NASA’s Webb Reveals New Details, Mysteries in Jupiter’s Aurora
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has captured new details of the auroras on our solar system’s largest planet. The dancing lights observed on Jupiter are hundreds of times brighter than those seen on Earth. With Webb’s advanced sensitivity, astronomers have studied the phenomena to better understand Jupiter’s magnetosphere. Auroras are created when high-energy particles enter […]

NASA’s Webb Reveals New Details, Mysteries in Jupiter’s Aurora
NASA, ESA, CSA, Jonathan Nichols (University of Leicester), Mahdi Zamani (ESA/Webb)
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has captured new details of the auroras on our solar system’s largest planet. The dancing lights observed on Jupiter are hundreds of times brighter than those seen on Earth. With Webb’s advanced sensitivity, astronomers have studied the phenomena to better understand Jupiter’s magnetosphere.
Auroras are created when high-energy particles enter a planet’s atmosphere near its magnetic poles and collide with atoms or molecules of gas. On Earth these are known as the Northern and Southern Lights. Not only are the auroras on Jupiter huge in size, they are also hundreds of times more energetic than those in Earth’s atmosphere. Earth’s auroras are caused by solar storms — when charged particles from the Sun rain down on the upper atmosphere, energize gases, and cause them to glow in shades of red, green and purple.
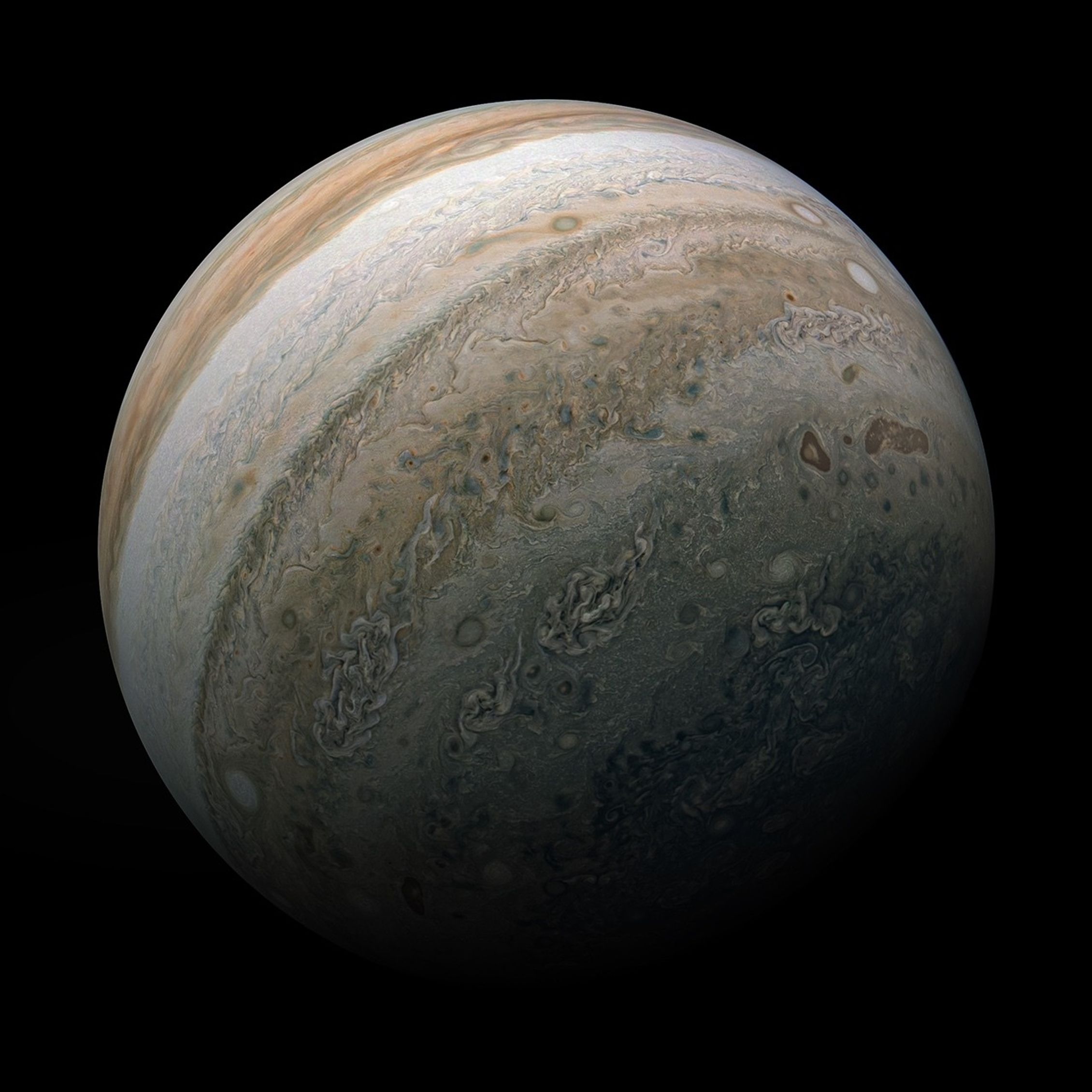
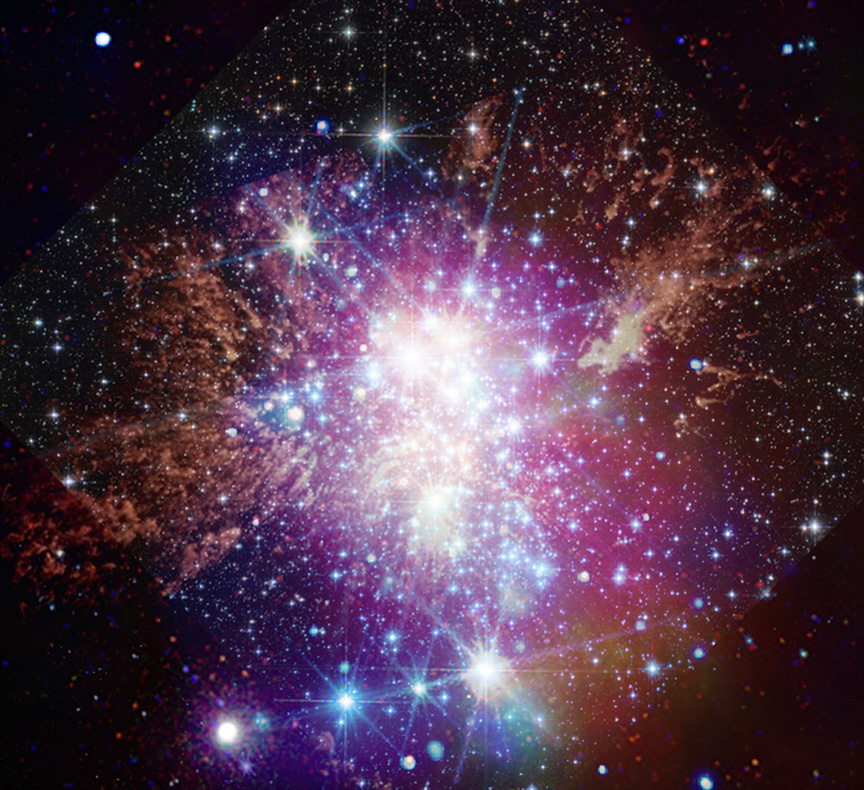
