25 Years Ago: STS-95, John Glenn Returns to Space
On Oct. 29, 1998, NASA astronaut John H. Glenn made history again when he returned to space aboard space shuttle Discovery’s STS-95 mission, nearly 37 years after becoming the first American in orbit during his February 1962 Friendship 7 mission. The seven-member STS-95 crew consisted of Commander Curtis L. Brown, Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission […]
On Oct. 29, 1998, NASA astronaut John H. Glenn made history again when he returned to space aboard space shuttle Discovery’s STS-95 mission, nearly 37 years after becoming the first American in orbit during his February 1962 Friendship 7 mission. The seven-member STS-95 crew consisted of Commander Curtis L. Brown, Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialists Stephen K. Robinson, Dr. Scott E. Parazynski, and Pedro F. Duque of the European Space Agency, and Payload Specialists Dr. Chiaki Mukai of the National Space Development Agency of Japan, now the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, and Glenn, who at age 77 became the oldest person to orbit the Earth, a record that stands to this day. During the nine-day mission, they conducted more than 80 experiments, many of them to study how exposure to weightlessness might relate to the aging process.
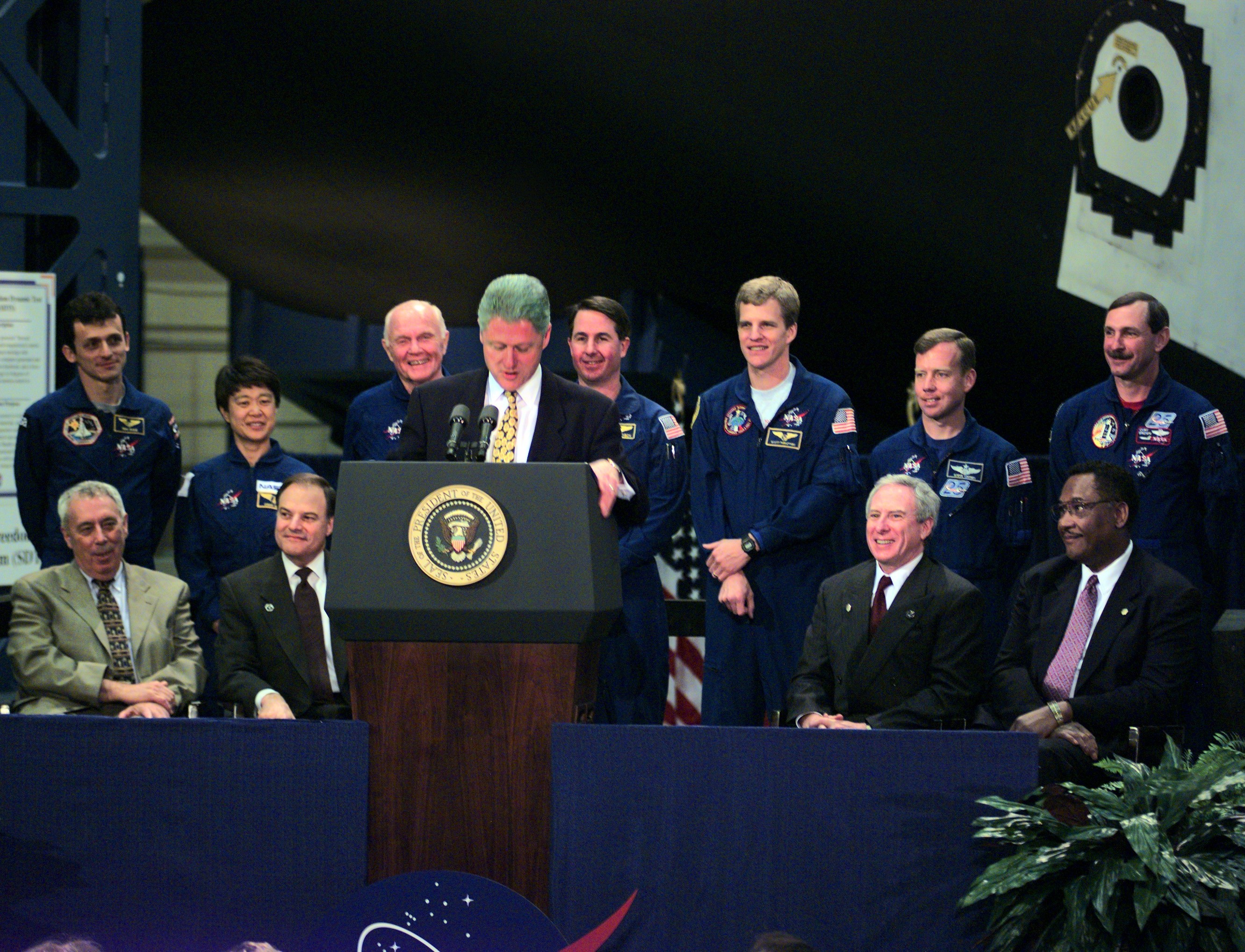


Left: The STS-95 crew during their introductory press conference. Right: President William J. “Bill” Clinton introduces the STS-95 crew, including Senator John H. Glenn, during a ceremony at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston.
Glenn, whom NASA essentially grounded after his historic 1962 mission for fear of losing a national hero in a spaceflight accident, had always dreamed of returning to space. Upon learning about the physiological changes that occur during spaceflight, and how they somewhat resemble those brought about by aging, now Senator Glenn began lobbying NASA Administrator Daniel S. Goldin for an opportunity to put that theory to the test, by volunteering himself as a subject. Goldin agreed in principle, providing Glenn passed the same physicals as all the other astronauts and that the flight included valuable peer-reviewed research. Glenn did, and teams at NASA working with the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute on Aging to put together a research program of experiments to study bone and muscle loss, balance disorders, sleep disturbances, and changes in the immune system. In addition, the mission conducted other experiments in fields such as materials processing, protein crystal growth, cell biology, and plant growth. Also part of the mission, the SPARTAN 201-5 free-flyer pallet carried instruments to study the Sun’s corona and the solar wind. On Jan. 16, 1998, NASA announced that Glenn would fly as a payload specialist on STS-95. On Feb. 13, the agency announced the rest of the STS-95 crew, who held a press conference at NASA’s Johnson Space Center (JSC) on Feb. 20, coincidentally the 36th anniversary of Glenn’s Friendship 7 flight. During a visit to JSC on April 14, President William J. “Bill” Clinton introduced the STS-95 astronauts.
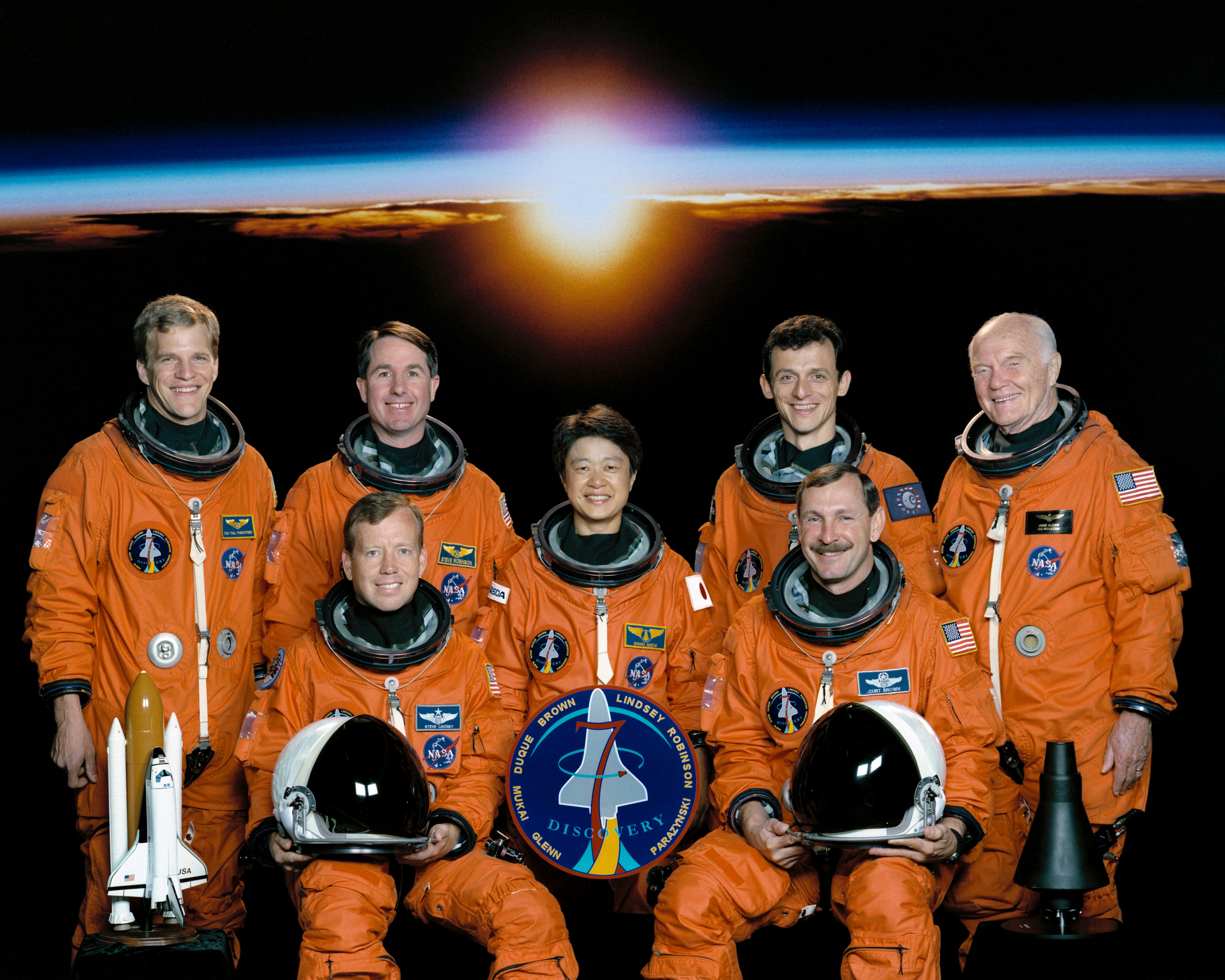
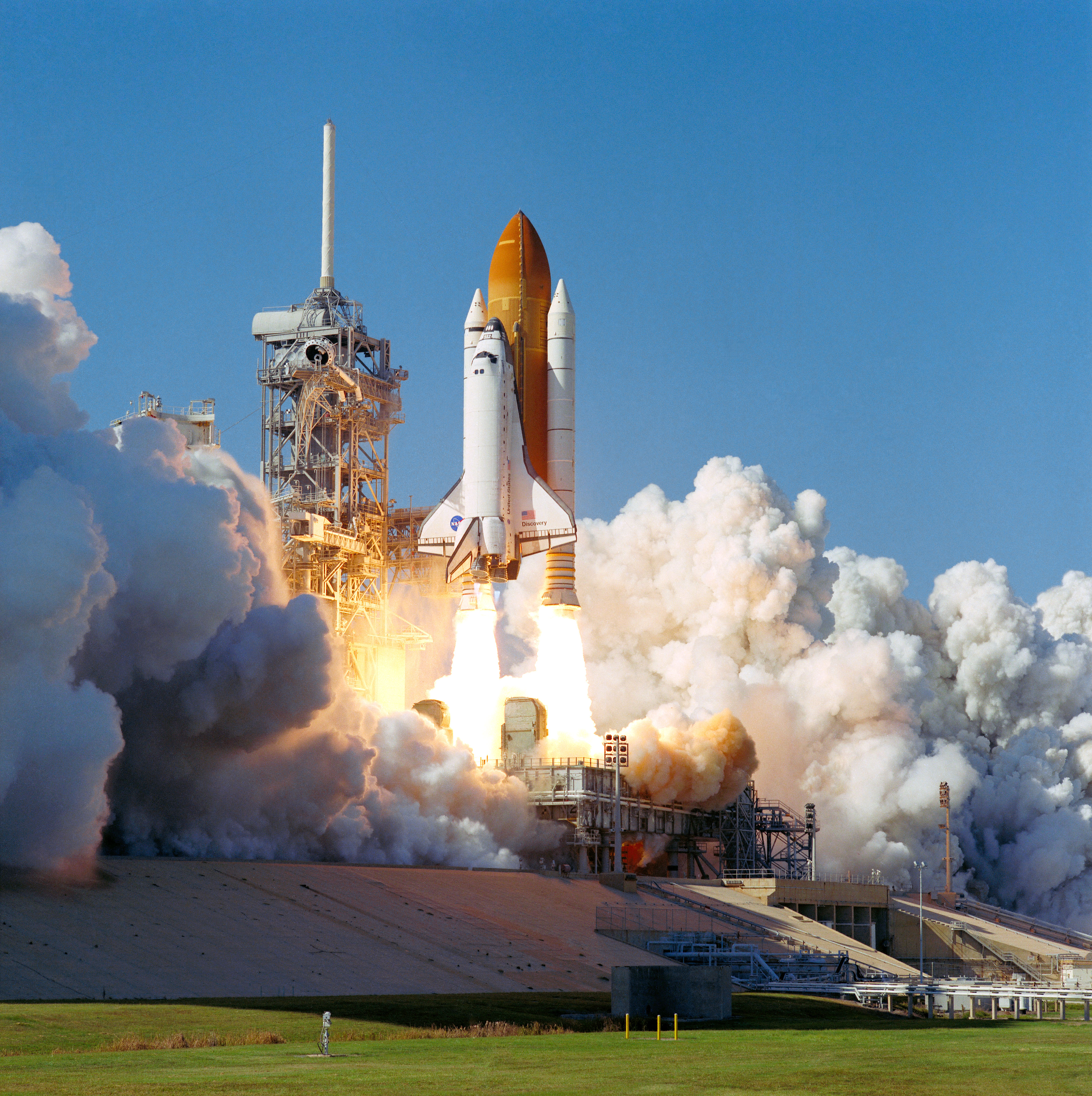



Left: STS-95 astronauts Steven W. Lindsey, seated left, and Curtis L. Brown; Scott E. Parazynski, standing left, Stephen K. Robinson, Chiaki Mukai of the National Space Development Agency of Japan, now the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, Pedro F. Duque of the European Space Agency, and John H. Glenn. Middle: The STS-95 crew patch. Right: Liftoff of space shuttle Discovery on the STS-95 mission, returning Glenn to orbit.
