NASA’s SpaceX Crew-10 to Explore Deep Space Exercise, Health
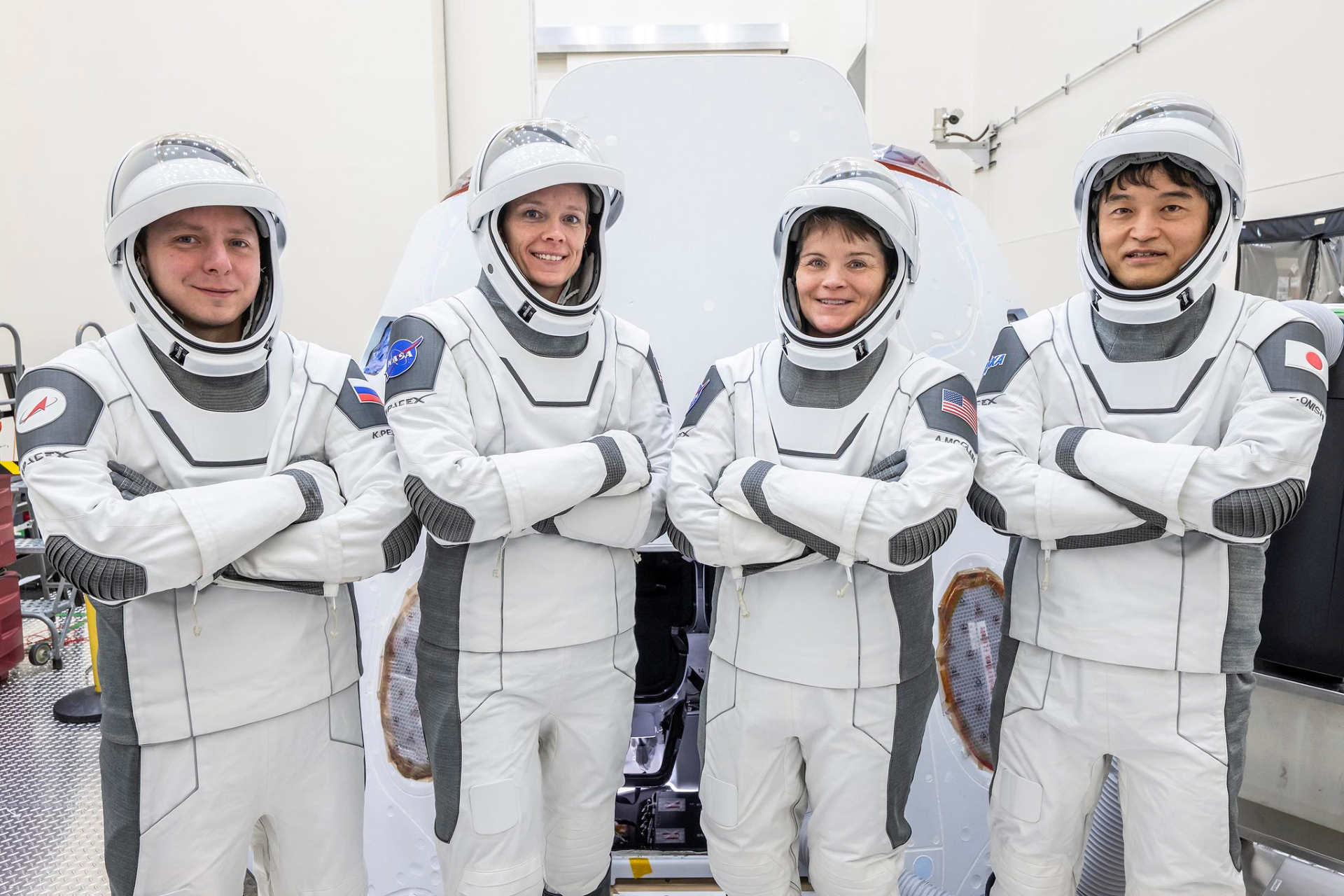
During NASA’s SpaceX Crew-10 mission to the International Space Station, which is scheduled to launch in March, select members of the four-person crew will participate in exercise and medical research aimed at keeping astronauts fit on future long-duration missions. Crew members living and working aboard the space station have access to a designated training area […]
During NASA’s SpaceX Crew-10 mission to the International Space Station, which is scheduled to launch in March, select members of the four-person crew will participate in exercise and medical research aimed at keeping astronauts fit on future long-duration missions.