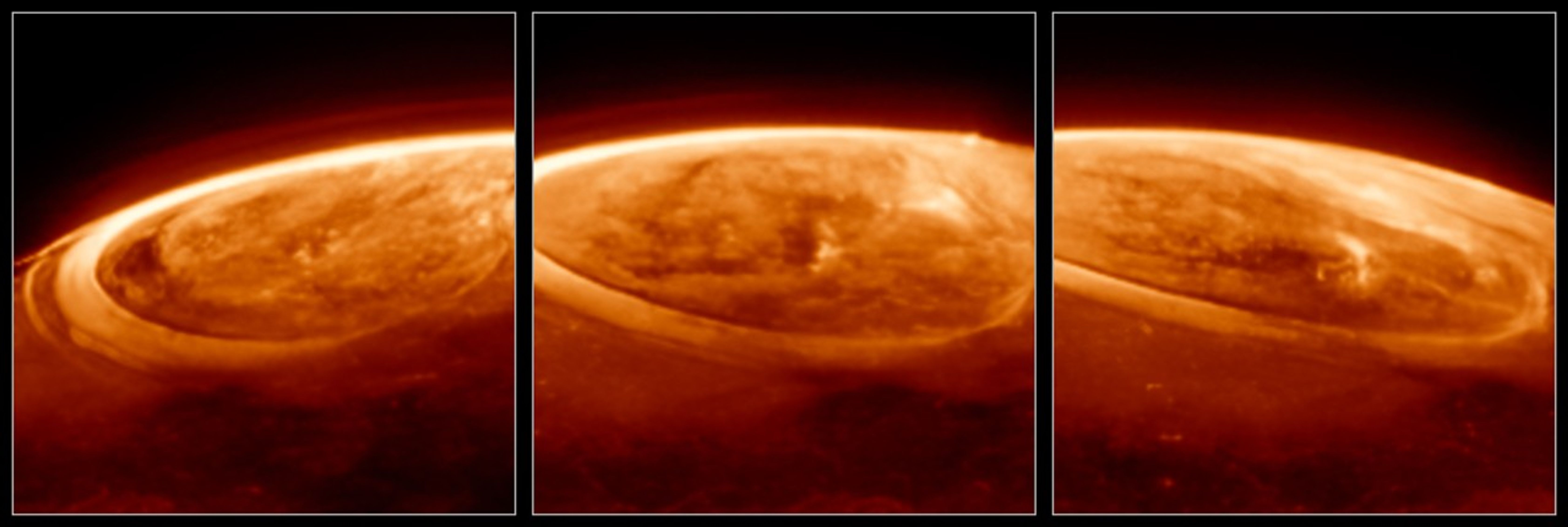
Image A: Close-up Observations of Auroras on Jupiter

These observations of Jupiter’s auroras, taken at a wavelength of 3.36 microns (F335M) were captured with Webb’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) on Dec. 25, 2023. Scientists found that the emission from trihydrogen cation, known as H3+, is far more variable than previously believed. H3+ is created by the impact of high energy electrons on molecular hydrogen. Because this emission shines brightly in the infrared, Webb’s instruments are well equipped to observe it.
Jupiter has an additional source for its auroras: The strong magnetic field of the gas giant grabs charged particles from its surroundings. This includes not only the charged particles within the solar wind but also the particles thrown into space by its orbiting moon Io, known for its numerous and large volcanoes. Io’s volcanoes spew particles that escape the moon’s gravity and orbit Jupiter. A barrage of charged particles unleashed by the Sun also reaches the planet. Jupiter’s large and powerful magnetic field captures all of the charged particles and accelerates them to tremendous speeds. These speedy particles slam into the planet’s atmosphere at high energies, which excites the gas and causes it to glow.
Image B: Pullout of Aurora Observations on Jupiter (NIRCam Image)
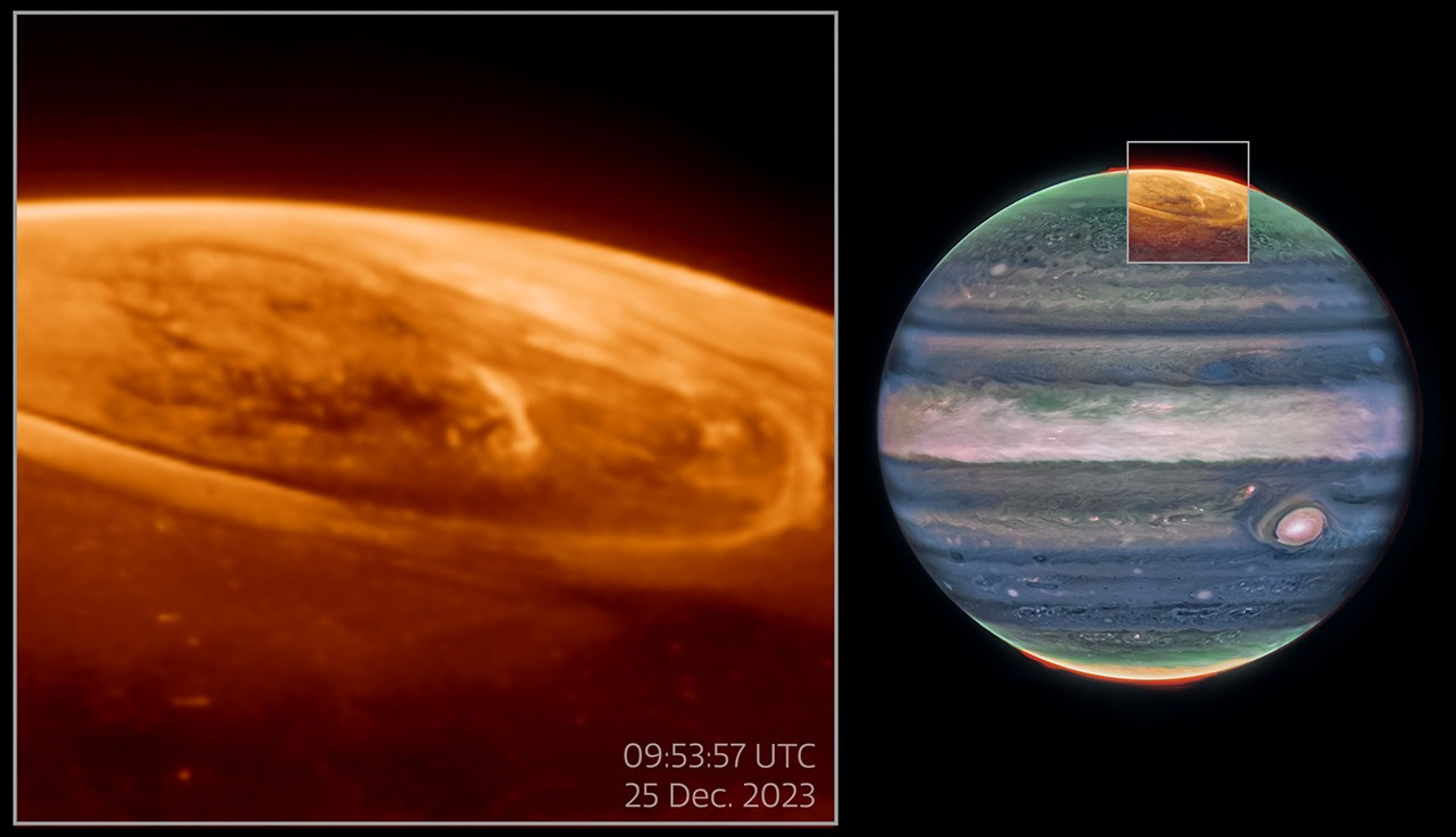