Space shuttle Discovery’s 25th liftoff took place at 2:19 p.m. EDT on Oct. 29, 1998, from Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida, carrying a double Spacehab module filled with scientific equipment. Brown, making his fifth trip into space and second as commander, and Pilot Lindsey on his second launch, monitored Discovery’s systems as they climbed into orbit, assisted by Mission Specialist Parazynski, a physician making his third trip into space, serving as the flight engineer. Mission Specialist Duque accompanied them on the flight deck. Mission Specialist Robinson, on his second mission, and Payload Specialists Mukai, also a physician and on her second trip to space, and Glenn experienced launch in the shuttle’s middeck.
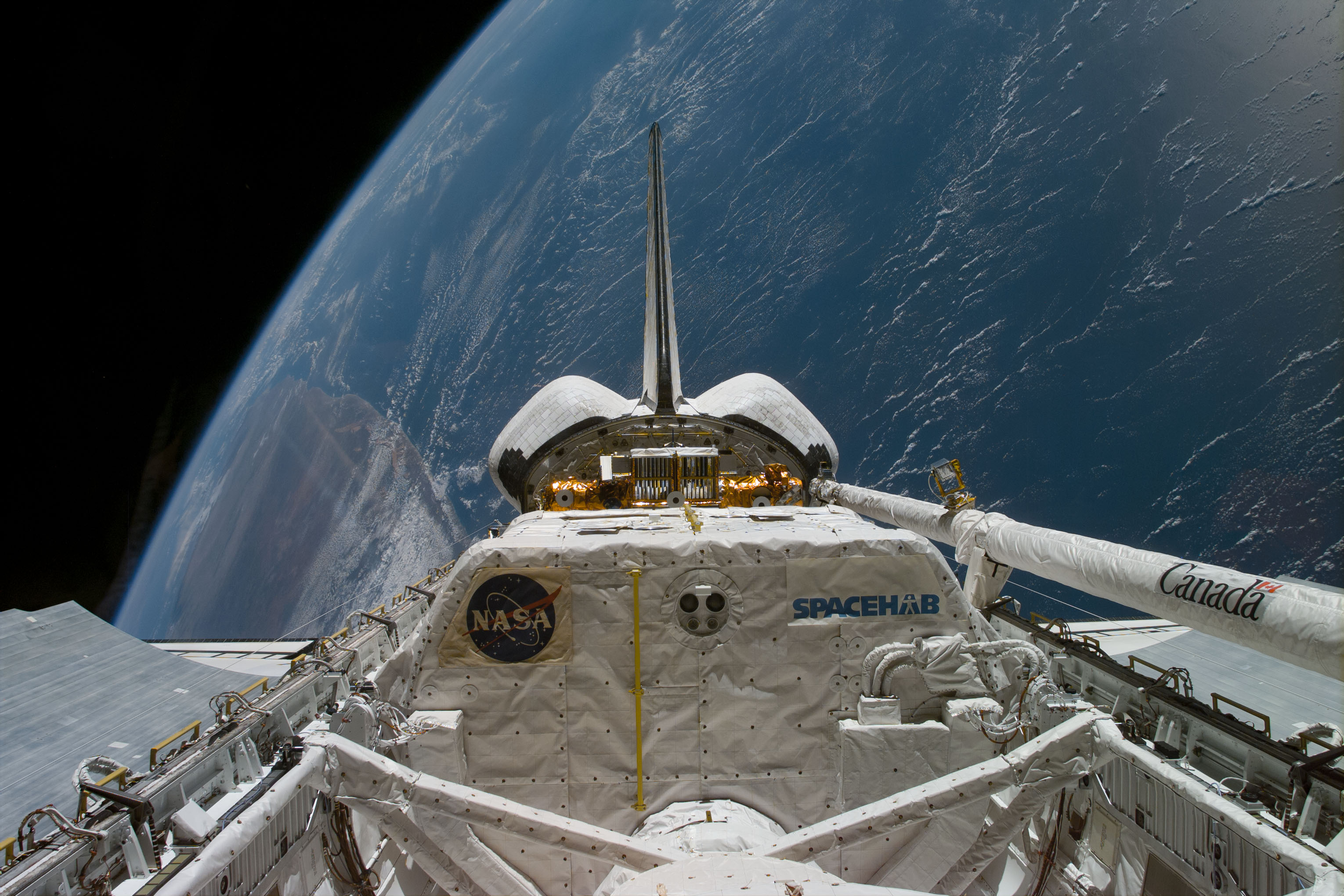



Left: View of the Spacehab module and the Canadian robotic arm in Discovery’s payload bay. Middle: The crew’s first view of the interior of the Spacehab module. Right: Chiaki Mukai, left, and Stephen K. Robinson begin activating the Spacehab.
Upon reaching orbit, the crew opened the payload bay doors, thus deploying the shuttle’s radiators. Shortly after, the crew opened the hatch from the shuttle’s middeck, translated down the transfer tunnel, and entered Spacehab for the first time, activating the module and turning on the first experiments. These included the life sciences experiments that Glenn conducted to compare the effects of weightlessness and aging.
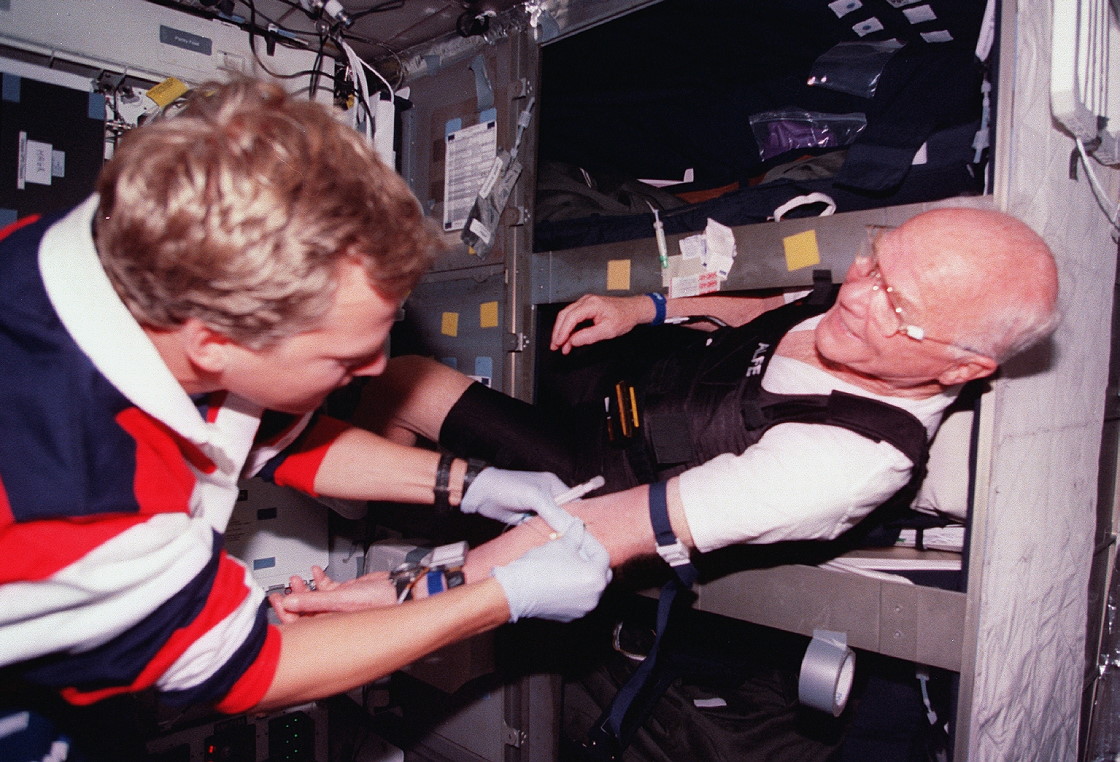


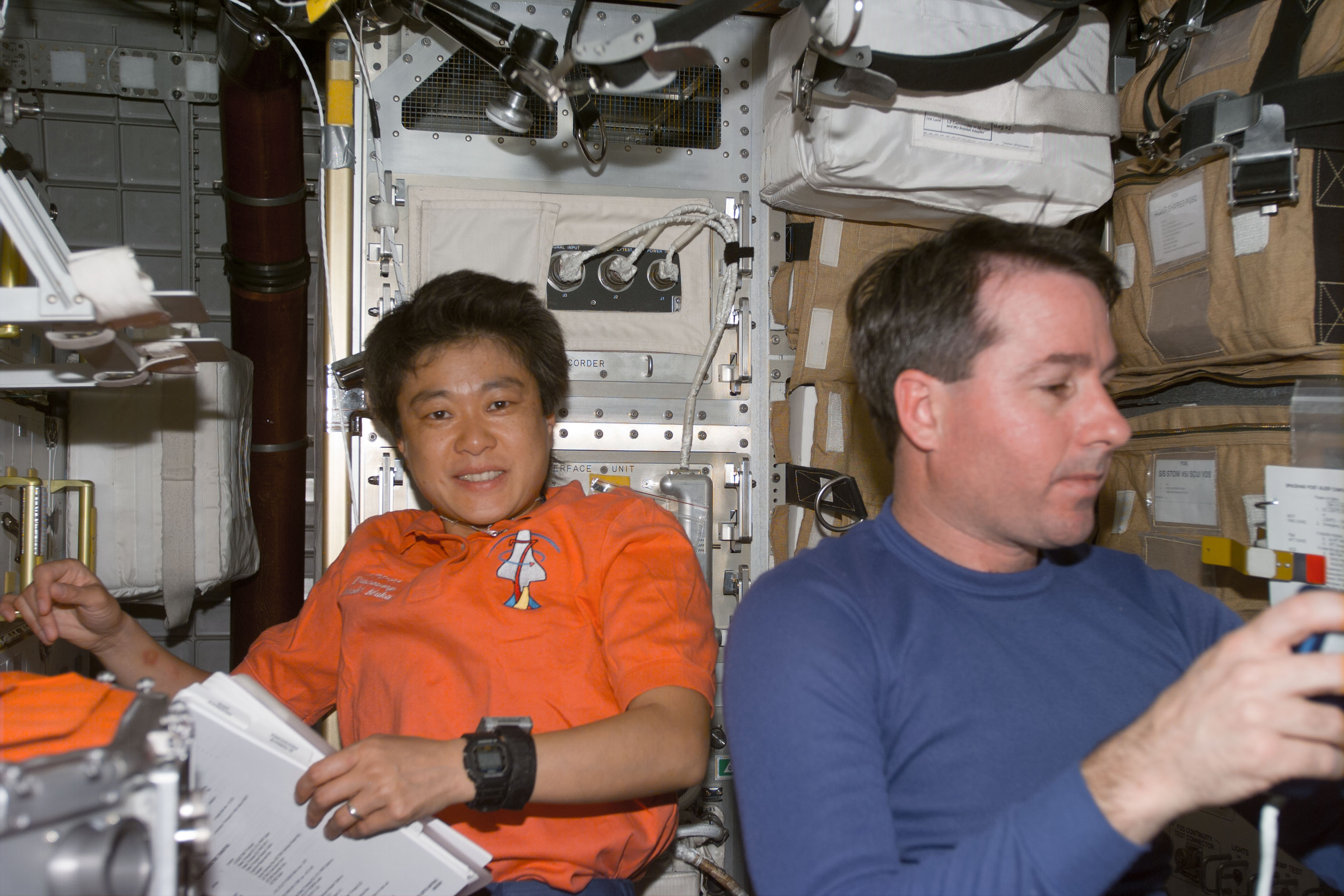
Left: Physician astronaut Dr. Scott E. Parazynski, left, prepares to draw a blood sample from John H. Glenn. Middle: Glenn, left, and Parazynski prepare to centrifuge the collected blood sample. Right: Glenn, instrumented for a sleep study, prepares to begin his sleep period.