Crew members living and working aboard the space station have access to a designated training area outfitted with a weight-lifting system, a stationary bike, and a specialized treadmill called T2. The space station is expansive enough for bulky exercise equipment that helps preserve the health and performance of astronauts in space and when they return to Earth.
However, as NASA looks to explore beyond low Earth orbit, the agency anticipates future spacecraft will not have room for large exercise equipment, like treadmills. Since walking and running are essential parts of workouts aboard the space station, NASA does not fully understand how long-duration spaceflights without a treadmill will impact crews’ health and motor functions. Consequently, NASA researchers are adjusting astronauts’ training regimens, including eliminating the use of the treadmill in some cases, to study ways that maintain crews’ strength, fitness, bone health, and balance.
In an ongoing study called Zero T2, expedition crews are divided into three groups with different workout regimens. One group continues exercising normally, using all the available equipment aboard the orbiting complex. A second group forgoes using the treadmill, relying solely on the other available equipment. While a third group will only exercise using a new, experimental, less bulky workout machine. NASA compares the groups’ health data collected before, during, and after flight to determine if the lack of treadmill use negatively impacts the crews’ fitness, muscle performance, and recovery after return to Earth.
“A treadmill takes up a lot of mass, space, and energy. This is not great for missions to Mars where every kilogram counts,” explained NASA astronaut Matthew Dominick, who participated in the same study while serving as commander of NASA’s SpaceX Crew-8 mission in 2024. “The Zero T2 experiment is helping us figure out if we can go without a treadmill and still be healthy.”
Results of the Zero T2 study will help researchers determine how treadmill-free workouts may affect crew health, which will, in turn, help NASA build realistic exercise protocols for future deep space missions. Additionally, this investigation could support design improvements for exercise devices used to prevent or treat bone, muscle, and cardiovascular health on Earth.
Beyond the Zero T2 study, select NASA crew members will perform additional studies supported by the agency’s Human Research Program during their mission. Participating crew will conduct medical exams, provide biological samples, and document spaceflight-related injuries, among other tasks.
“Astronauts choose which studies to participate in based on their interests,” explained Cherie Oubre, a NASA scientist at the agency’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, who helps oversee human research studies carried out aboard the space station. “The experiments address important risks and gaps associated with human spaceflight.”
