Summary of Special Engage Session on “Remote Sensing and the Future of Earth Observations”
Introduction On October 16, 2024, a special session of the NASA Goddard Engage series took place in the Goett Auditorium (Building 3) at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC). The Engage series is intended to explain work at GSFC in an immersive and nontechnical setting. GSFC’s Office of Communications, Earth Sciences Division, and Scientific Colloquium […]

27 min read
Summary of Special Engage Session on “Remote Sensing and the Future of Earth Observations”
Introduction
On October 16, 2024, a special session of the NASA Goddard Engage series took place in the Goett Auditorium (Building 3) at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC). The Engage series is intended to explain work at GSFC in an immersive and nontechnical setting. GSFC’s Office of Communications, Earth Sciences Division, and Scientific Colloquium organized this special session.
The featured speaker for this event was The Honorable Al Gore [former Vice President of the U.S.], who has a long history of advocating for the environment and raising public awareness of the worsening “climate crisis” – having received the Nobel Peace Prize for his efforts.
The event also featured a panel discussion called “Remote Sensing and the Future of Earth Observations.” Three distinguished scientists spoke about what drew their interest in Earth science and responded to questions from the moderator and the in-person and online audience.
Editor’s Note: This is not intended to be a comprehensive review of all NASA’s future plans regarding Earth Remote Sensing. Rather the panelists focused on some specific activities on which they had expertise that was intended to give a sense of the full suite of activities planned for the coming decade.
While The Earth Observer typically does not usually report on Center-specific events, the newsletter makes an exception for this event because the former Vice President participated – and because the topic of the panel discussion is directly relevant to this publications’ wider audience. The remainder of this article summarizes the Engage session, including Gore’s remarks, the panel discussion, and the question-and-answer (Q&A) session that followed. A YouTube video of the full event is available for viewing.
Opening Remarks
Dalia Kirschbaum [GSFC—Director of Earth Sciences Division] welcomed the participants – both in-person and virtual. Casey Swails [NASA Headquarters—Deputy Associate Administrator] continued by thanking Gore for being one of most influential voices in the U.S. on climate . She said that Gore’s words and actions have inspired much more than just the Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR) mission. NASA – and GSFC in particular – has been conducting environmental studies since its beginning. She named historical missions, such as Vanguard, the Television Infrared Observation Satellite (TIROS), Landsat (partnership with U.S. Geological Service), and the Earth Observing System (EOS) – including more than 20 years of observations from the three Flagship Missions: Terra, Aqua, and Aura. (The Earth Observer’s Archives Page includes a “Bibliography of Articles with Historical Content” in which links to articles written on most of the missions mentioned in the previous sentence can be found.)
Swails pointed out that GSFC is home to the largest population of Earth Scientists who produce more than 400 journal articles each year.
“It will be you and your successors who will also make NASA (GSFC) the future of Earth observations,” said Swails. “You are continuing to accelerate core science research and enable action through the newly established Earth System Observatory project office, the Greenhouse Gas (GHG) project office, and new flagship missions, such as the Atmospheric Observing System (AOS) and Landsat Next.”
On behalf of – at the time of the meeting – NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, Swails thanked Gore for participating in the Engage event, and she thanked all the scientists and engineers – past and present – that have led the way in making NASA (GSFC) a leader in Earth observations for more than six decades.
Featured Speaker: The Honorable Al Gore
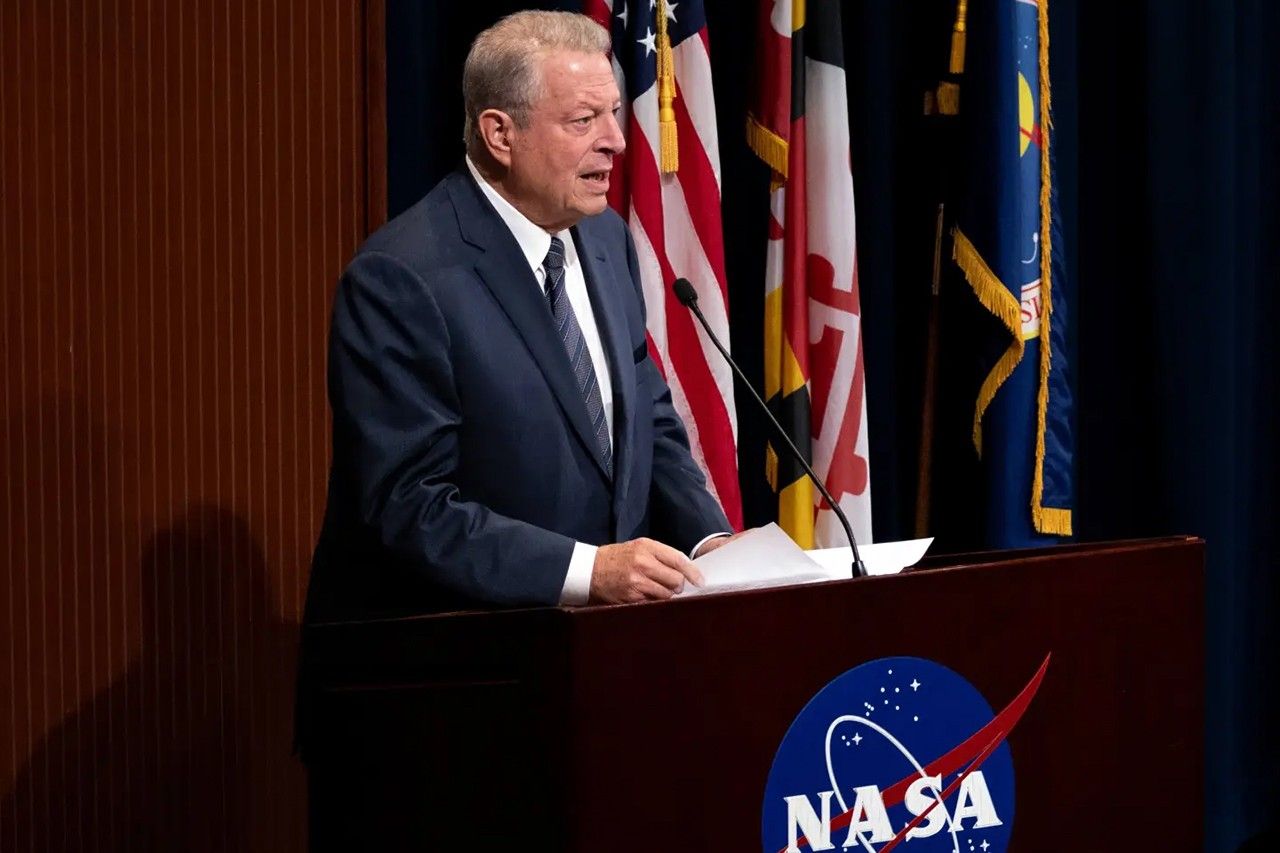
Kirschbaum then introduced Al Gore – shown in Photo 1 – whom she described as an environmental advocate and a central figure in advancing public discourse on climate and sustainability. Following Gore’s many years of political service, he confronted the world with “An Inconvenient Truth,” a documentary on climate change that helped raise global awareness of the worsening state of Earth’s climate. For these efforts, Gore received the Nobel Peace Prize on October 12, 2007.