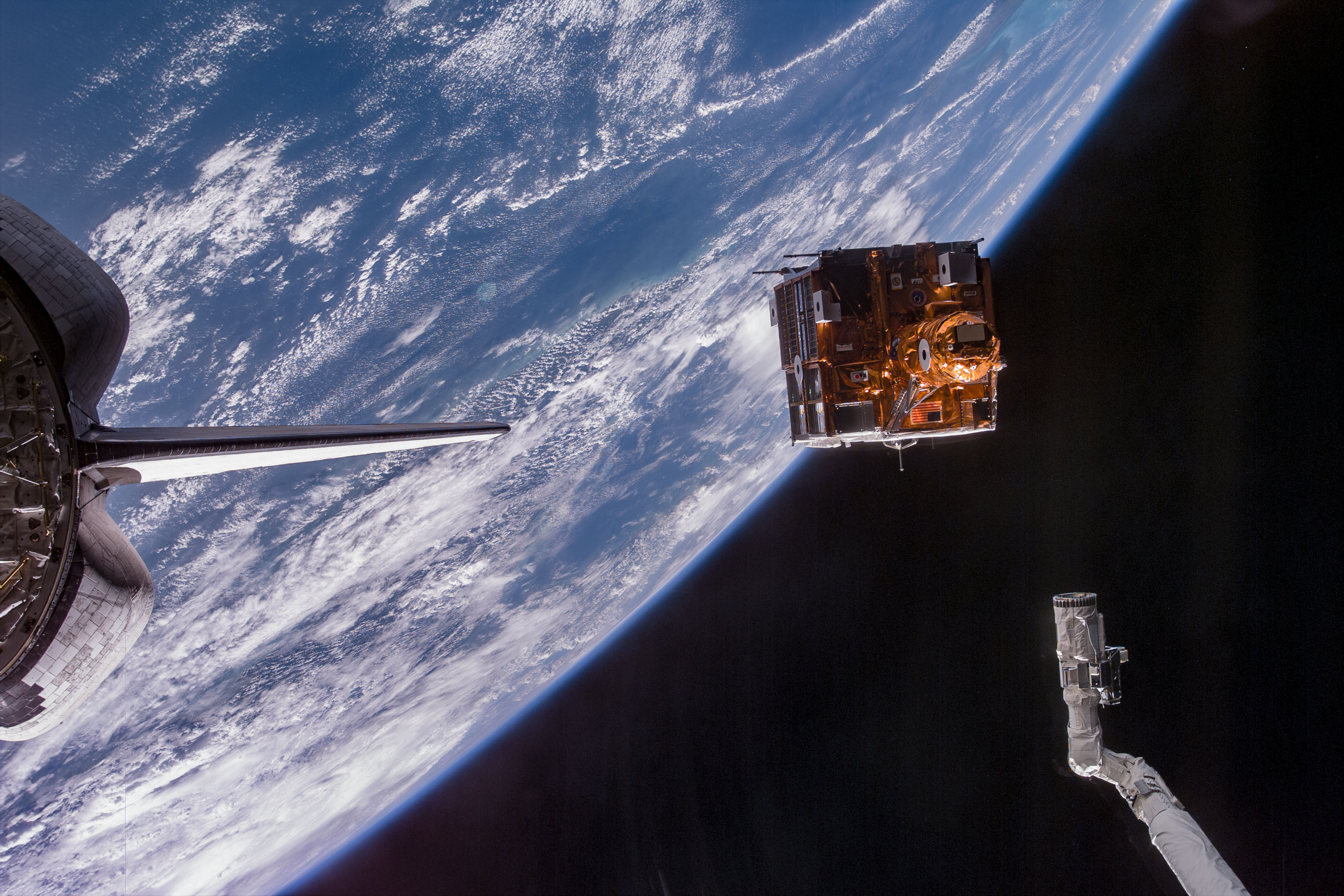
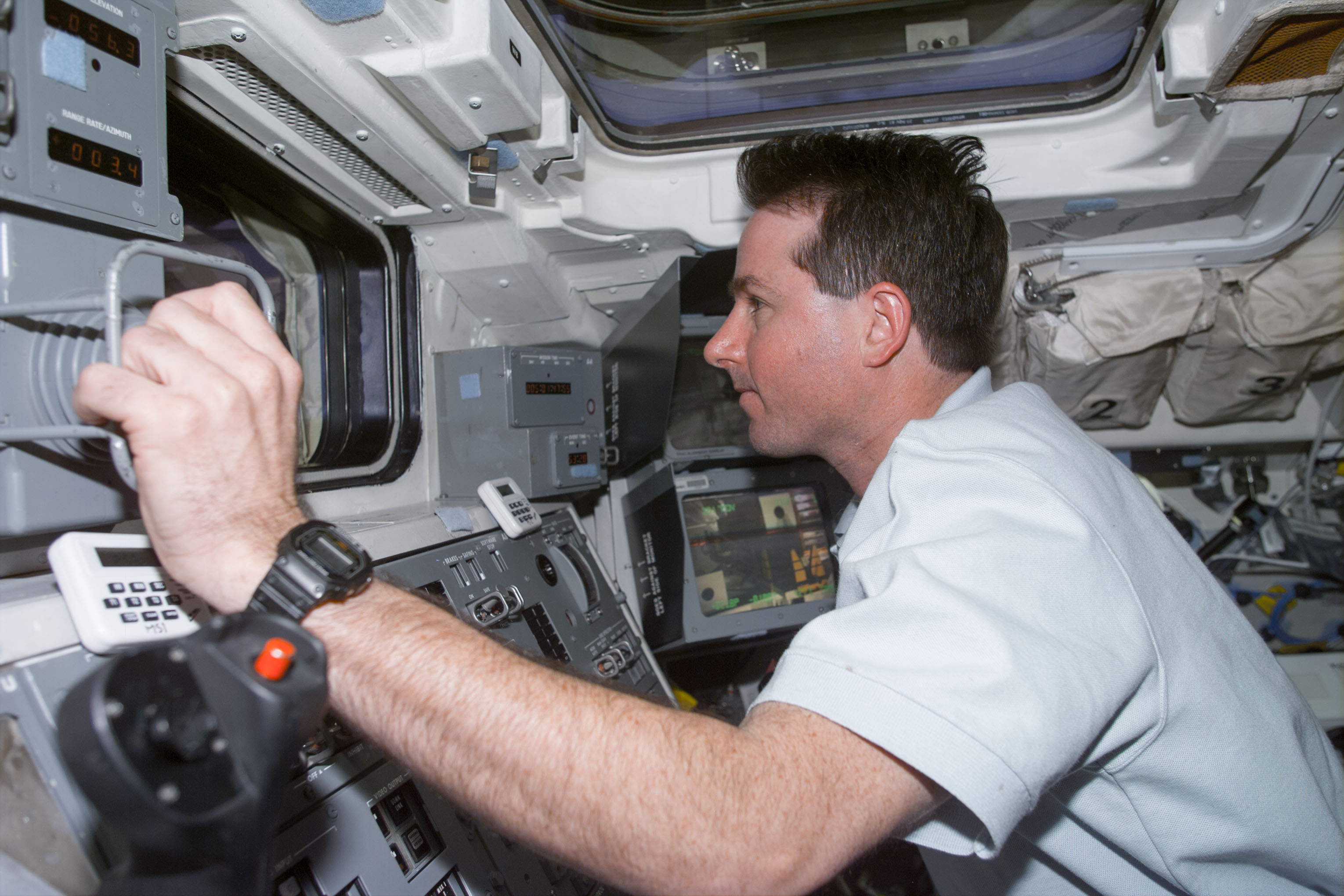
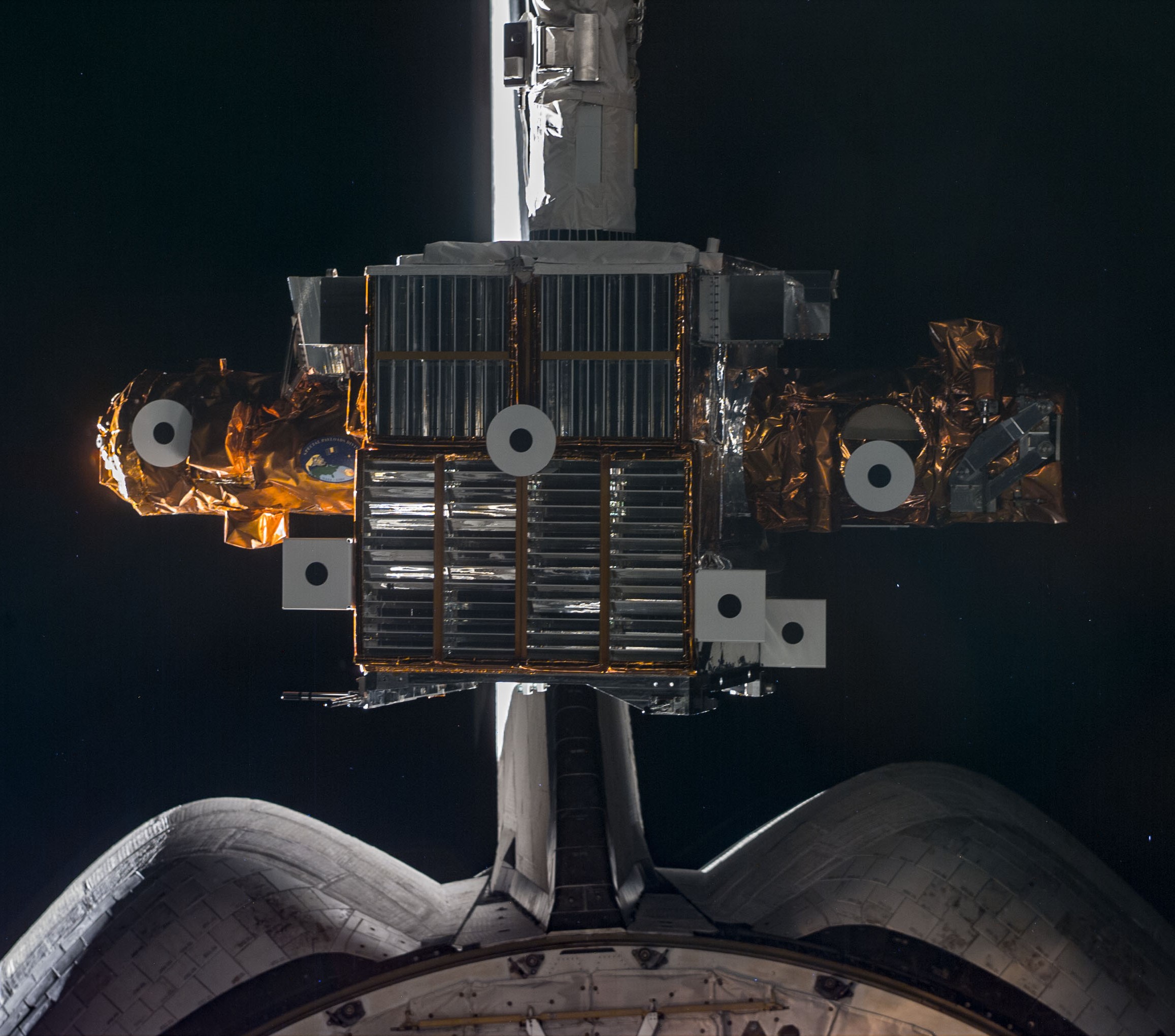



Left: The STS-95 astronauts use the Canadian-built Remote Manipulator system, or robotic arm, to release the SPARATAN 201-5 free flyer. Middle: Stephen K. Robinson operates the RMS to retrieve the SPARTAN after its four-day autonomous flight. Right: Robinson places the SPARTAN back in the shuttle’s payload bay.
On the mission’s second day, the crew deployed the PANSAT, a small experimental communications satellite built by the Naval Postgraduate School in Monterey, California. Later in the day, Robinson used the Canadian-built Remote Manipulator System (RMS) or robotic arm to grapple the SPARTAN free flyer. He removed it from its cradle in the payload bay and deployed it for its four-day independent mission. It successfully completed its autonomous flight, traveling up to 30 miles from the shuttle. On flight day 6, Robinson used the RMS to capture SPARTAN and placed it back in its cradle in the payload bay.
