NASA’s Laser Navigation Tech Enables Commercial Lunar Exploration
Later this month, NASA’s commercial lunar delivery services provider Intuitive Machines will launch its Nova-C lunar lander carrying several NASA science and technology payloads, including the Navigation Doppler Lidar (NDL). This innovative guidance system, developed by NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, under the agency’s Space Technology Mission Directorate (STMD), can potentially revolutionize landing […]
NASA’s Laser Navigation Tech Enables Commercial Lunar Exploration
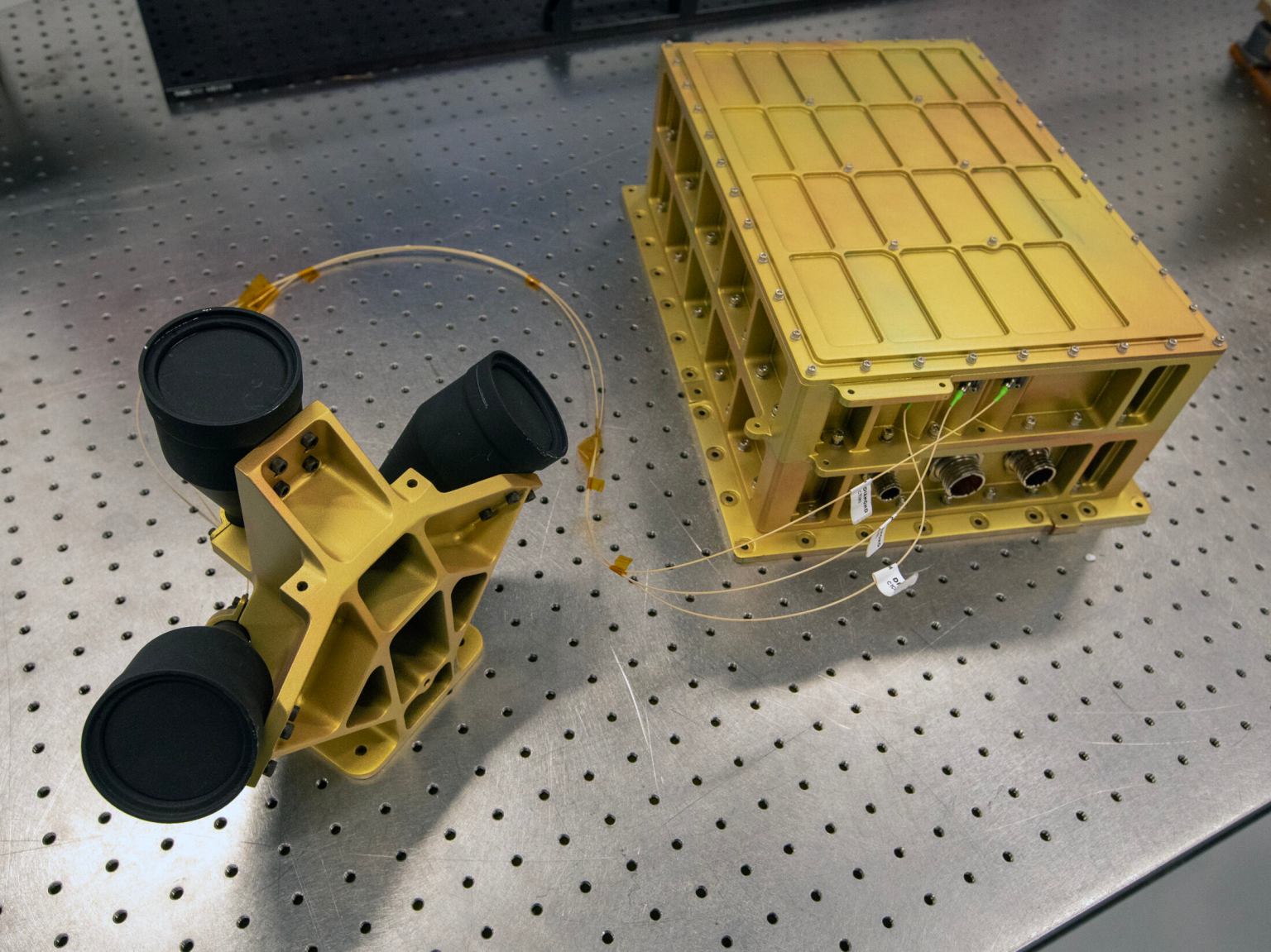
Later this month, NASA’s commercial lunar delivery services provider Intuitive Machines will launch its Nova-C lunar lander carrying several NASA science and technology payloads, including the Navigation Doppler Lidar (NDL). This innovative guidance system, developed by NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, under the agency’s Space Technology Mission Directorate (STMD), can potentially revolutionize landing spacecraft on extraterrestrial worlds.