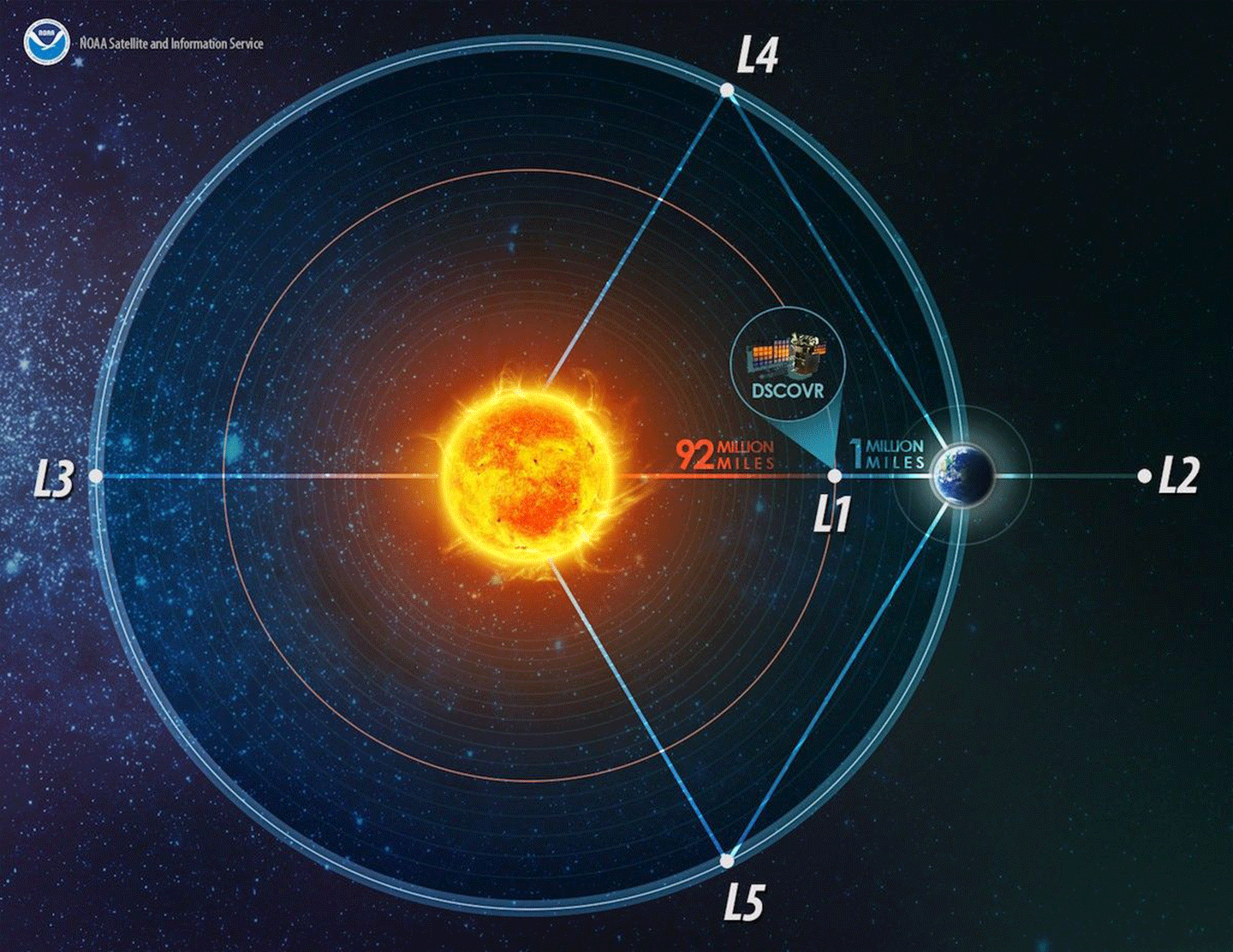
Kirschbaum continued that Gore played a pivotal role in inspiring Triana , a NASA Earth science mission that would provide a near continuous view of Earth and measure Earth’s complete albedo while orbiting the first Sun–Earth Lagrange Point (hereinafter referred to as “the L1 point”). While Triana was canceled, the concept would live on and ultimately transition into the NASA–NOAA DSCOVR mission, which celebrates the 10th anniversary of its launch in February 2025. Gore made brief remarks at the opening session of the 10th DSCOVR Science Team meeting earlier in the day before coming to this meeting. A full “Summary of the 10th DSCOVR EPIC/ NISTAR Science Team Meeting” is published as a separate article in The Earth Observer.
Gore began by thanking all who worked on DSCOVR and other missions at NASA and NOAA. He thanked Makenize Lystrup [GSFC—Center Director] and the team for welcoming him. He also acknowledged the DSCOVR project leaders from GSFC: Adam Szabo [DSCOVR Project Scientist (PS)], Alexander Marshak [DSCOVR Deputy PS], Jay Herman [Earth Polychromatic Imaging Camera (EPIC) Instrument Scientist], Richard Eckman [National Institutes of Health’s Advanced Radiometer (NISTAR) Instrument Scientist], and all those who worked on the mission.
Gore reminisced about when the Triana mission was put into storage in 2001. He remembered his former Senate colleague, Barbara Mikulski [longtime MD Senator] assuring him that they would “feed [the satellite] space snacks” and take care of it until it was ready to use – which ultimately happened in 2008. He also acknowledged those who’ve worked on the DSCOVR mission since launch to extend its capabilities. He also recognized Francisco Valero [former Triana Principal Investigator] who was at University of California, San Diego’s Scripps Institute of Oceanography at the time, and was integral in championing the first iteration of this mission (i.e., Triana), as well as Alan Lazarus [Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT)—Research Scientist], who helped design DSCOVR’s solar particle sensor. (Jay Herman was also involved in Triana.) He also mentioned how Bill Nelson chaired the House Space Subcommittee contemporaneously to when Gore chaired the Senate Space Subcommittee.