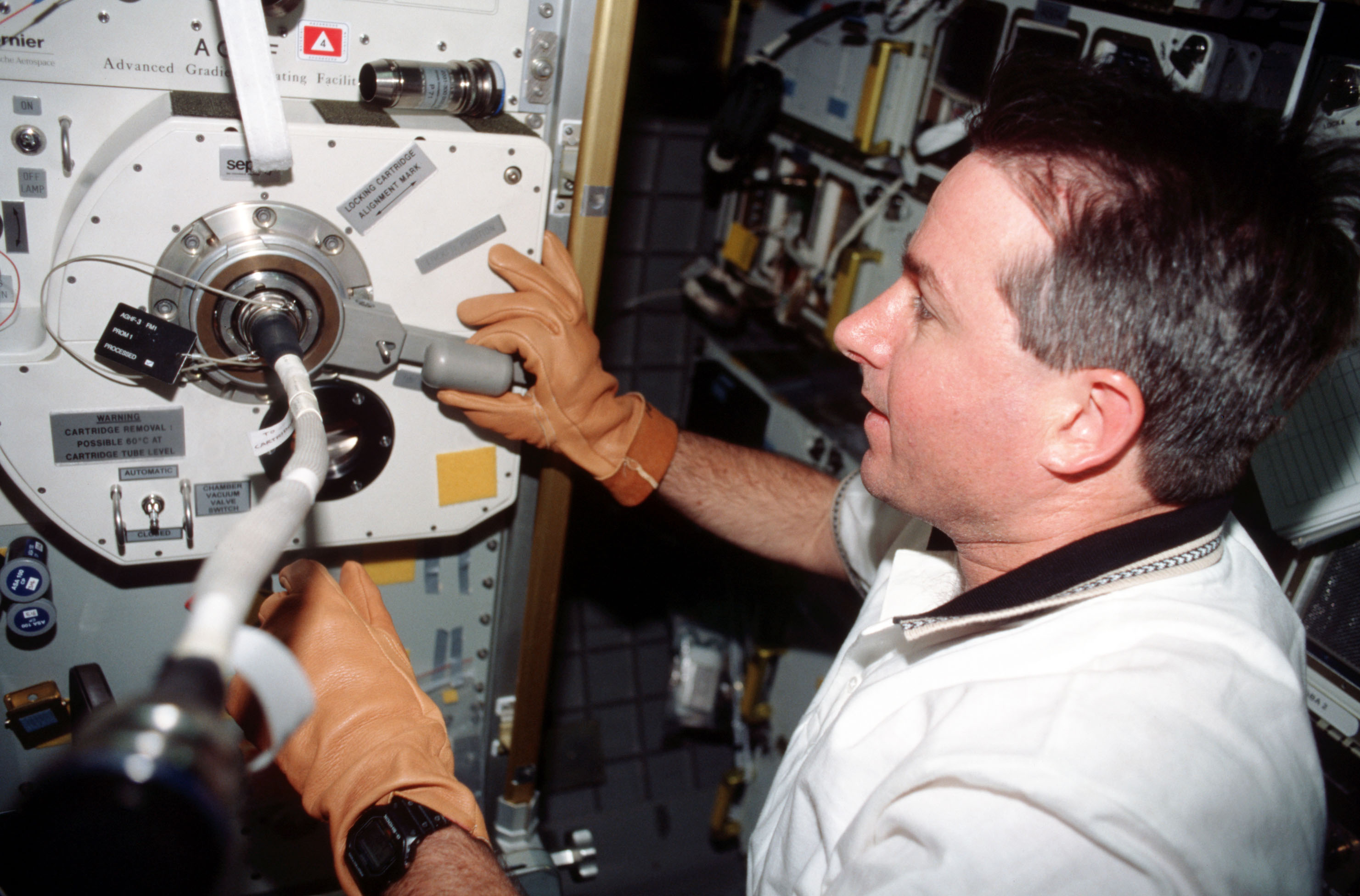
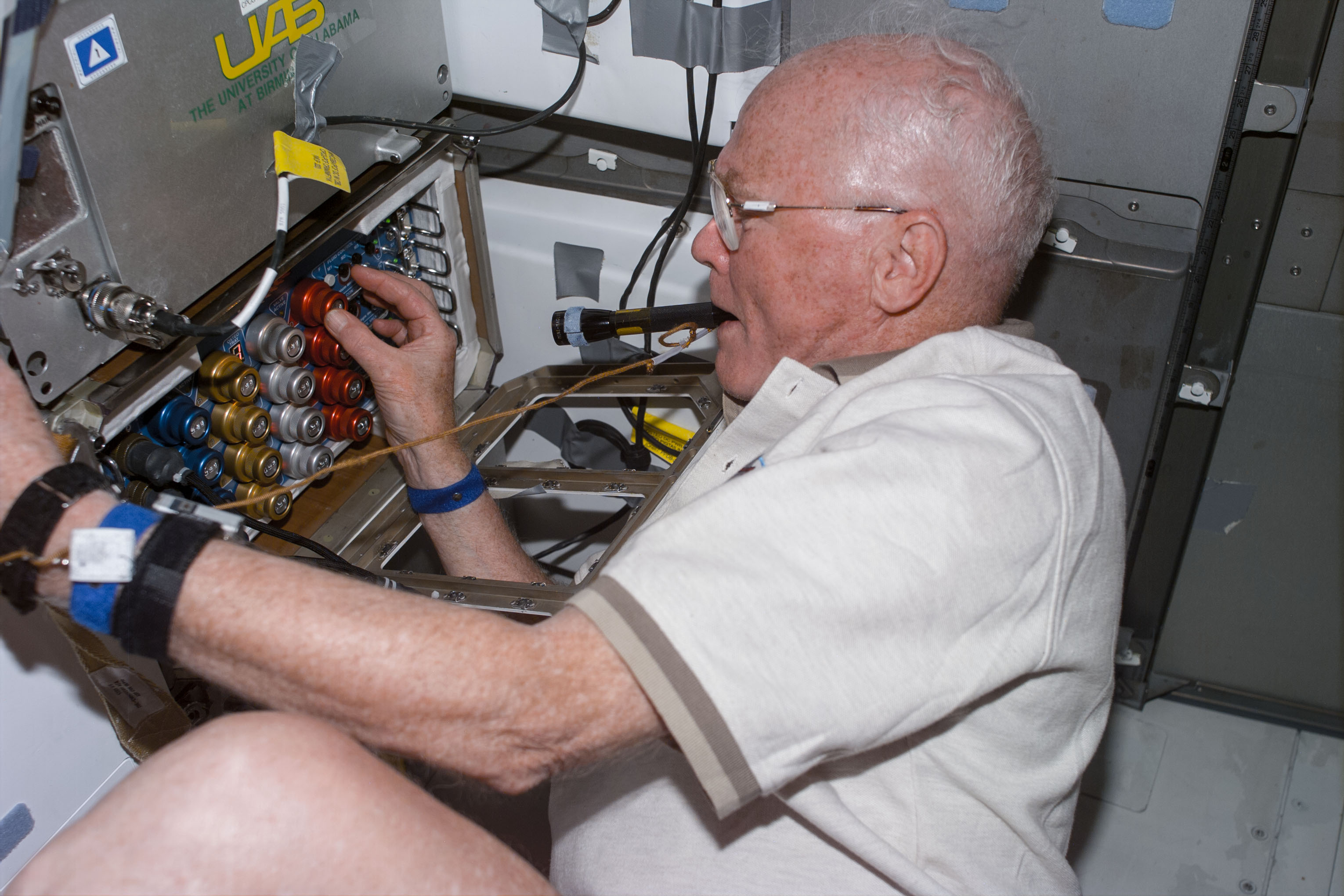


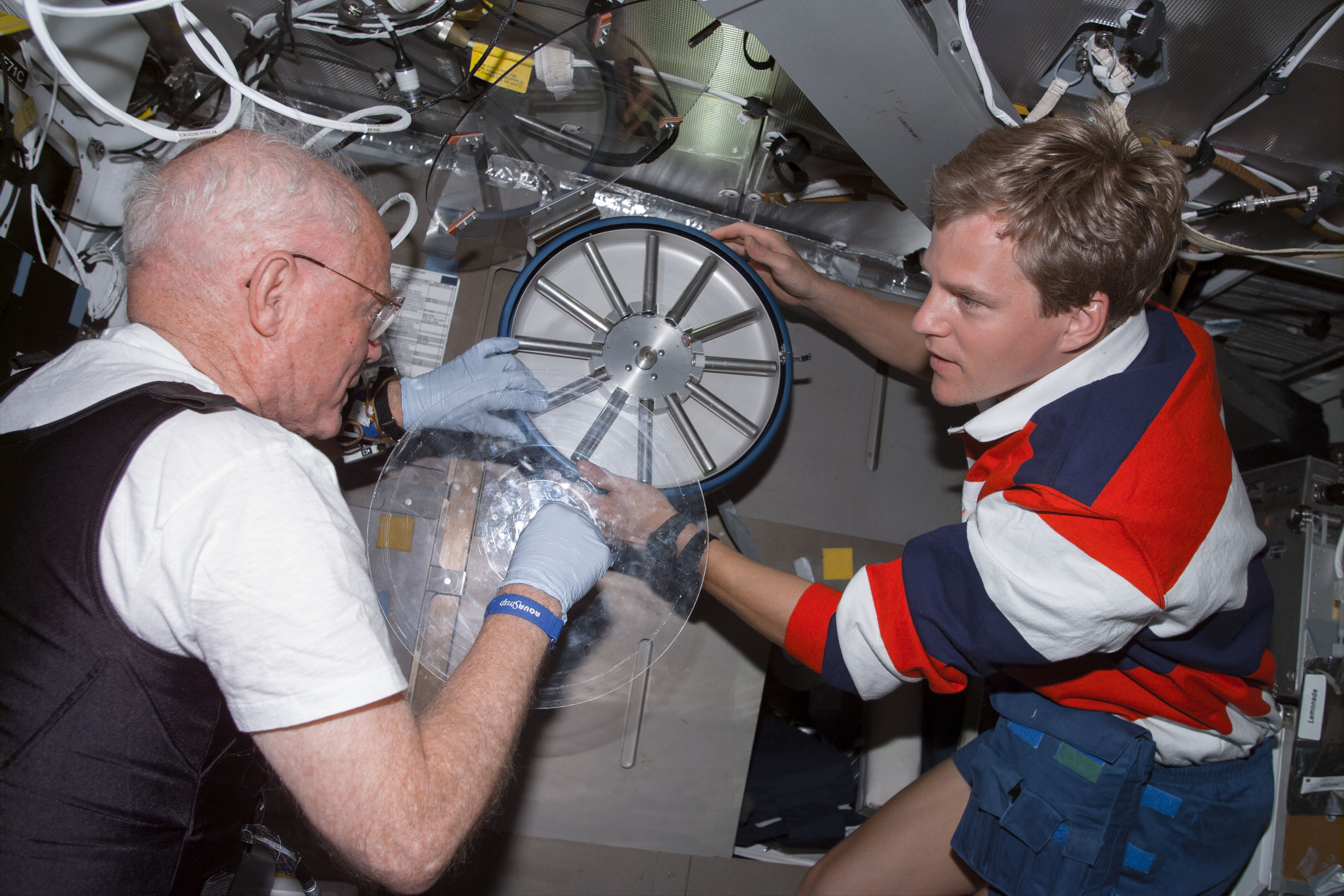
Left: Stephen K. Robinson processes a sample in the Advanced Gradient Heating Facility (AGHF). Right: John H. Glenn operates the Osteoporosis Experiment in Orbit (OSTEO) payload investigating the behavior of bone cells in microgravity.
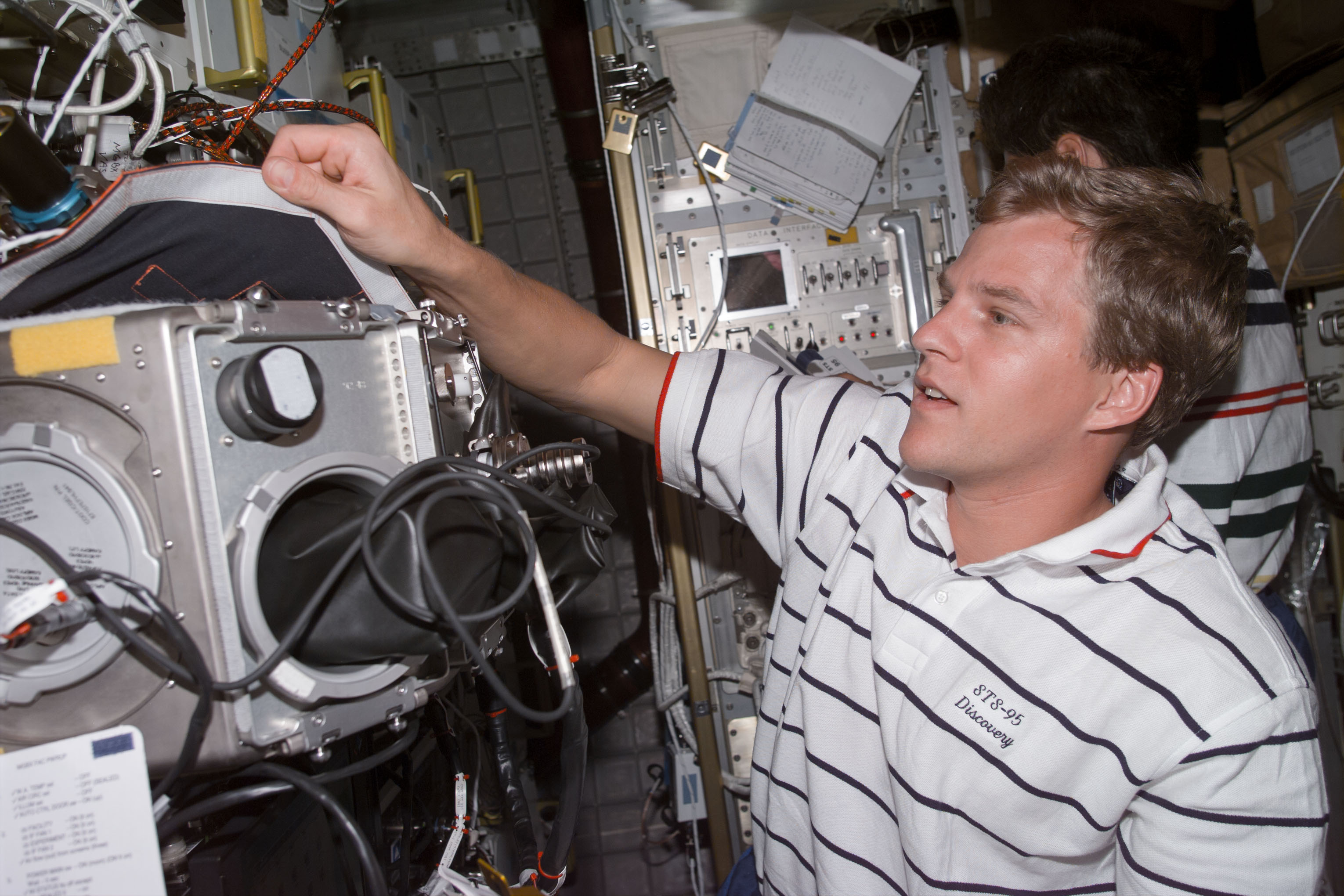
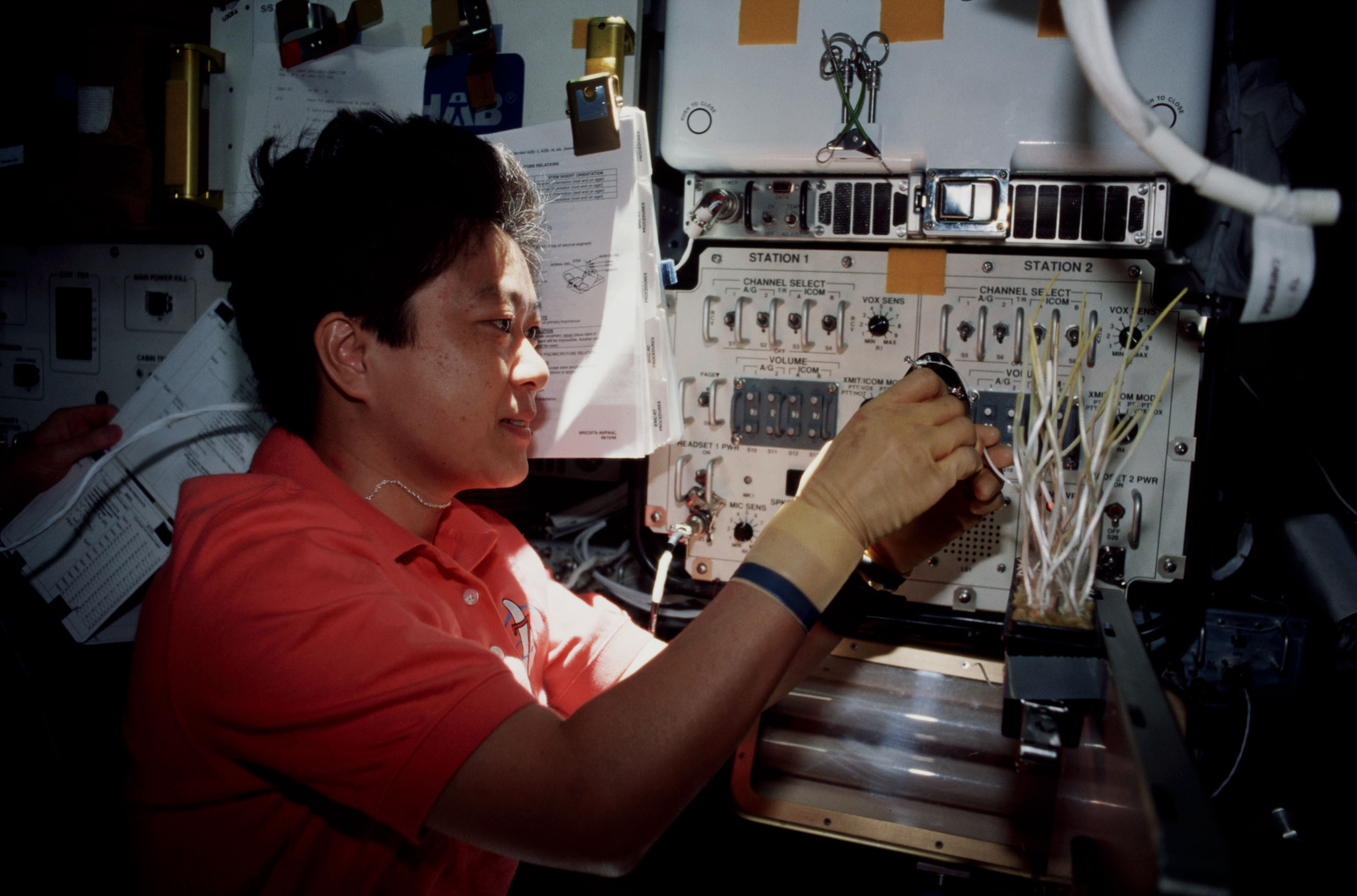


Left: Scott E. Parazynski prepares an experiment in the Microgravity Science Glovebox. Right: Chiaki Mukai examines plants grown in the Biological Research in Canisters (BRIC) experiment.
