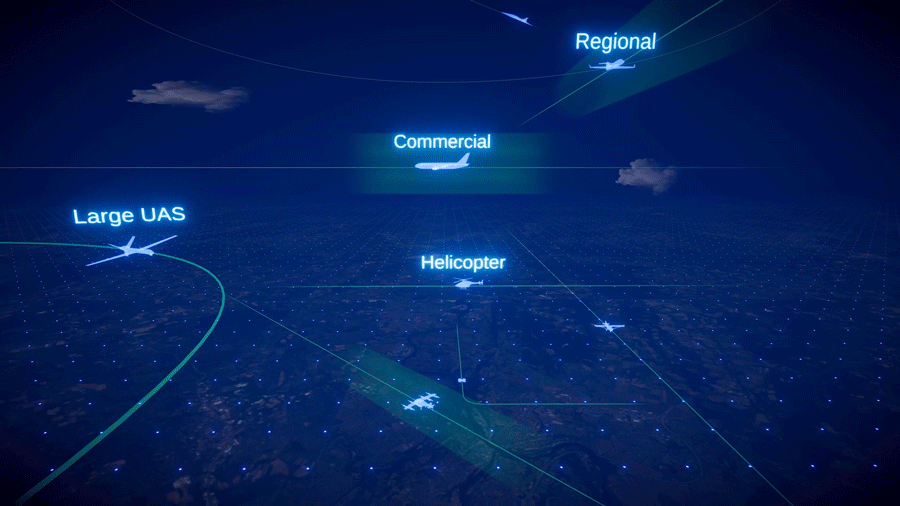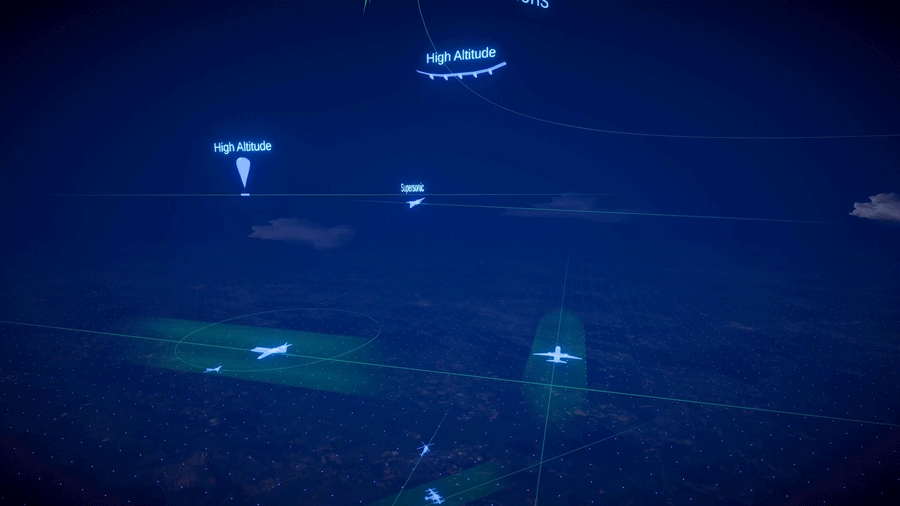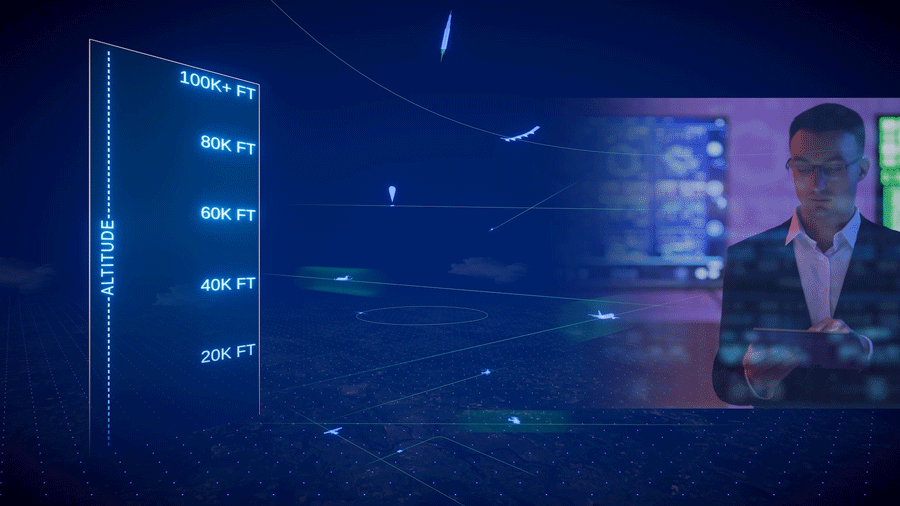
As air taxis, drones, and other innovative aircraft enter U.S. airspace, systems that communicate an aircraft’s location will be critical to ensure air traffic safety. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) requires aircraft to communicate their locations to other aircraft and air traffic control in real time using an Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) system. NASA is […]

3 min read
Preparations for Next Moonwalk Simulations Underway (and Underwater)

As air taxis, drones, and other innovative aircraft enter U.S. airspace, systems that communicate an aircraft’s location will be critical to ensure air traffic safety.
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) requires aircraft to communicate their locations to other aircraft and air traffic control in real time using an Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) system. NASA is currently evaluating