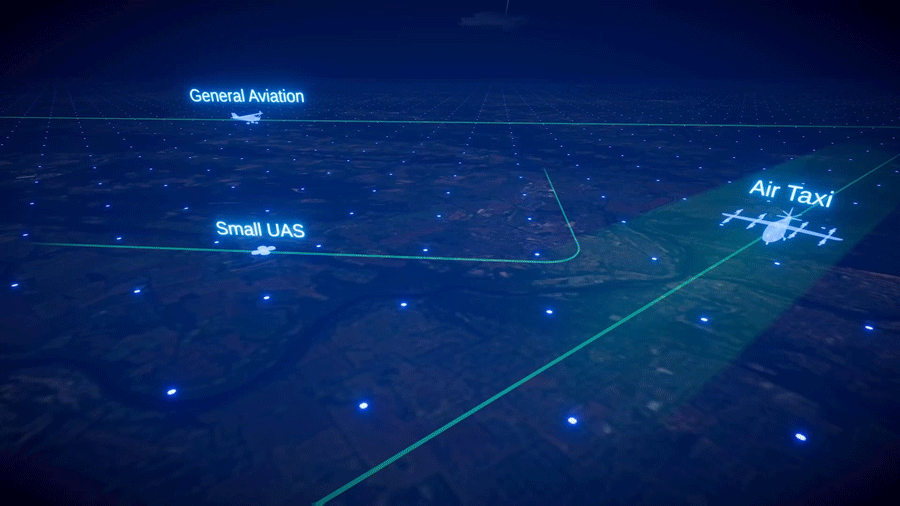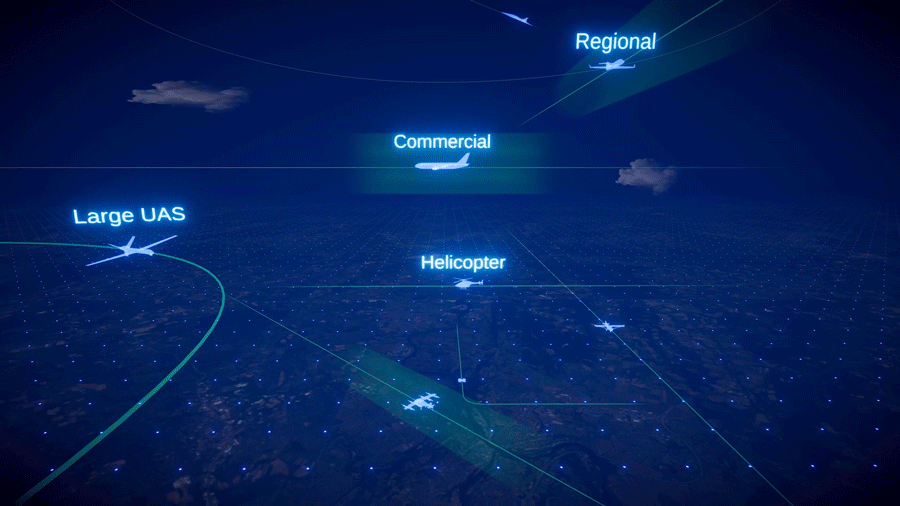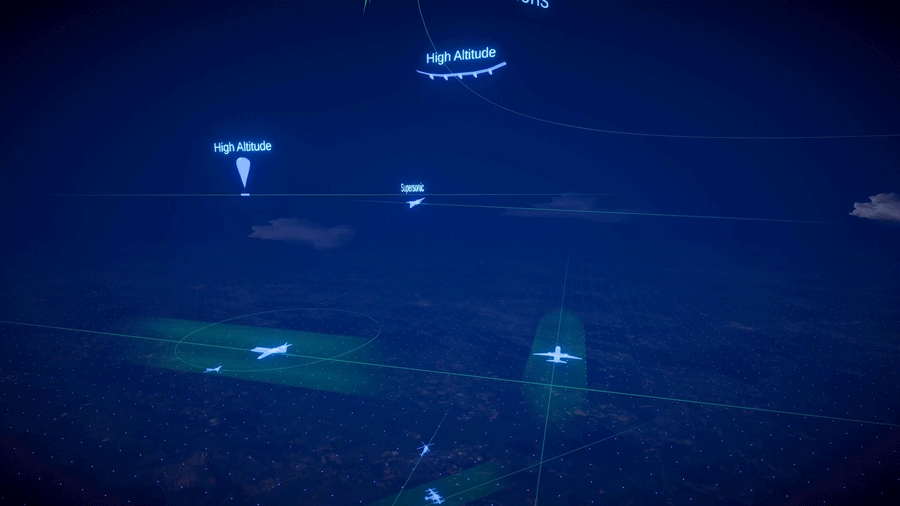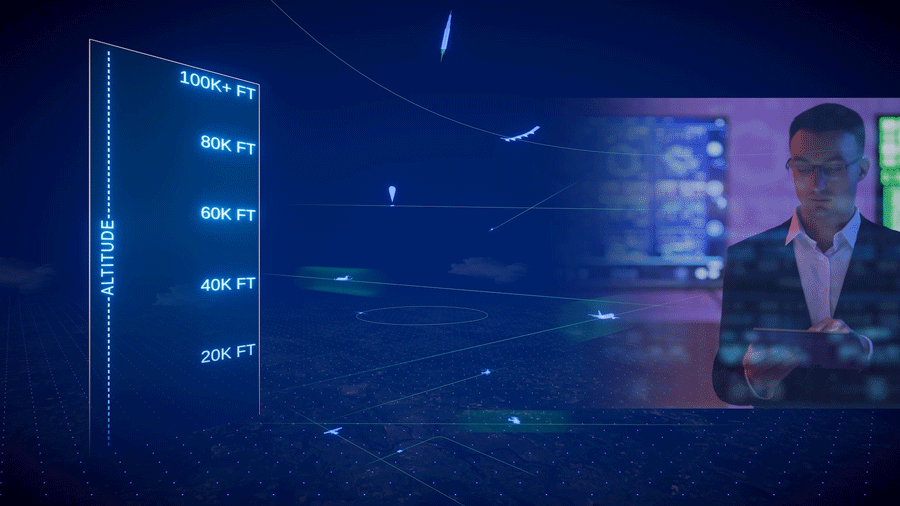
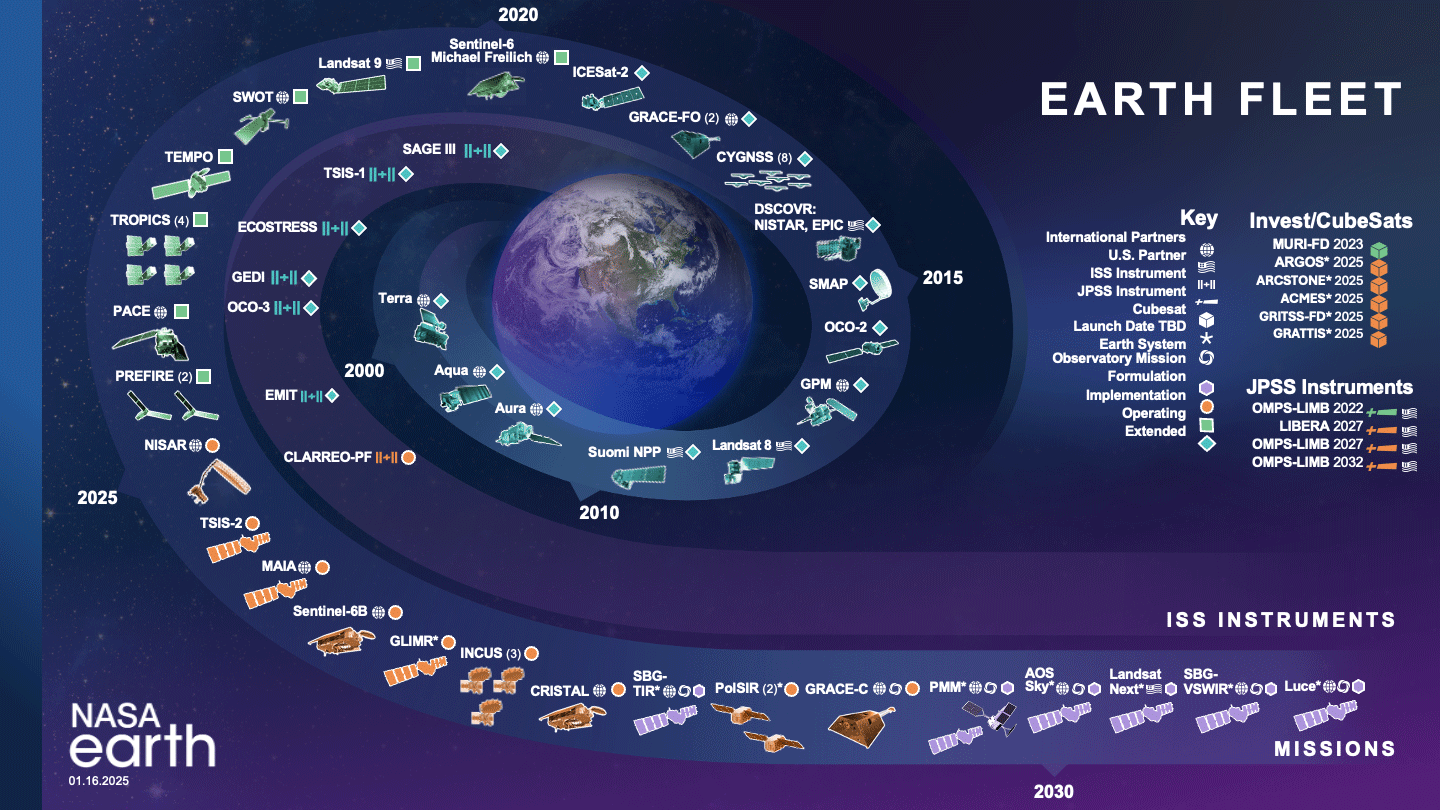
Gore acknowledged that DSCOVR is just one member of NASA’s fleet of Earth observing satellites – see Figure 1 er– plus those of domestic and international partners. What’s unique about DSCOVR, however, is its location – orbiting the L1 point, nearly one million miles (1.1 million km) away from Earth.
It can be argued that the modern environmental movement – which resulted in the development NASA’s Earth Observing System and other Earth observing missions – was inspired by a single image – “Earthrise,” which NASA Astronaut Bill Anders took of Earth on Christmas Eve 1968 during the Apollo 8 mission. The adage that “a picture is worth 1000 words” proved true in this instance as this single image changed how society viewed Earth, opening society’s awareness to the fragility and beauty of our home planet. Four years later, on Christmas Eve 1972, the first “Blue Marble” image was released, having been taken by Apollo-12 astronauts, as the spacecraft approached the Moon. (The image inspired subsequent “Blue Marble” images created using composites of satellite data.)
Per the Wikipedia page linked above, “The [Blue Marble image] has been identified as one of the most widely publicized and influential images since its release – particularly in the advocacy for environmental protection.”
Gore mentioned this in his remarks and stressed that this iconic image helped inspire the Triana/DSCOVR concept. This mission has helped scientists develop a more “complete picture” of Earth. He noted that today, DSCOVR/EPIC obtains a new “Blue Marble” (i.e. a full-disc image of Earth) every fifteen minutes – e.g., a set of images of Africa obtained on the 50th anniversary to mimic the original image from Apollo 12. Gore said that we learn so much about Earth from observing it from above (e.g., cloud dynamics, heating, vegetation, and the concentrations of ozone, sulfur dioxide, and particulate matter in the atmosphere). More than 100 peer-reviewed papers have been published on the unique science done at the L1 point by DSCOVR.