For the remainder of the mission, the seven-member crew busied itself with conducting the 80 experiments in the shuttle’s middeck, the Spacehab, and in the payload bay.
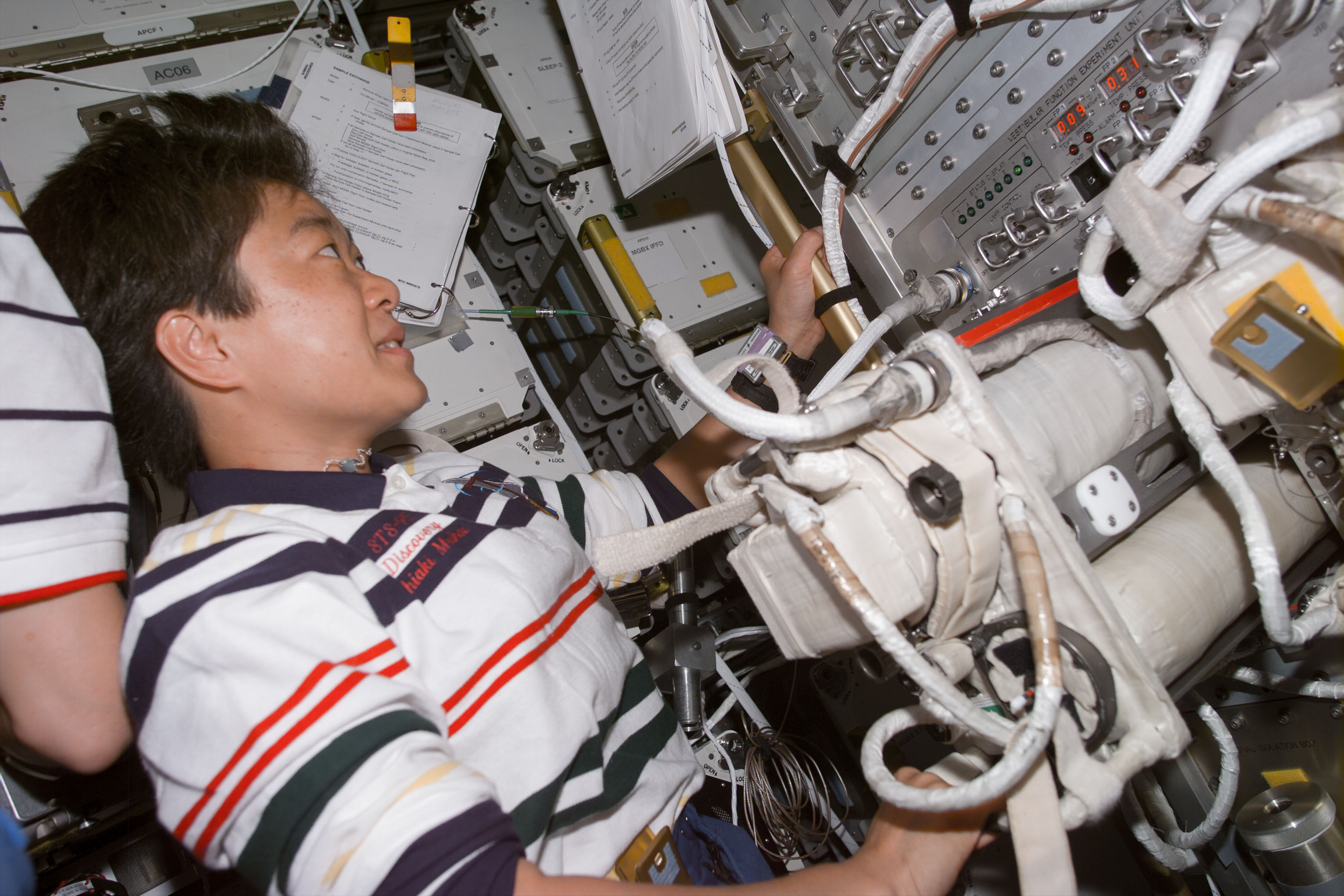
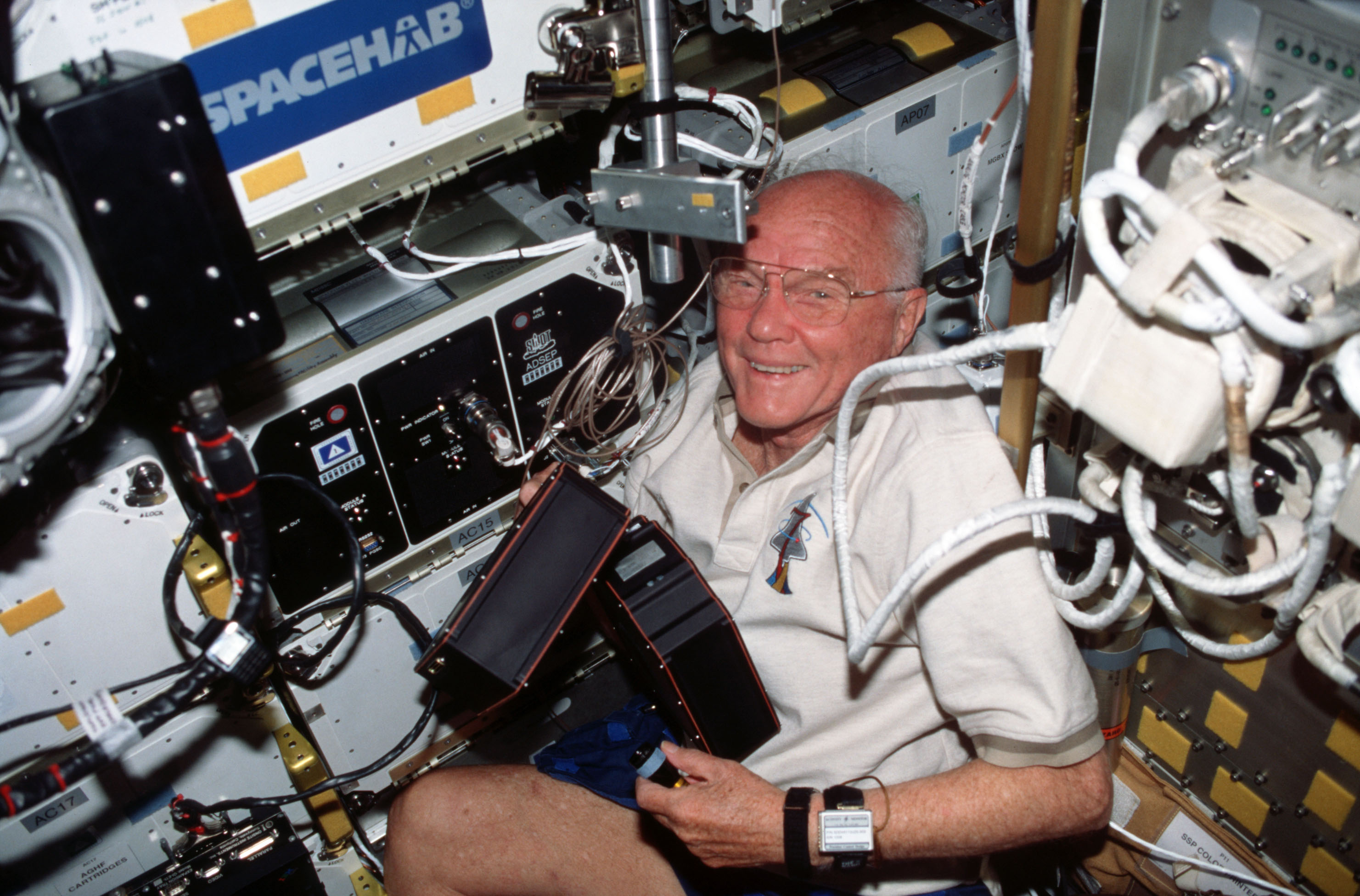
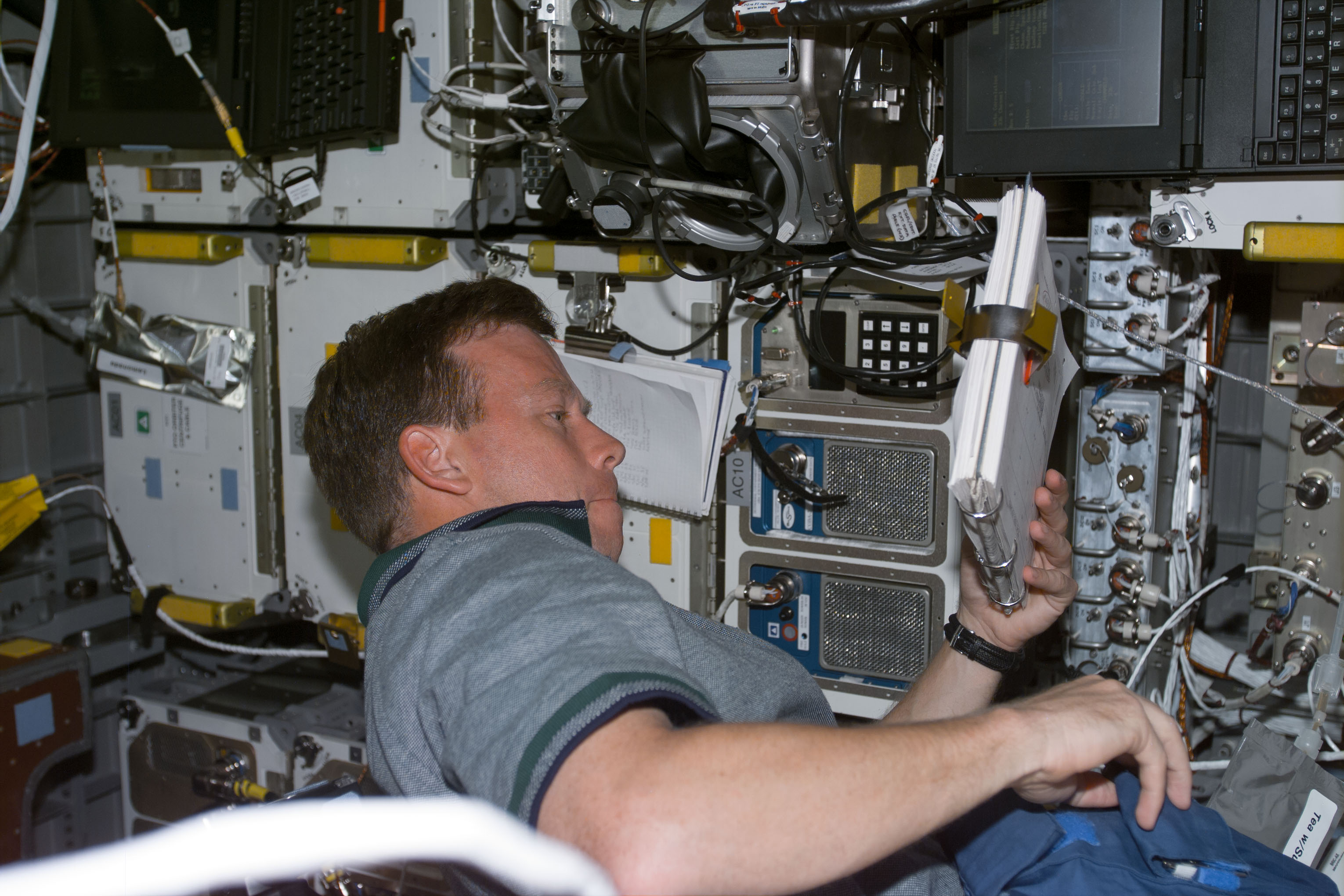



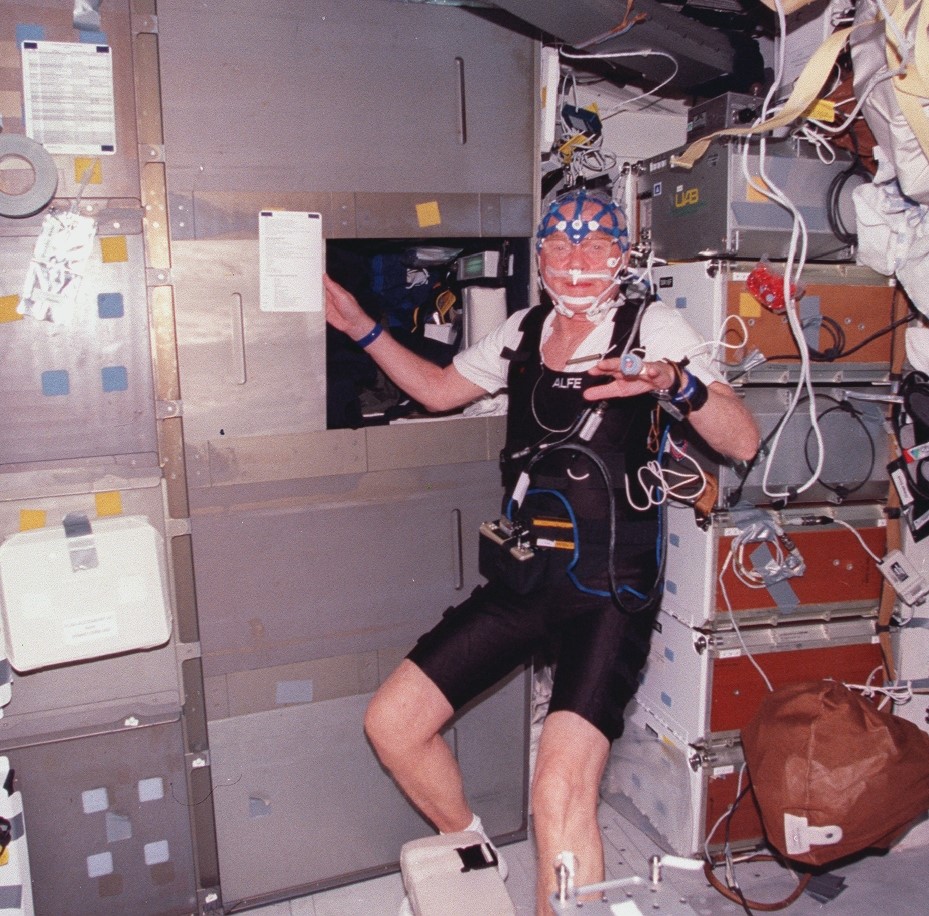
Left: Chiaki Mukai operates the Vestibular Function Experiment Unit (VFEU) investigation the vestibular systems of toadfish. Middle: John H. Glenn removes cartridges from the Advanced Separation (ADSEP) experiment. Right: Steven Lindsey operates the BIOBOX used to store biological samples.
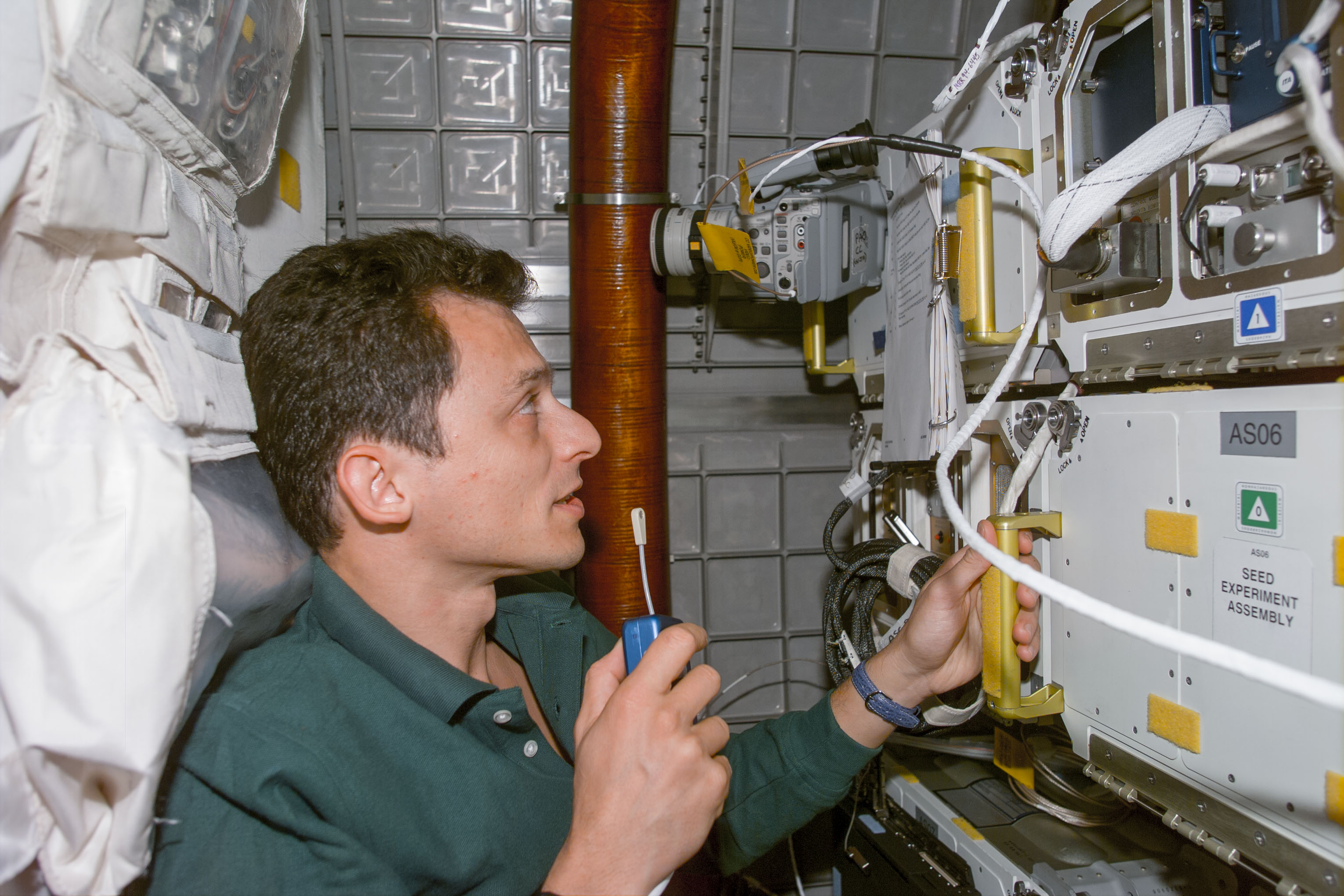
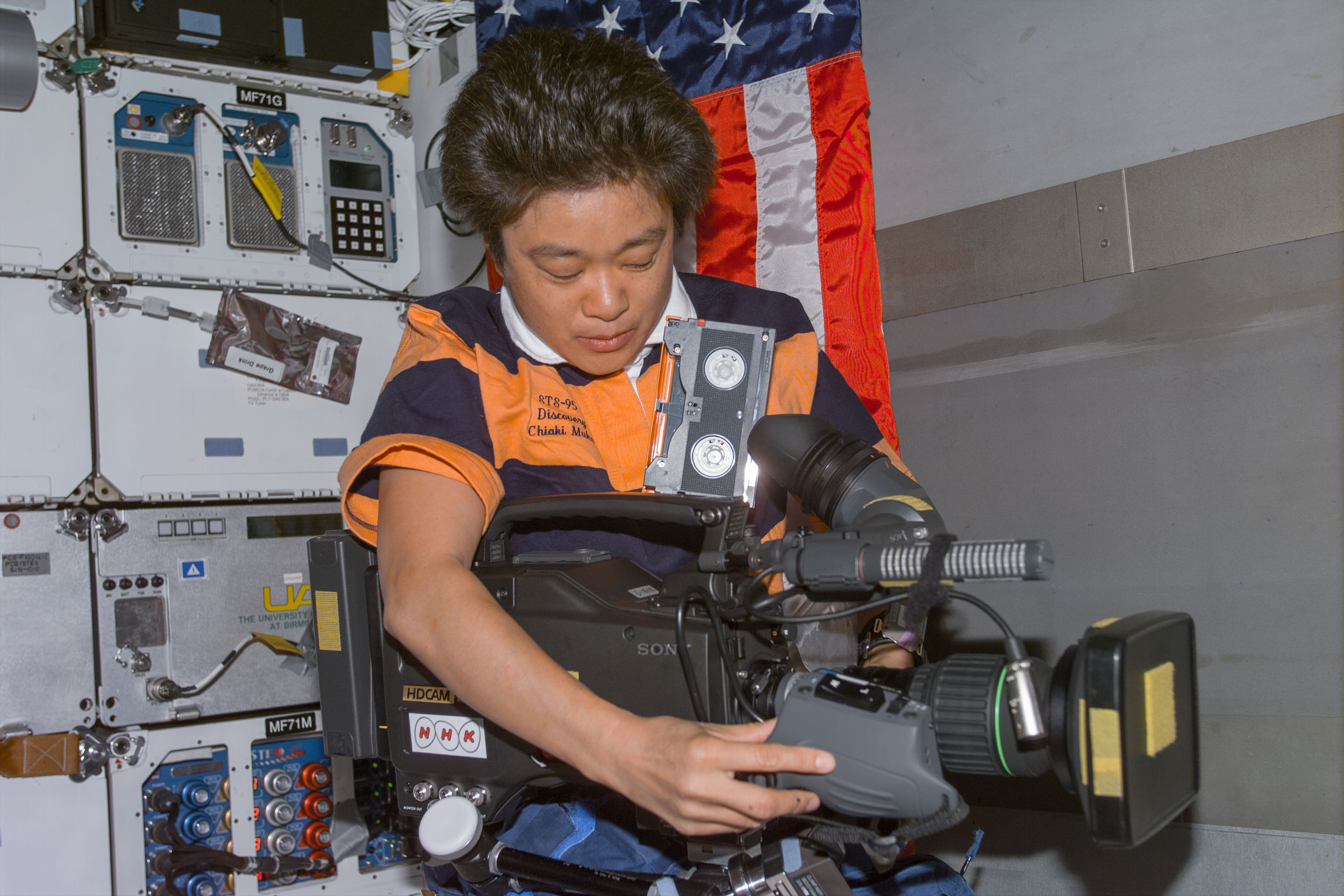
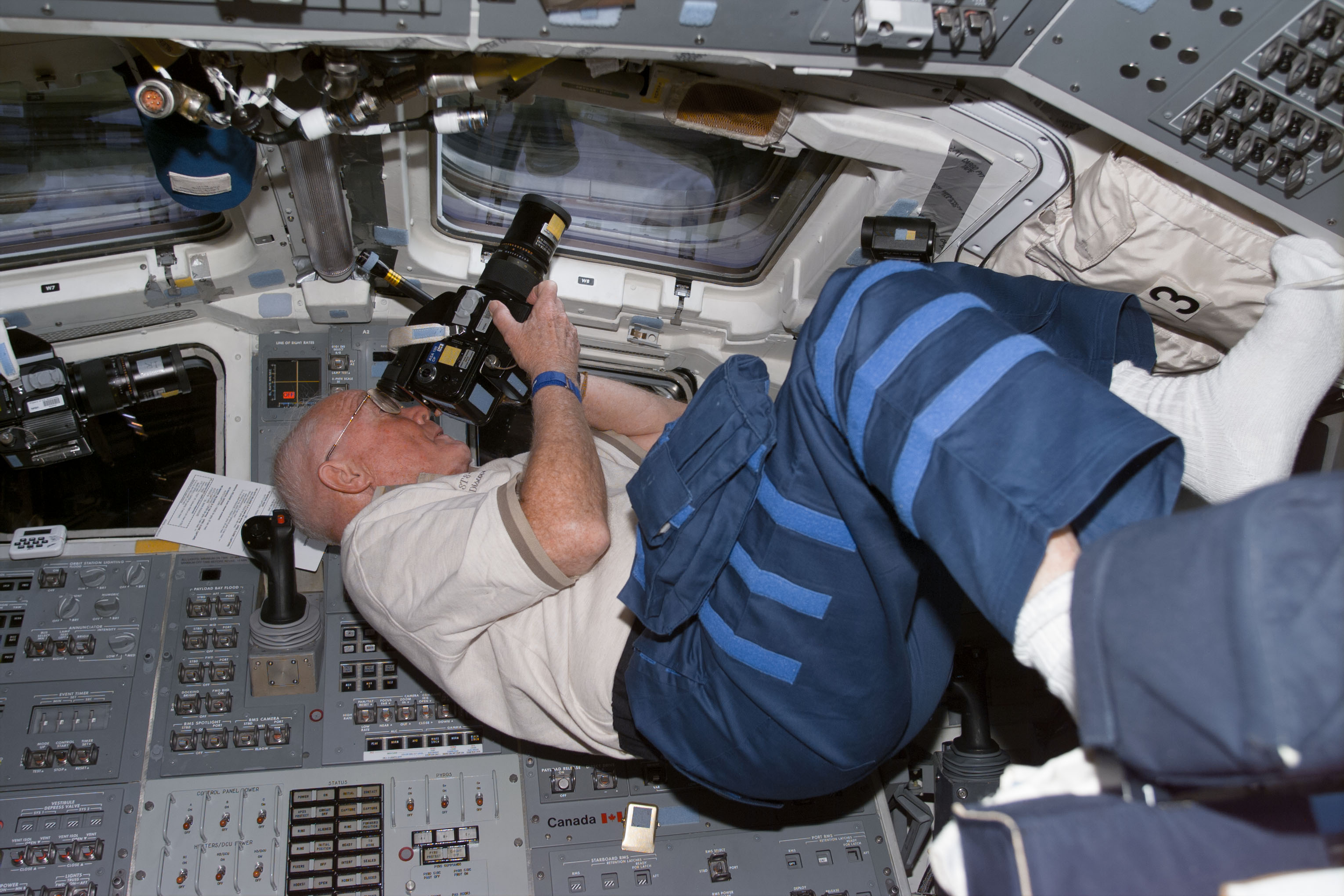



Left: Pedro F. Duque operates the Microencapsulation Electrostatic Processing System (MEPS) experiment. Middle: Chiaki Mukai operates the high-definition camcorder provided by the Japanese company NHK. Right: John H. Glenn takes one of the 2,500 Earth observation images obtained during the STS-95 mission.