Now, Webb’s unique capabilities are providing new insights into the auroras on Jupiter. The telescope’s sensitivity allows astronomers to capture fast-varying auroral features. New data was captured with Webb’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) Dec. 25, 2023, by a team of scientists led by Jonathan Nichols from the University of Leicester in the United Kingdom.
“What a Christmas present it was – it just blew me away!” shared Nichols. “We wanted to see how quickly the auroras change, expecting them to fade in and out ponderously, perhaps over a quarter of an hour or so. Instead, we observed the whole auroral region fizzing and popping with light, sometimes varying by the second.”
In particular, the team studied emission from the trihydrogen cation (H3+), which can be created in auroras. They found that this emission is far more variable than previously believed. The observations will help develop scientists’ understanding of how Jupiter’s upper atmosphere is heated and cooled.
The team also uncovered some unexplained observations in their data.
“What made these observations even more special is that we also took pictures simultaneously in the ultraviolet with NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope,” added Nichols. “Bizarrely, the brightest light observed by Webb had no real counterpart in Hubble’s pictures. This has left us scratching our heads. In order to cause the combination of brightness seen by both Webb and Hubble, we need to have a combination of high quantities of very low-energy particles hitting the atmosphere, which was previously thought to be impossible. We still don’t understand how this happens.”
Video: Webb Captures Jupiter’s Aurora