Gore said that DSCOVR – along with the rest of NASA’s Earth observing fleet – has produced a treasure trove of information that makes it possible to make the invisible, visible. What was once a mystery can now be explained with scientific data. When DSCOVR was proposed in 1998, the scientific community was on the verge of a technological explosion via the Internet that would allow the collection, storage, processing, and display of untold mountains of information about Earth. It has now evolved even further with the advent of Artificial Intelligence (AI), leading to another potential information explosion just at the time when having such information is crucial.
“We are in the midst of a violent collision between our current society’s organization and the surprisingly fragile ecological systems on which human flourishing depends,” said Gore.
As the participants convened to celebrate the 10th anniversary of DSCOVR, he encouraged those present to think about how this data can be applied to address the incredible challenges of our generation – chief among them the Earth’s rapidly changing climate.
“It’s hard to grapple with just how serious the [situation] is,” said Gore. However, he noted that, “Mother nature is a persuasive advocate. She has our attention!”
He cited the two hurricanes – Helene and Milton – that impacted the U.S. in the weeks prior to this event. Despite the ever-present threat, Gore also pointed to the problematic “assault on funding” for science throughout the Federal budget. To address this need, Gore spoke of the growing need for private–public partnerships to address the imposing climate crisis.
Gore discussed how Climate TRACE, the organization he cofounded, is harnessing NASA data and fusing it with other sources to pinpoint the sources of GHGs. Climate TRACE has determined the 500 million most relevant point sources, along with metadate (data describing the data). In essence, Climate TRACE seeks to reverse-engineer the GHG levels based on other environmental variables. He said that the newest Climate TRACE dataset will be released on November 14, 2024 at COP-29. Gore acknowledged that NASA [Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL)] contributes data and conducts analysis of data used in Climate TRACE.
Quoting Lord Kelvin, Gore said, “you can only manage what you measure,” noting that our society has been having trouble managing global warming to date. However, thanks to organizations like NASA, our society is gaining the ability to measure it accurately.