One set of experiments, called CIPHER (Complement of Integrated Protocols for Human Exploration Research), will help researchers understand how multiple systems within the human body adjust to varying mission durations. CIPHER study members will complete vision assessments, cognitive tests, and MRI scans to help provide a clearer picture of how the entire body is affected by space.
“The CIPHER experiment tracks changes in the eyes, bones, heart, muscles, immune system, and more,” Oubre said. “The investigation provides the most comprehensive overview of how long-duration spaceflight affects the entire human body ever conducted, helping us advance human expeditions to the Moon, Mars, and elsewhere.”
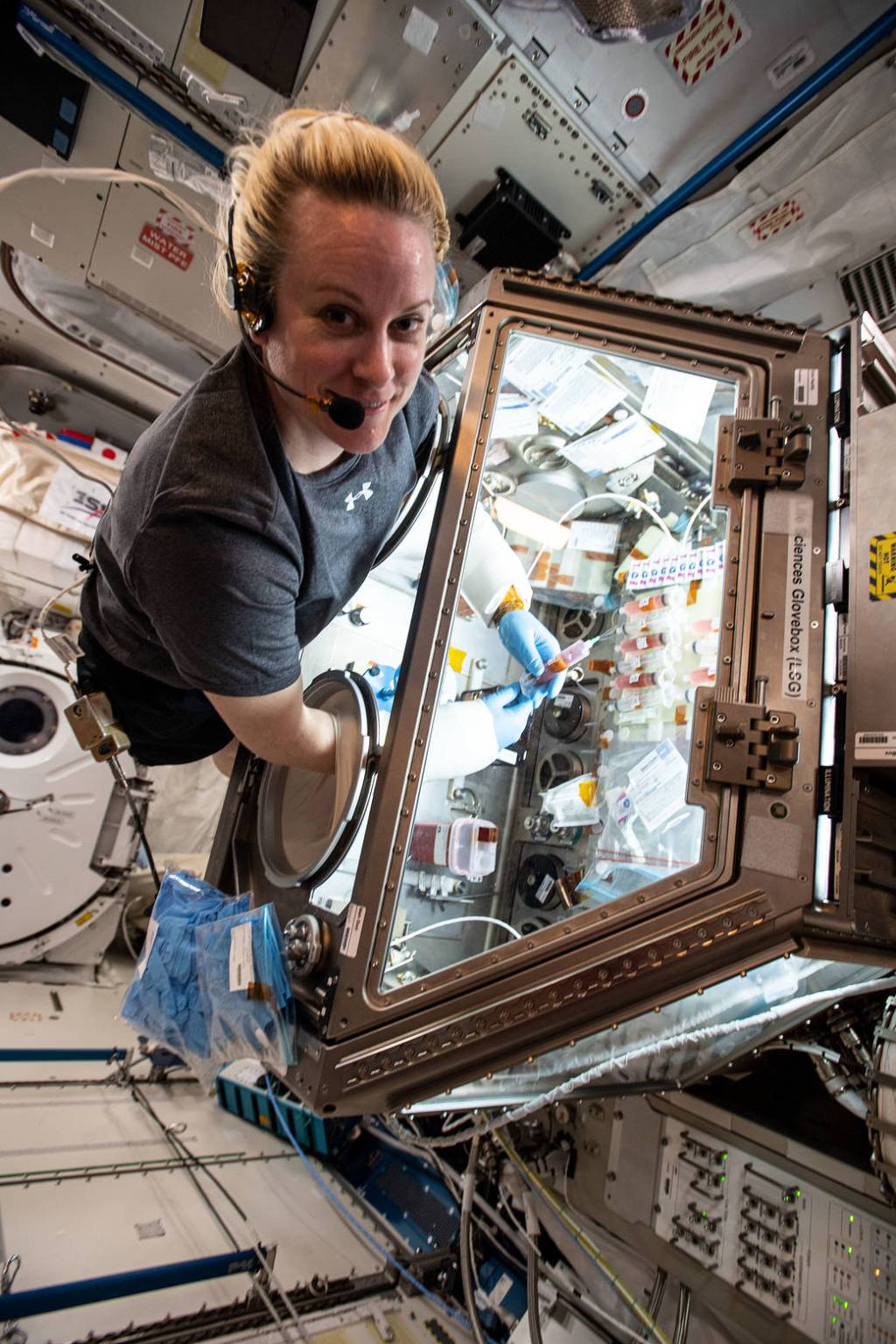
Some crew members also will contribute to a core set of measurements called Spaceflight Standard Measures. The measurements represent how the human body and mind adapt to space travel over time and serve as a basis for other spaceflight studies like CIPHER. Additionally, crew members may provide biological samples for Omics Archive, a separate study analyzing how the body reacts to long-duration spaceflight at the molecular level.
In another study, select crew members will test a potential treatment for spaceflight-associated neuro-ocular syndrome, a condition associated with brain changes and swelling of the back of the eye. Researchers are unsure what causes the syndrome or why only certain astronauts develop it, but the shift of bodily fluids toward the head in weightlessness may play a role. Some scientists believe genetics related to how the body processes B vitamins may affect how astronauts respond to those fluid shifts. Participating crew will test whether a daily B vitamin supplement can ease or prevent the development of symptoms. They also will investigate if cuffs worn on astronauts’ thighs to keep fluids in the legs could be an effective intervention.
Upon return, the select crew members will complete surveys that record any discomfort or injuries associated with landing, such as scrapes and bruises. Results of the surveys ̶ when combined with data retrieved by sensors in the vehicle ̶ will help researchers catalog these injuries and improve the design of spacecraft.
Crew members began participating in the studies about a year before their mission, learning about the work and offering baseline health data. They will continue to provide data for the experiments for up to two years after returning home.
____
NASA’s Human Research Program pursues the best methods and technologies to support safe, productive human space travel. Through science conducted in laboratories, ground-based analogs, commercial missions, and the International Space Station, the program scrutinizes how spaceflight affects human bodies and behaviors. Such research drives NASA’s quest to innovate ways that keep astronauts healthy and mission-ready as human space exploration expands to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
Learn More About Exercising in Space
What's Your Reaction?