an ADS-B system’s ability to prevent collisions in a simulated urban environment. Using NASA’s Pilatus PC-12 aircraft, researchers are investigating how these systems could handle the demands of air taxis flying at low altitudes through cities.
When operating in urban areas, one particular challenge for ADS-B systems is consistent signal coverage. Like losing cell-phone signal, air taxis flying through densely populated areas may have trouble maintaining ADS-B signals due to distance or interference. If that happens, those vehicles become less visible to air traffic control and other aircraft in the area, increasing the likelihood of collisions.
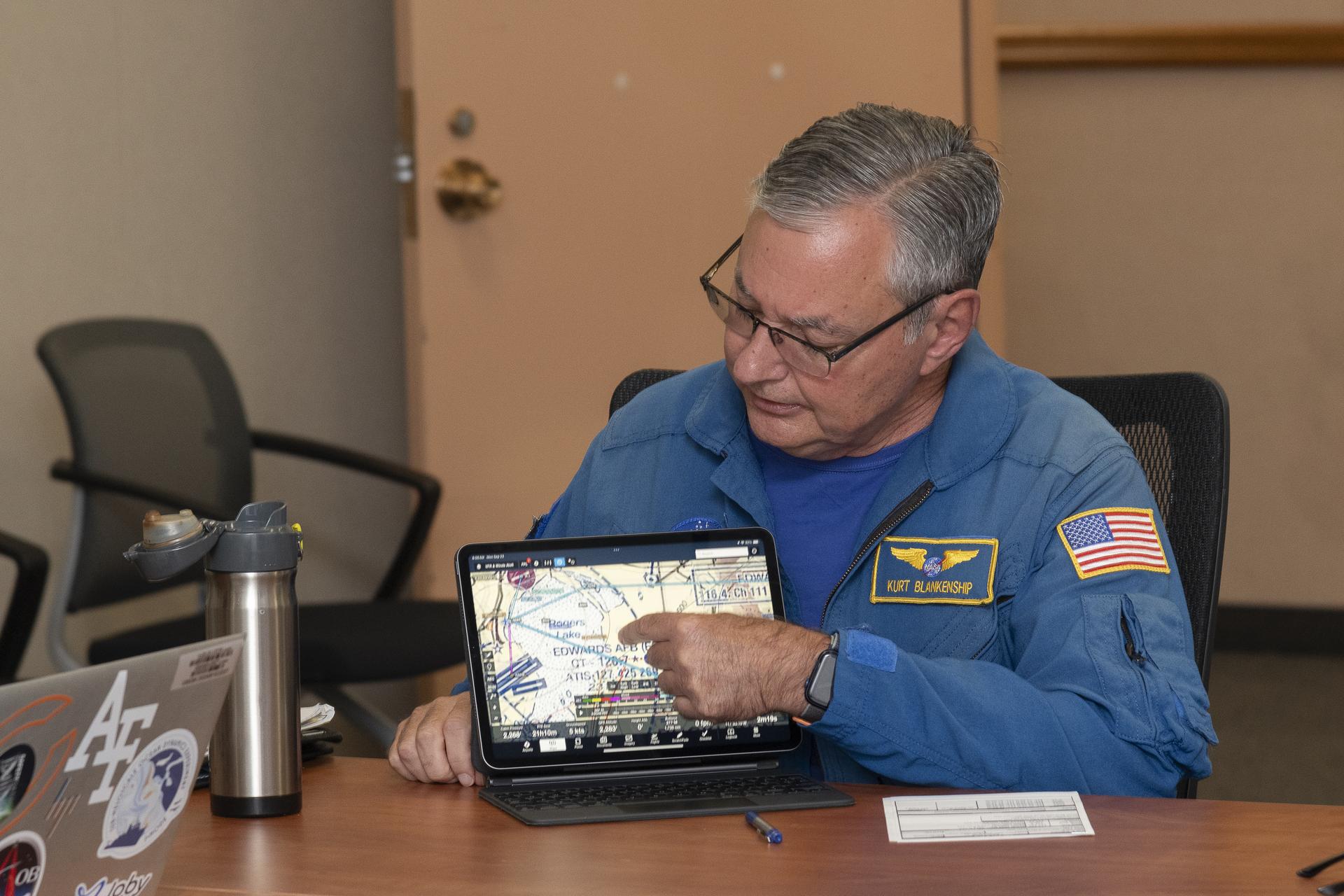

To simulate the conditions of an urban flight area and better understand signal loss patterns, NASA researchers established a test zone at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, on Sept. 23 and 24, 2024.
Flying in the agency’s Pilatus PC-12 in a grid pattern over four ADS-B stations, researchers collected data on signal coverage from multiple ground locations and equipment configurations. Researchers were able to pinpoint where signal dropouts occurred from the strategically placed ground stations in connection to the plane’s altitude and distance from the stations. This data will inform future placement of additional ground stations to enhance signal boosting coverage.
“Like all antennas, those used for ADS-B signal reception do not have a constant pattern,” said Brad Snelling, vehicle test team chief engineer for NASA’s Air Mobility Pathfinders project. “There are certain areas where the terrain will block ADS-B signals and depending on the type of antenna and location characteristics, there are also flight elevation angles where reception can cause signal dropouts,” Snelling said. “This would mean we need to place additional ground stations at multiple locations to boost the signal for future test flights. We can use the test results to help us configure the equipment to reduce signal loss when we conduct future air taxi flight tests.”