Gore then referenced John F. Kennedy’s famous speech at Rice University in 1961 that is most remembered for the line about “going to the Moon in this decade.” But in that speech Kennedy also said, “We set sail on this new sea, because there is new knowledge to be gained and new rights to be won. And they must be won and used for the progress of all people.”
Gore applied this quote to the ongoing study of Earth’s climate. He said that our society is continuing to “sail on this new sea.” He gave kudos to all the people at NASA who are seizing all the opportunities to gather and reflect on “new knowledge” and apply it to issues directly relevant to societal flourishing.
Gore concluded by saying that the DSCOVR mission is a great example of combining scientific discovery and public enlightenment. It has been incredibly successful, and he feels it should be extended, counting on scientists to expand our access to the knowledge we need to ensure the survival of human civilization.
“If you ever doubt we have the political will to make changes,” said Gore, “just remember that political will is itself a renewable resource.”
After a standing ovation from the audience, Kirschbaum thanked Gore for his remarks and his continued support of the Earth science community.
Panel Discussion on the Future of Earth Science Remote Sensing
Kirschbaum then transitioned to the panel discussion. She reflected on how we live with the impacts of climate every day – e.g., air quality impacting students, hurricanes impacting coastlines and coastal communities, shifting storm patterns impacting farmers.
Since its inception in 1958, NASA has been a leader in studying Earth. The agency makes critical observations from space, aircraft, and the ground to understand climate change. NASA researchers integrate this information into climate models to understand the past, represent the present, and project the future state of our home planet.
Kirschbaum said that today’s panel discussion focuses on the future. While questions remain, she emphasized that the agency works with partners on opportunities to do things differently and open new possibilities. She then introduced three NASA scientists, who also provide leadership beyond the walls of NASA.
- Miguel Román[GSFC Earth Sciences Division—Deputy Director for Atmospheres];
- Lesley Ott [GSFC—Project Scientist for the U.S. Greenhouse Gas Center]; and
- John Bolten [GSFC—Chief of Hydrological Sciences Branch].
She asked each panelist – shown in Photo 2 – to start with by sharing a bit of their story with the audience to give some initial insights into their work and background on how they themselves became interested in studying climate.
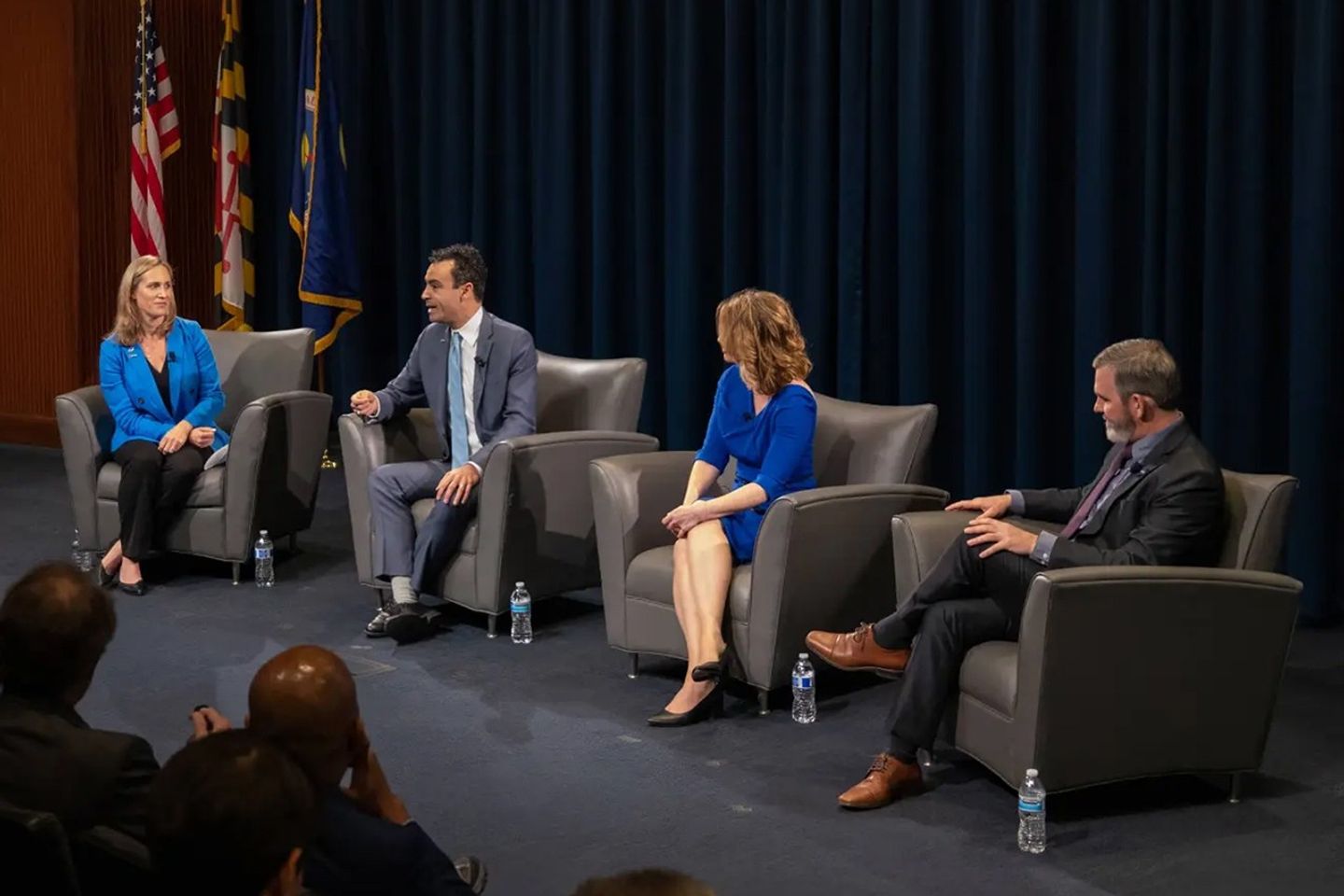

Román began his career as an intern at NASA. After rising through the ranks, he left NASA to work in private industry before recently returning to GSFC. Originally from Puerto Rico, Román has been “inside the walls of a hurricane six times in his life.” He said that American citizens are increasingly experiencing what he experienced as a youth. He noted that two things happen when one in the middle of a hurricane – barometric pressure drops (ears pop) and there is a distinctive hissing sound.
Román said the term hurricane is derived from a Taino word. He explained that in Puerto Rican folklore, Juracán (i.e., the “evil” Goddess of wind – especially hurricanes) was in opposition to Yucahu (i.e., the “good” God of creation, agriculture, peace, and tranquility).
“The hissing winds of Juracán now reverberate across Florida, “ said Román—see Figure 2.