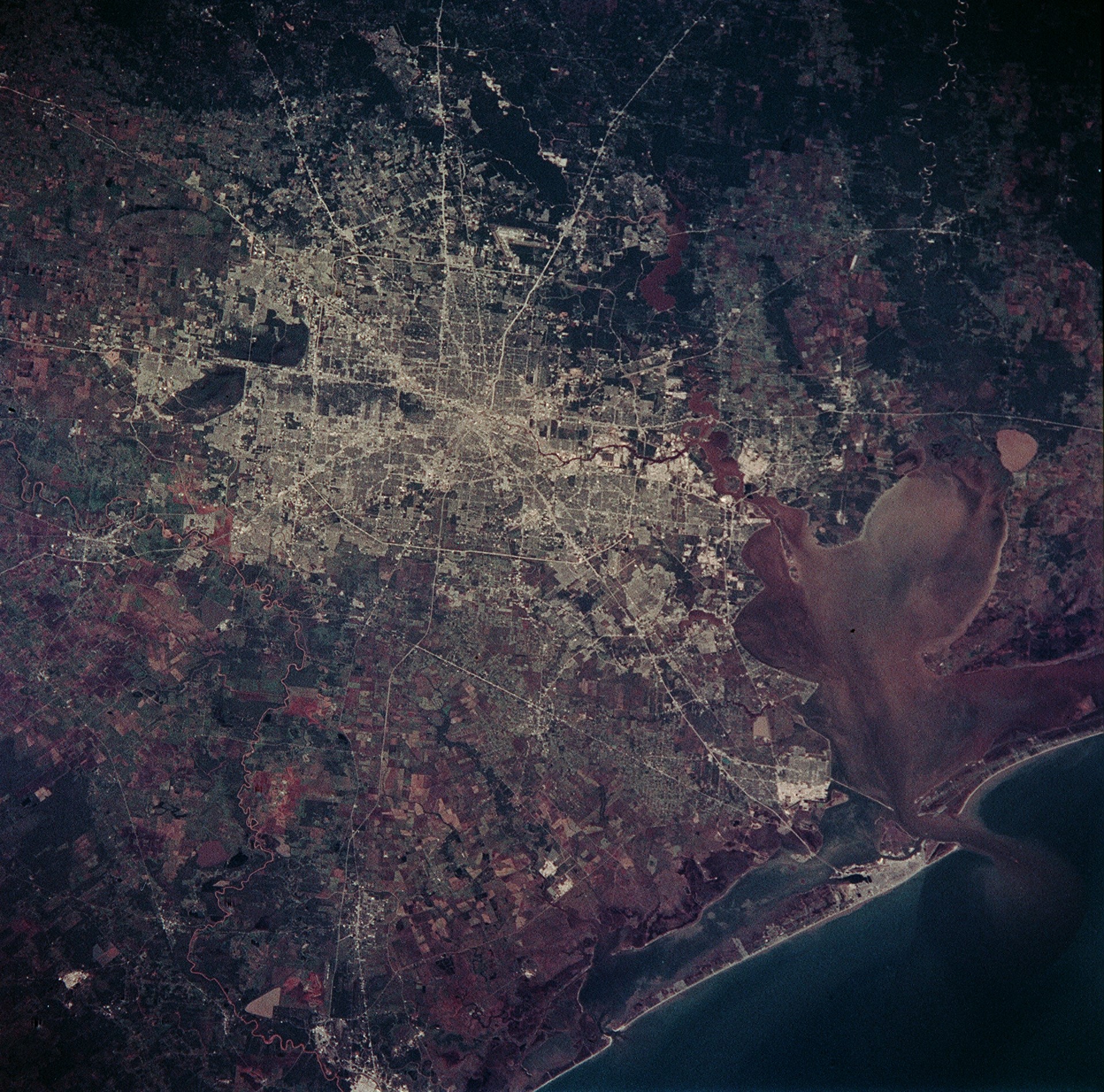
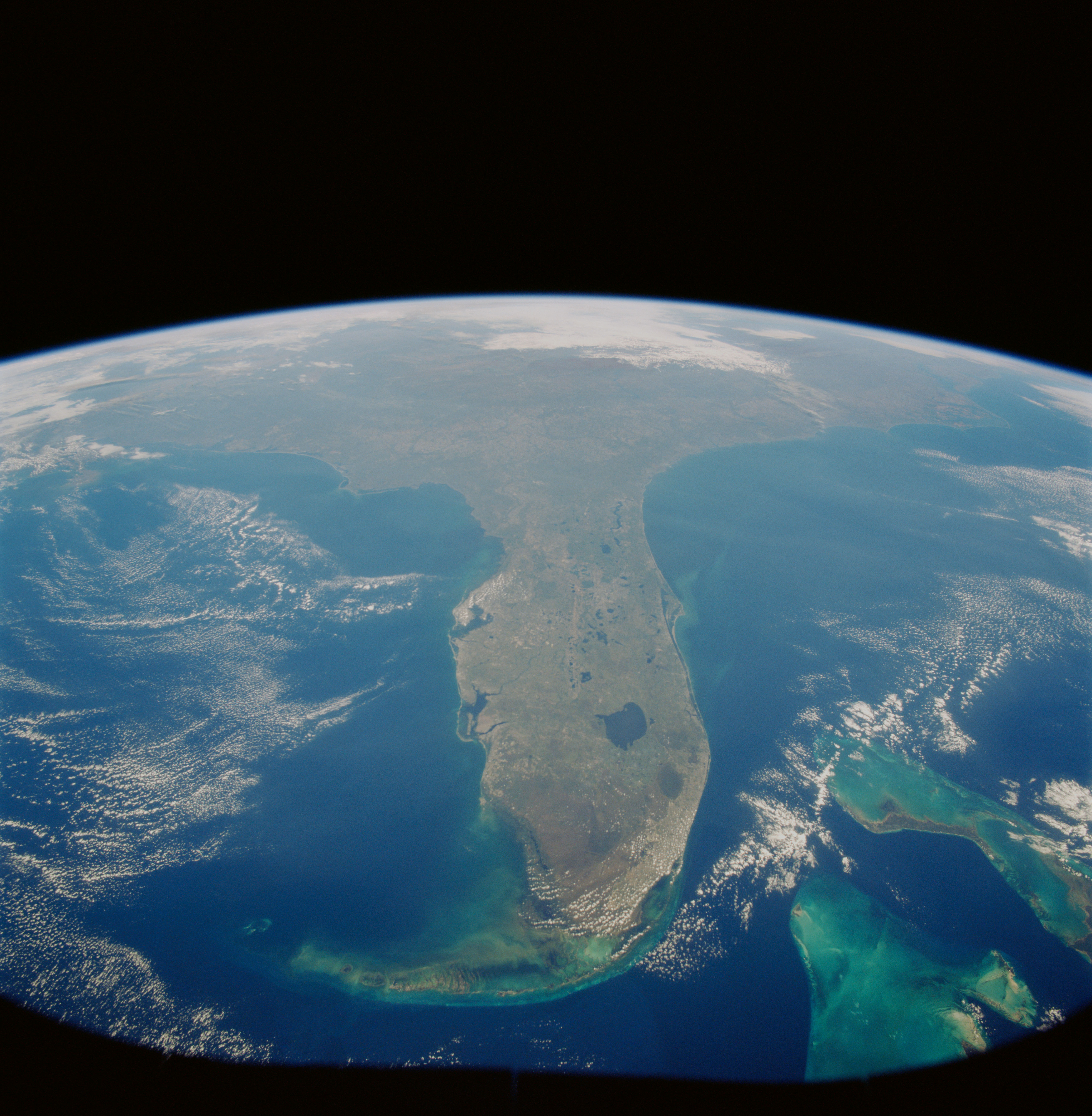
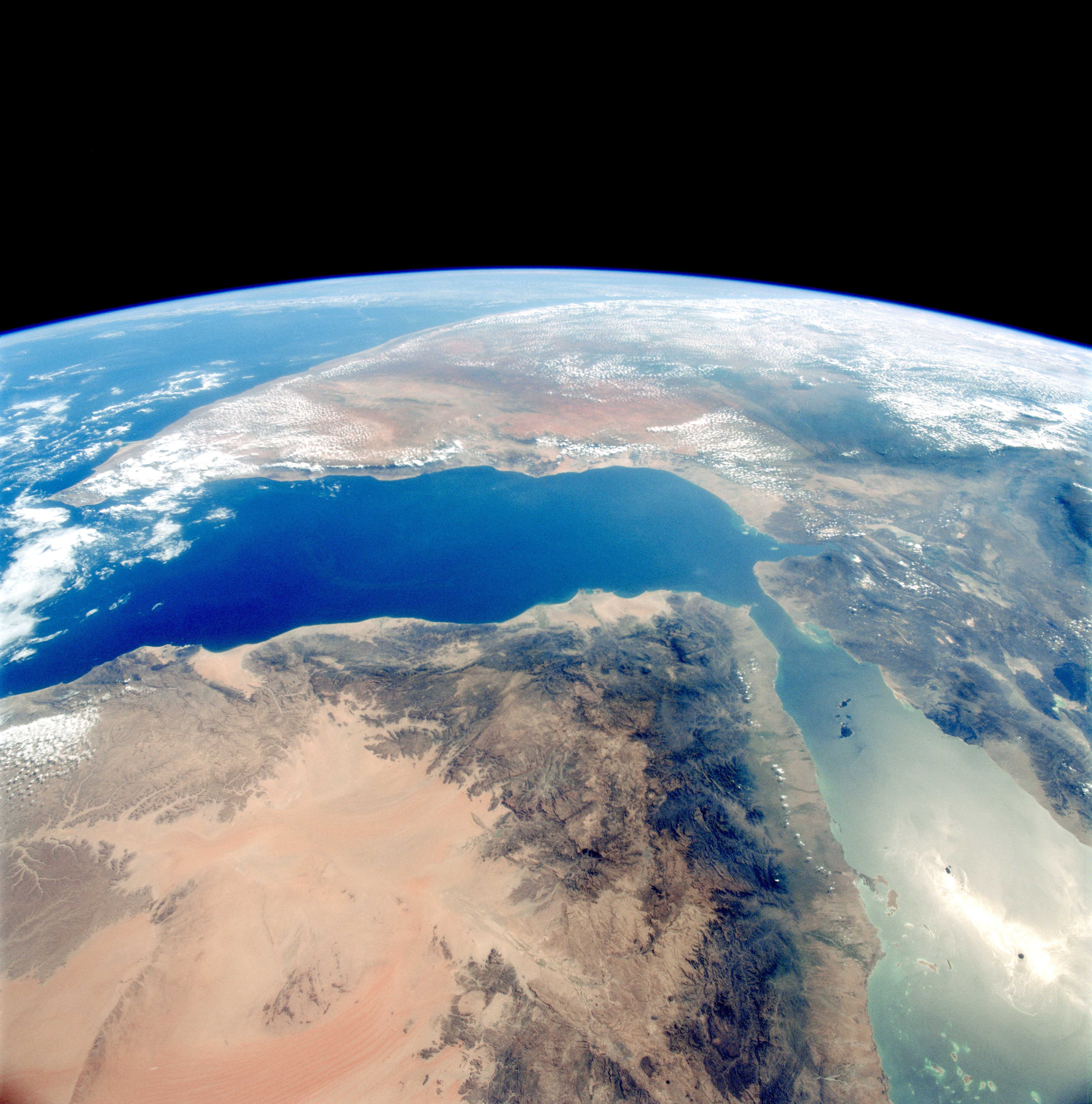




A selection of the Earth observation photographs taken by the STS-95 crew. Left: The Hawaiian Islands. Middle left: Houston. Middle right: Florida. Right: Yemen and the Horn of Africa.