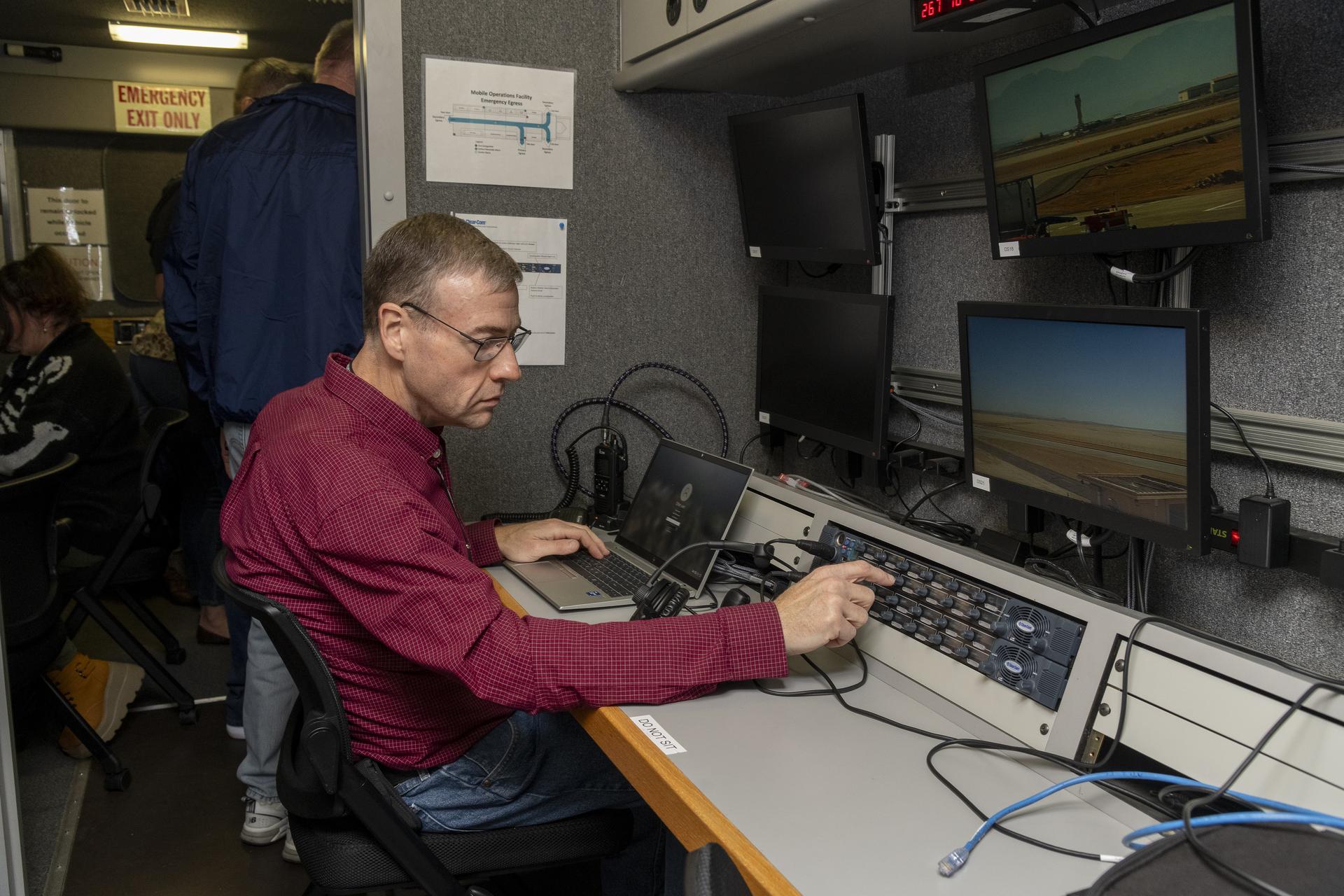

The September flights at NASA Armstrong built upon earlier tests of ADS-B in different environments. In June, researchers at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland flew the Pilatus PC-12 and found a consistent ADS-B signal between the aircraft and communications antennas mounted on the roof of the center’s Aerospace Communications Facility. Data from these flights helped researchers plan out the recent tests at NASA Armstrong. In December 2020, test flights performed under NASA’s Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign used an OH-58C Kiowa helicopter and ground-based ADS-B stations at NASA Armstrong to collect baseline signal information.
NASA’s research in ADS-B signals and other communication, navigation, and surveillance systems will help revolutionize U.S. air transportation. Air Mobility Pathfinders researchers will evaluate the data from the three separate flight tests to understand the different signal transmission conditions and equipment needed for air taxis and drones to safely operate in the National Air Space. NASA will use the results of this research to design infrastructure to support future air taxi communication, navigation, and surveillance research and to develop new ADS-B-like concepts for uncrewed aircraft systems.
Share
Details
Related Terms
What's Your Reaction?