Figure 2. Animation of brightness temperature data obtained by the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) on NASA’s Aqua mission, showing Hurricane Milton as it approached and impacted Florida in October 2024. Colder temperatures (blues) are associated with the tops of high clouds, so the storm track stands out from the warmer temperature over the waters of the Gulf of Mexico.
Figure credit: TBD
He stressed that these winds are “different” – more intense – than the ones dealt with in the past. He added that we now have “land hurricanes” – called derechos, which are intense, widespread, and fast-moving lines of storms.
Ott said that, in a sense, “science chose her.” She was raised by two scientists who met while studying physics. But she chose to study meteorology because it seemed to her to be the most ‘personal’ of the sciences. As Kirschbaum alluded to in her remarks earlier, weather impacts us all – physically and even emotionally. She loved this aspect of weather and wanted to understand the science behind the “air that we all swim in.”
“Weather seems to be less in background and more on the ‘front page’ these days,” said Ott. “We regularly hear news stories about superstorms and devastating fires. We’re all increasingly impacted by extreme weather.”
She also spoke about the ‘untold’ costs of climate change (e.g., lost school days, lost wages, not knowing if your home will survive a natural disaster), which has impacted how Ott practices meteorology. While she is a meteorologist, Ott doesn’t work on weather prediction. Instead, she uses the same kind of predictive models that are used for weather forecasting to focus on GHGs, which could help society navigate the realities of a changing planet.
In her work, Ott tracks how climate changes – for better or worse. While the trend toward a warming world (climate) fuels more frequent and powerful extreme events (weather), e.g., heat waves, droughts, and storms, there are exceptions achieved through intentional human intervention – e.g., the recovery of the ozone hole (bought about through enforcement of the Montreal Protocol and its Amendments) and improvements of air quality. Both of these examples of positive change illustrate the value of international collaboration to address environmental issues. Ott said that research efforts can help to “track the future of the planet,” leading to more positive changes. Extending these positive changes to GHGs will help communities more effectively plan for and respond to a rapidly changing world.
Bolten began by saying that he comes from Wood County WV and is the youngest of five boys. He could see the Ohio River from his kitchen window where he swam and canoed. Bolten explained that Wood County is in an area known as chemical valley, because a large number of chemical plants in the region provide important products for the world. These plants employ many of the people living in the region.
Bolten’s father designed wastewater treatment systems for these chemical plants and passed along a deep appreciation of the impact humans can have on the environment. Similarly, Bolten spent many years enjoying the Ohio River and West Virginia wilderness, which instilled in him the value of protecting our freshwater resources. He grew up immersed in the environment and wanted to contribute to the greater good of society and make a positive difference in the world. He said that NASA is championing these same core values as an innovator and leader in Earth System Science. Bolten thanked Gore for spurring public discourse around climate.
Question and Answer Session
Kirschbaum began the Q&A session with several prepared questions followed by questions from both in-person and virtual participants – along with some more interspersed comments from the guest of honor.
Kirschbaum posed the first question to Román: How do you see GSFC (NASA) advancements in tech and science helping us to predict extreme weather (e.g., heatwaves and hurricanes)?
Román began his answer by stating that NASA’s EOS era is coming to an end – after more than two decades of observations. NASA’s EOS flagship missions – Terra, Aqua, and Aura – have each far exceeded their scheduled mission life. While scientists and engineers work together to extend the function as long as possible, practical realities (e.g., fuel supply, orbit decay) dictate that all the satellites must be decommissioned in the next few years. The EOS era has taught NASA and its partners many lessons about how to operate under what he described as “an accelerated set of extreme climate events.”
“We simply could not have anticipated some of things we’re facing now when the EOS missions were designed,” said Ramon, citing the development of derechos and the rapid intensification of tropical cyclones.
The EOS mission instrument teams developed a whole Earth observing technology toolbox on the fly. For example, scientists learned that while microwave sounders work well over water, these instruments face challenges over land due to surface emissivity variations. Infrared (IR) sounders, on the other hand, provide valuable data over all surfaces during clear conditions, but they can’t penetrate thick clouds. Investigators combined both measurements, producing a powerful tool for observing the changing Earth system and beginning to quantify the impact of those changes.
While it is sad to see the EOS era end, Román said that NASA is entering an exciting new era where new technologies will allow for miniaturization of sounders. He also mentioned new observing technologies, such as the Hyperspectral Microwave Photonic Instrument (HyMPI) . The microwave sounders currently flying – which are part of NASA’s current Program of Record – retrieve atmospheric profiles with approximately 20 vertical layers. By contrast, HyMPI can produce as many as 1000 layers, offering enhanced thermodynamic sounding skill in the Earth’s planetary boundary layer (PBL) – the first 2 km (~1 mi) of the atmosphere – over conventional microwave sounders from the current Program of Record.
Román emphasized that the PBL is an area that is still poorly observed and understood. This lowest level of the atmosphere is where humans and other plants and animals live – and where most climate impacts occur. It is thus vitally important to improve our understanding of the PBL. To emphasize this point, Román cited that one million stillbirths can be linked to tropospheric ozone pollution every year. The encouraging news is that NASA’s data can inform public health policy to help mitigate these harmful impacts.
“The problem is an integrated one,” said Román, “and the Earth System Observatory (ESO) is designed for all of its missions to be integrated.”
Román stressed that the climate challenges are complex, and ESO provides a model for all future campaigns to integrate many approaches to solve big problems.
Kirschbaum directed the next question to Ott: As the NASA leader of the U.S. Greenhouse Gas Center, where do you see NASA making contributions?
Ott responded that there has been tremendous innovation and advancement in the field of Earth observations over the past several decades – i.e., during the EOS era. As Al Gore alluded to in his earlier remarks, increasingly, this innovation comes from the pairing of private sector with the public data from satellites, aircraft campaigns, and ground networks that provide the infrastructure that companies need to test and improve new approaches.
NASA has also played a foundational role in developing the systems approach to studying Earth. For example, half of human-produced emissions (sources) of carbon dioxide (CO2) are absorbed by vegetation and the ocean (sinks). It remains unclear how long this balance will continue, however. NASA aims to bring together different measurements of vegetation, ocean productivity, and gases in the atmosphere and make them readily available to the public. A wholistic approach to climate requires input from multiple satellites to successfully model changes in the concentration GHGs throughout the Earth system. To achieve this goal, the best from the government (e.g., NASA data) needs to merge with private industry to produce consistent long term data records that people can trust.
Kirschbaum agreed that delivering trusted information and providing foundational datasets are core activities for NASA, and used that to segue to the next question, which she addressed to Bolten: NASA (GSFC) sits at the nexus of satellite observations and modeling. Where do you see progress of Earth Science to Action particularly in area of water quality?