The NDL technology is a NASA payload for this Intuitive Machines Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) delivery, meaning NASA will demonstrate NDL’s capabilities in the lunar environment during the mission but the data is not considered mission-critical for the successful landing of Nova-C, as Intuitive Machines has its own navigation and landing systems.
The NDL story started almost 20 years ago when Dr. Farzin Amzajerdian, NDL project manager at NASA Langley, made a breakthrough and successfully found a precise way to land rovers on Mars. In the late 1990s and early 2000s, several attempts at landing rovers on the surface of Mars were met with several significant challenges.
Radar was inherently imprecise for this application. Radio waves cover a large area on the ground, meaning smaller craters and boulders that are commonly found on the Martian surface could ‘hide’ from detection and cause unexpected hazards for landers.
“The landers needed the radar sensor to tell them how far they were off the ground and how fast they were moving so they could time their parachute deployment,” said Amzajerdian. “Too early or too late, the lander would miss its target or crash into the surface.”
Radio waves also couldn’t measure velocity and range independently of one another, which is important, according to Aram Gragossian, electro-optics lead for NDL at NASA Langley, who joined the team about six years ago.
“If you go over a steep slope, the range changes very quickly, but that doesn’t mean your velocity has changed,” he said. “So if you just feed that information back to your system, it may cause catastrophic reactions.”
Amzajerdian knew about this problem, and he knew how to fix it.
“Why not use a lidar instead of a radar?” he asked.
LiDAR, which stands for light detection and ranging, is a technology that uses visible or infrared light the same way radar uses radio waves. Lidar sends laser pulses to a target, which reflects some of that light back onto a detector. As the instrument moves in relation to its target, the change in frequency of the returning signal – also known as the Doppler effect – allows the lidar to measure velocity directly and precisely. Distance is measured based on the travel time of the light to the target and back.
Lidar offered several advantages over radar, notably the fact that a laser transmits a pencil beam of light that can give a more precise and accurate measurement.
In 2004, Amzajerdian proposed NDL as a concept to the Mars Science Laboratory team. In 2005, he and his team received funding from Langley to put together a proof of concept. Then, in 2007, they received funding for building and testing a prototype of a helicopter. This is when Langley’s Dr. Glenn Hines joined NDL — first as electronic lead and now as chief engineer.
Since then, Amzajerdian, Hines, and numerous other team members have worked tirelessly to ensure NDL’s success.
Hines credits the various NASA personnel who have continued to advocate for NDL. “In almost everything in life, you’ve got to have a champion,” Hines said, “somebody in your corner saying, ‘Look, what you’re doing is good. This has credibility.’ ”
The Intuitive Machines delivery is just the beginning of the NDL story; a next-generation system is already in the works. The team has developed a companion sensor to NDL, a multi-functional Flash Lidar camera. Flash Lidar is a 3D camera technology that surveys the surrounding terrain — even in complete darkness. When combined with NDL, Flash Lidar will allow you to go “anywhere, anytime.”
Other future versions of NDL could have uses outside the tricky business of landing on extraterrestrial surfaces. In fact, they may have uses in a very terrestrial setting, like helping self-driving cars navigate local streets and highways.
Looking at the history and trajectory of NDL, one thing is certain: The initial journey to the Moon will be the culmination of decades of hard work, perseverance, determination, and a steadfast belief in the project across the team, but held most fervently by NDL’s champions, Amzajerdian and Hines.
NDL was NASA’s Invention of the Year in 2022. Four programs within STMD contributed to NDL’s development: Flight Opportunities, Technology Transfer, Small Business Innovation Research & Small Business Technology Transfer, and Game Changing Development.
NASA is working with multiple CLPS vendors to establish a regular cadence of payload deliveries to the Moon to perform experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the lunar surface. Payloads delivered through CLPS will help NASA advance capabilities for science, technology, and exploration on the Moon.
Simone Williams
NASA Langley Research Center
Share
Details
Related Terms
What's Your Reaction?