Producer: Paul Morris. Writer: Thaddeus Cesari. Narrator: Professor Jonathan Nichols. Images: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI. Music Credit: “Zero Gravity” by Brice Davoli [SACEM] via Koka Media [SACEM], Universal Production Music France [SACEM], and Universal Production Music.
The team now plans to study this discrepancy between the Hubble and Webb data and to explore the wider implications for Jupiter’s atmosphere and space environment. They also intend to follow up this research with more Webb observations, which they can compare with data from NASA’s Juno spacecraft to better explore the cause of the enigmatic bright emission.
These results were published today in the journal Nature Communications.
The James Webb Space Telescope is the world’s premier space science observatory. Webb is solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and CSA (Canadian Space Agency).
To learn more about Webb, visit:
Downloads
Click any image to open a larger version.
View/Download all image products at all resolutions for this article from the Space Telescope Science Institute.
View/Download the research results from the journal Nature Communications.
Media Contacts
Laura Betz – laura.e.betz@nasa.gov
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.
Bethany Downer – Bethany.Downer@esawebb.org
ESA/Webb, Baltimore, Md.
Christine Pulliam – cpulliam@stsci.edu
Space Telescope Science Institute, Baltimore, Md.
Related Information
Read more: NASA’s Webb Captures Neptune’s Auroras for the First Time
Related For Kids
En Español
Share
Related Terms
What's Your Reaction?