Bolten said that the first image of Earth was obtained 78 years ago in 1946. It happened somewhat by chance. Soldiers and scientists at White Sands Missile Range strapped a camera to a captured German V2 rocket, and they were fortunate to get a clear image of Earth. Fast forward to today, NASA has a fleet of more than 20 Earth-observing satellites – see Figure 1 [top] – that provide routine Earth observations. These data are vital for understanding our home planet, and for decision making. The observations from these satellites can be analyzed and used to inform decisions about Earth.
The Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC) was created the same year as the first Earth image. He noted that ENIAC took up an entire room. Today, his smart phone, which fits in his pocket, is more than 230 million times faster than ENIAC – driving home the point that technology has advanced beyond what most could imagine. Bolten also noted that 2024 is NASA’s Year of Open Science.
Bolten said that his job focuses on food and water insecure areas, which often correlates with areas that lack data infrastructure. There is a vital need to strategically integrate open science and cloud-based services.
“We can’t do this [work] in a bubble,” said Bolten. “We must work together.”
Kirschbaum elevated a question from an attendee: There have been various climate change scenarios that have been offered as possibilities. Which one seems most likely to you to be correct?
Ott explained that the worst- or best-case scenarios are usually outliers (i.e., the conditions in the “real world” typically lie somewhere in between the extremes). She commented that we’ve seen a large climate change investment from the Biden Administration. Those kinds of investments will have impact and have the power to change the trajectory for the future. Part of what NASA does is to show the world that the data we collect does make a tangible difference. That gives society reason for hope. The point of U.S. Greenhouse Gas Center is to bring together all these GHG observations in one place to analyze them and study them to show that we’re making progress on confronting this challenging issue. The objective is to create tangible evidence that, “when we take action, we can change things.”
As if to underscore Ott’s point, Gore responded during her presentation that he believes that public choice does significantly impact how the future unfolds.
“What we decide has consequences,” he said.
Gore is convinced the issue of our changing climate could be addressed if our society made up our collective mind to do it and then committed ourselves to take the decisive action needed to make that decision a reality in the near future.
“The future is really up to us,” said Gore.
The final three questions came from online participants.
How can NASA improve its messaging?
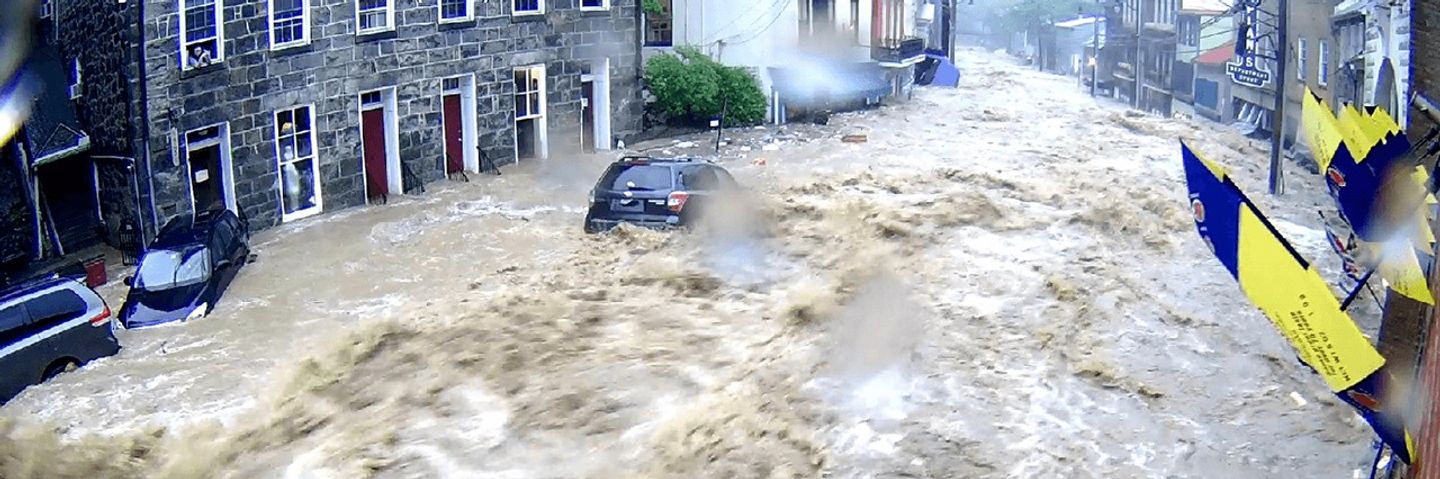
Bolten replied that this is a question that comes up repeatedly in the context of NASA outreach and communications. In the context of today’s discussion, he suggested the need to produce information that is not just useful but also usable (i.e., it can be applied in ways that directly benefit society). As an example, he pointed to the use of machine learning to model a flash flooding event in Ellicott City, MD (described in a 2020 article in Journal of Hydrometeorology) where waters rose from a normal levels to a devastating flash flood in about seven minutes – see Photo 3. Bolten continued that transparency, as well as connecting to people’s motivations, are keys to being more successful with NASA’s messaging.

What big challenges could NASA turn to an opportunity to address climate change?
Román said that advances in forecasting on seasonal to sub-seasonal scales are key areas of focus for studies of Earth’s atmosphere. He noted that it is important to have observations and understand these observations to model events. For sub-seasonal prediction, we need to understand stratospheric dynamics and the chemistry going on in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere.
“Major fires and volcanic eruptions create massive changes in the atmosphere,” said Román. “We can’t see them like we can when we view a Landsat image.”
One tool that could help us with sub-seasonal forecasting is the Stratosphere Troposphere Response using Infrared Vertically-resolved light Explorer (STRIVE) mission, which is one of four mission proposals for the first Earth System Explorer missions chosen for initial Phase A study. This mission aims to examine the interaction between the upper troposphere and the lower stratosphere. In particular, STRIVE will make observations of Earth’s limb (i.e., a narrow slice of atmosphere), which can help scientists gain insight into aerosol loading. According to Román, this data will be key to getting an accurate 30-day forecast. He referred to this information as the “holy grail” in terms of preparedness and resilience by improving early warnings for extreme weather. Some nations are limited to only using Doppler radar and if it fails, they are essentially blind to what is coming.
Kirschbaum cited NASA’s AOS mission, which will be part of ESO, as another example of an important new measuring capability. This mission will represent the “next generation” for precipitations and aerosol observations. Scientists can use the data collected to understand how these phenomena interact with each other and with other atmospheric constituents to form storms.
“AOS will be the baseline while STRIVE would be the bottom line,” concluded Román.
What is the path forward to develop capacity for new observations while still maintaining high-quality, long-term time series and making the data accessible to the public?
Ott cited the Carbon Mapper coalition as a current example where such a balance is being achieved/. Carbon Mapper made its first light images available to the public last week. This mission brings together a unique coalition of partners (including NASA/JPL and Planet, a private company) to develop and deploy two satellites with capabilities to detect and quantify methane (CH4) – e.g., see Figure 3 – and CO2 super-emitters at a level of granularity needed to support direct mitigation action.
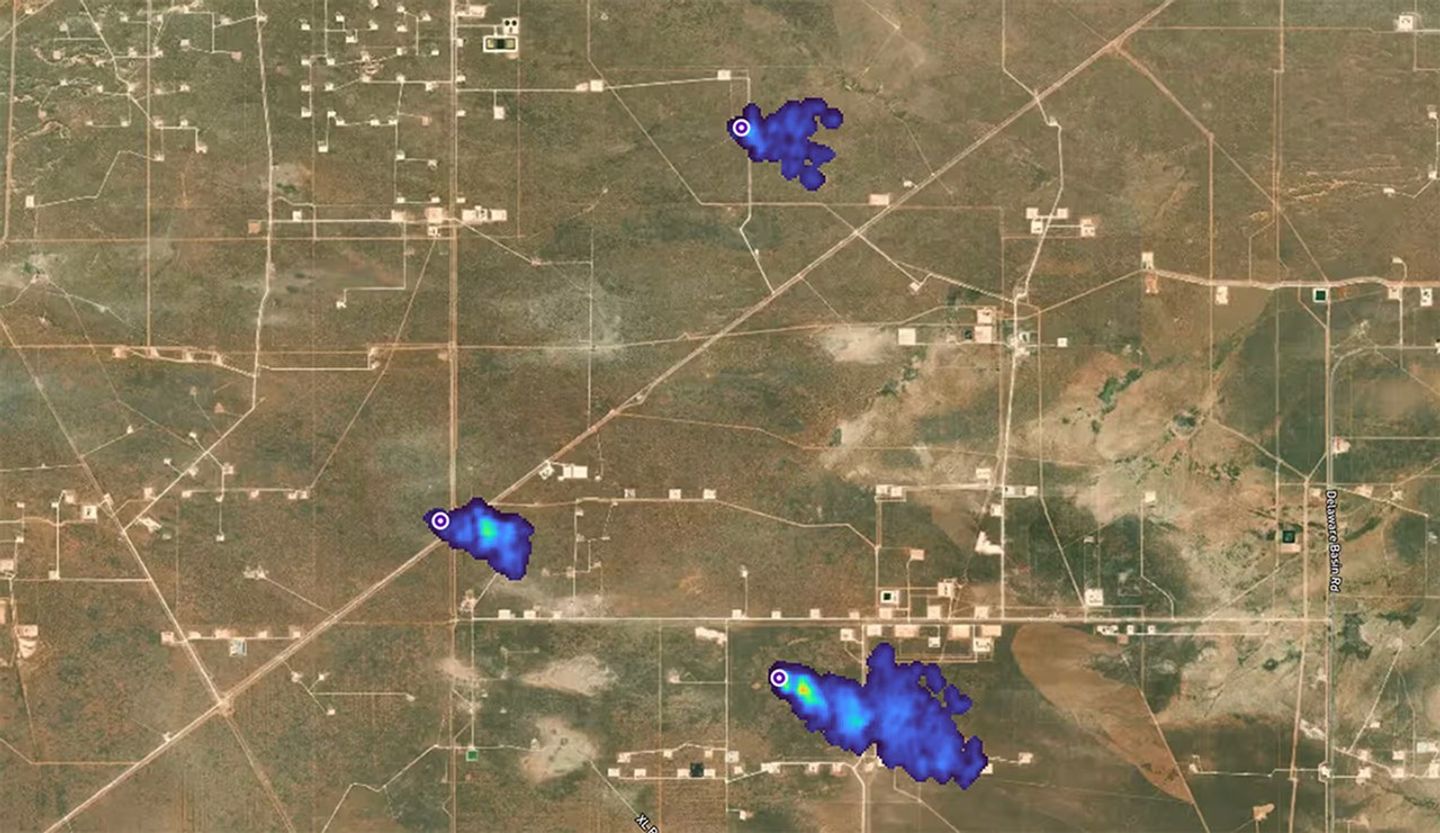
NASA’s investments in technology via its Earth Science Technology Office (ESTO) have enabled new airborne instruments that can be deployed in partnership with industry to demonstrate the quality of present-day satellite technologies and to provide a pathway toward next generation technologies. She stressed that the Federal government continues to play a crucial role in establishing standards and ensuring data integrity and continuity. NASA, for example, invests in ground-based systems and data services that help enable the commercial satellite industry. Long-term continuity of measurements is essential to connect new observations to existing ones. In this way, we can enable the continuing rise of NewSpace, while still providing foundational integrity and stability of the long-term climate data records that NASA and other Federal agencies maintain. This framework helps tie all the NewSpace endeavors together.
Gore cited an example of a public–private partnership that happened in the past. He commented that in 1998 (the same year that Triana was proposed) he was also involved in proposal for Digital Earth. The guiding vision behind Digital Earth was to be able to hover over any point and drop down through successively more detailed layers. NASA contracted with a company called Keyhole, which Google acquired in the early 2000s. Gore raised this example to point out that Google Earth is the result of those initial efforts.
Gore also connected this discussion to his work on Climate TRACE, which he had mentioned in his remarks earlier as a current example of public–private partnership. He stated that while we can see CH4 from space, the resolution is relatively low, i.e., a wide area must be scanned to get a CH4 measurement) and higher resolution is required to identify specific (or point) sources of CH4. Climate TRACE offers such higher resolution CH4 measurements, allowing researchers to focus more on identifying specific sources of pollution. By contrast the atmosphere is so enriched with CO2 that the signal-to-noise ratio is too high to measure the gas from space. For CO2 analysis, Climate TRACE uses AI to fuse together various images to allow CO2 to be detectable. The resulting measurements are precise enough to detect ripple ponds created by rotating fan blades.
Closing Remarks
Dalia Kirschbaum closed the meeting by thanking the guest of honor, Al Gore, once again for coming to the GSFC event. Gore not only spoke but was an active participant who demonstrated his knowledge of this subject area gained from years of experience working on climate issues. She quipped that “he’s the only former Vice President ever to use the Term signal-to-noise ratio correctly when talking to scientists.”.
Kirschbaum also thanked everyone who participated in this event – including the over 800 online participants. While the discussions today offered numerous glimpses into the future of Earth remote-sensing observations, this information barely scratches the surface of all the work being carried out by scientists and engineers at NASA to make these plans a reality. She thanked all of those who work at NASA – who often put in long hours, quietly, behind the scenes without much recognition – for the work they do daily to enable NASA’s mission.
Alan B. Ward
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center/Global Science & Technology Inc.
alan.b.ward@nasa.gov
Share
Details
Related Terms
What's Your Reaction?