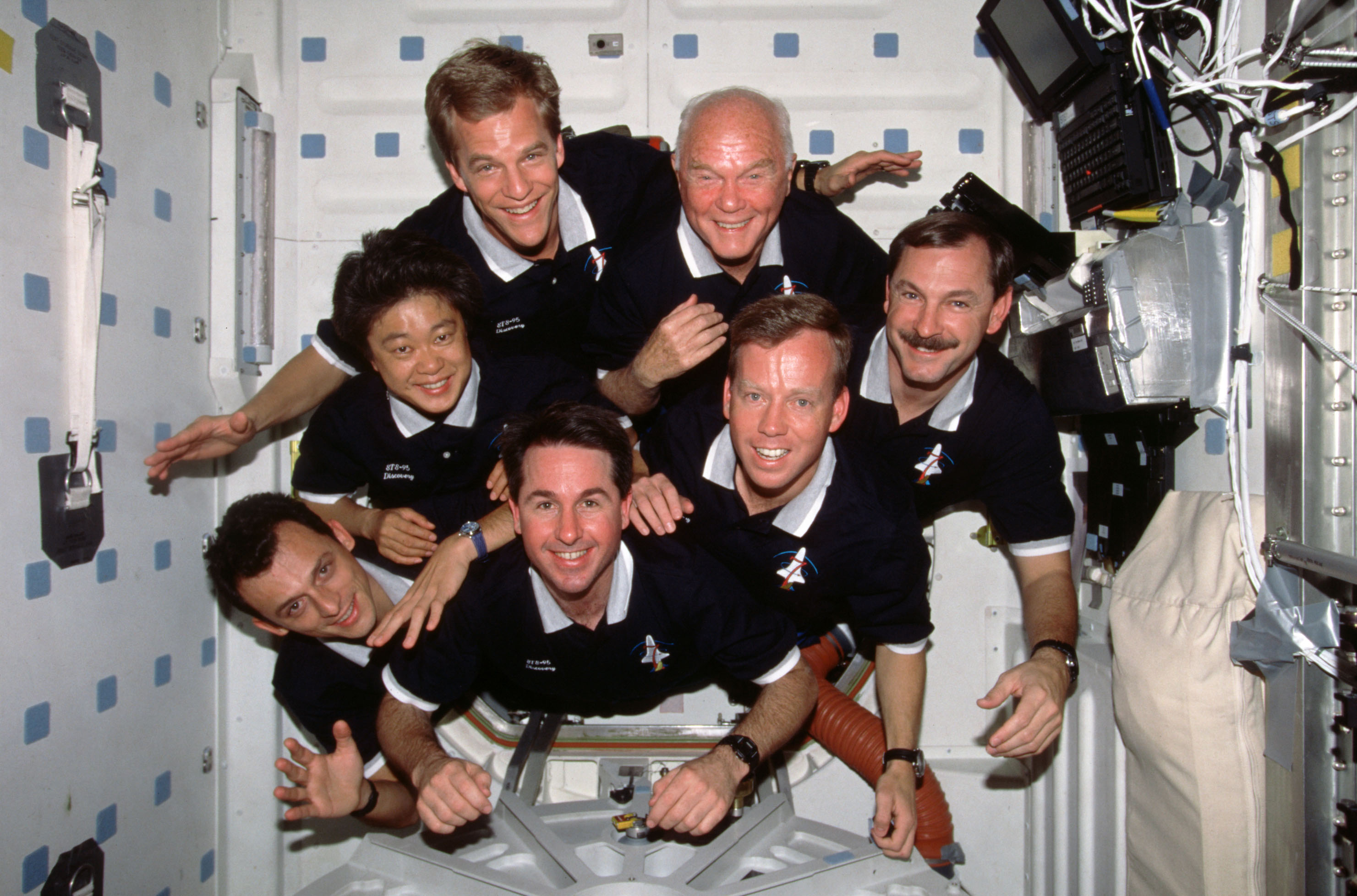
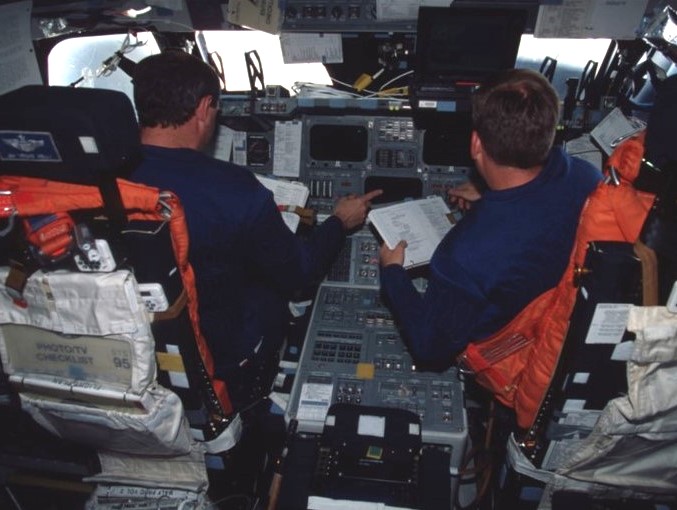
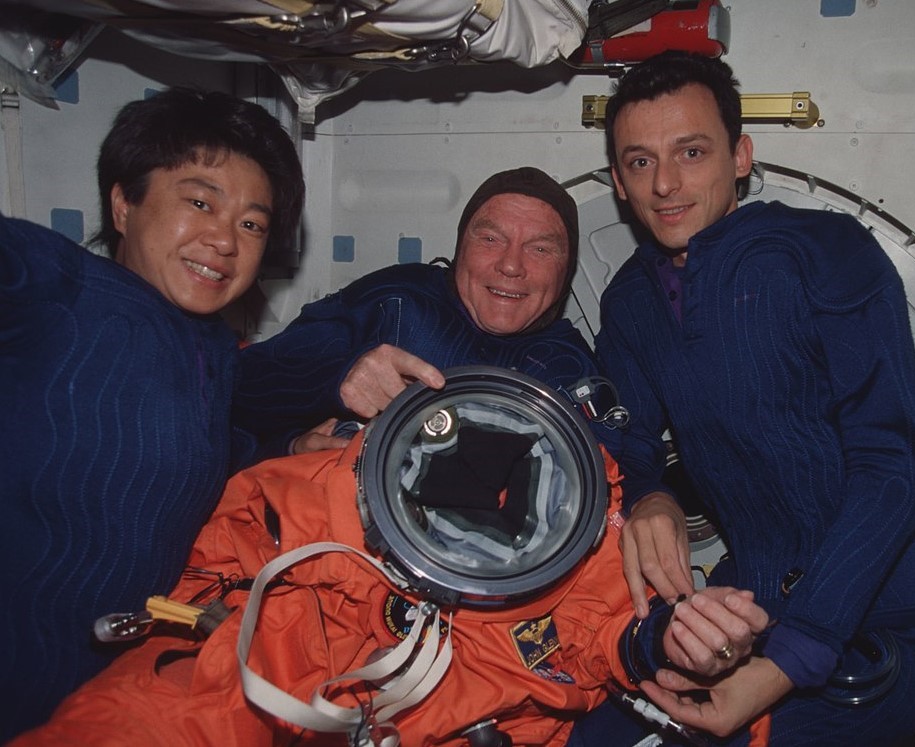



Left: STS-95 astronauts, clockwise from lower left, Pedro F. Duque, Chiaki Mukai, Scott E. Parazynski, John H. Glenn, Curtis L. Brown, Steven W. Lindsey, and Stephen K. Robinson. Middle: Brown, left, and Lindsey review entry checklists before donning their launch and entry suits in preparation for returning to Earth. Right: Mukai, left, and Duque help Glenn, center, put on his launch and entry suit for reentry.
On their last day in space, the crew finished the experiments, closed up the Spacehab module, donned their launch and entry suits, and strapped themselves into their seats to prepare for their return to Earth. They fired the shuttle’s Orbital Maneuvering System engines to begin the descent from orbit. Brown piloted Discovery to a smooth landing at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility on Nov. 7, after completing 134 orbits around the Earth in 8 days, 21 hours, and 44 minutes. The astronauts exited Discovery about one hour after landing and immediately began their postflight data collection to measure their immediate physiological responses after returning to a 1 g environment. Ground crews towed Discovery to the Orbiter Processing Facility to begin preparing it for its next mission, STS-96, the first shuttle docking to the International Space Station. The astronauts returned to Houston’s Ellington Field, where a large crowd of well-wishers, including government officials and the media, welcomed them home.
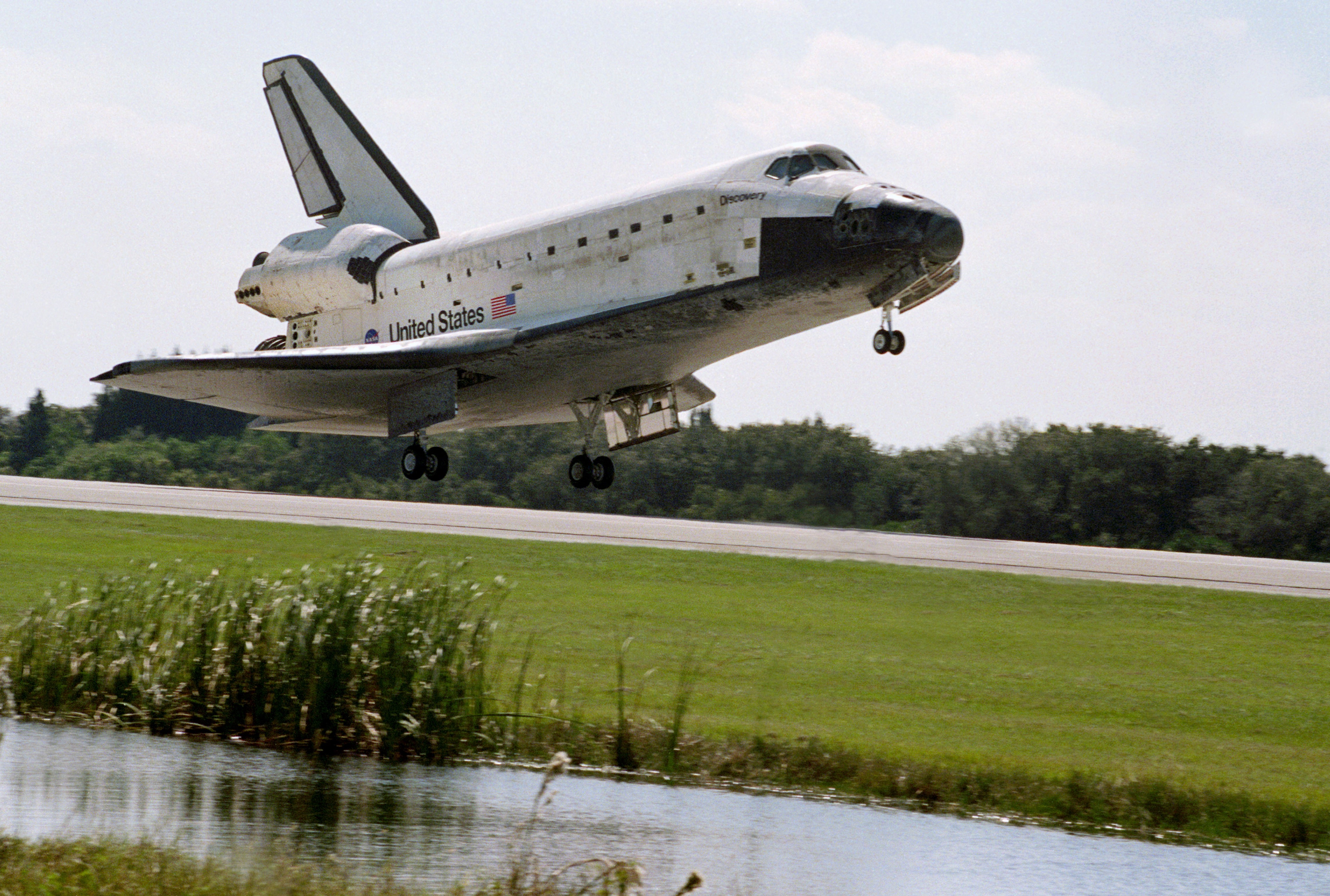
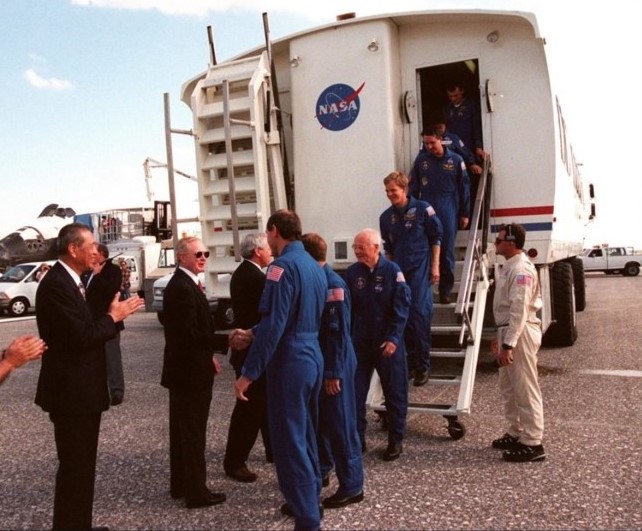
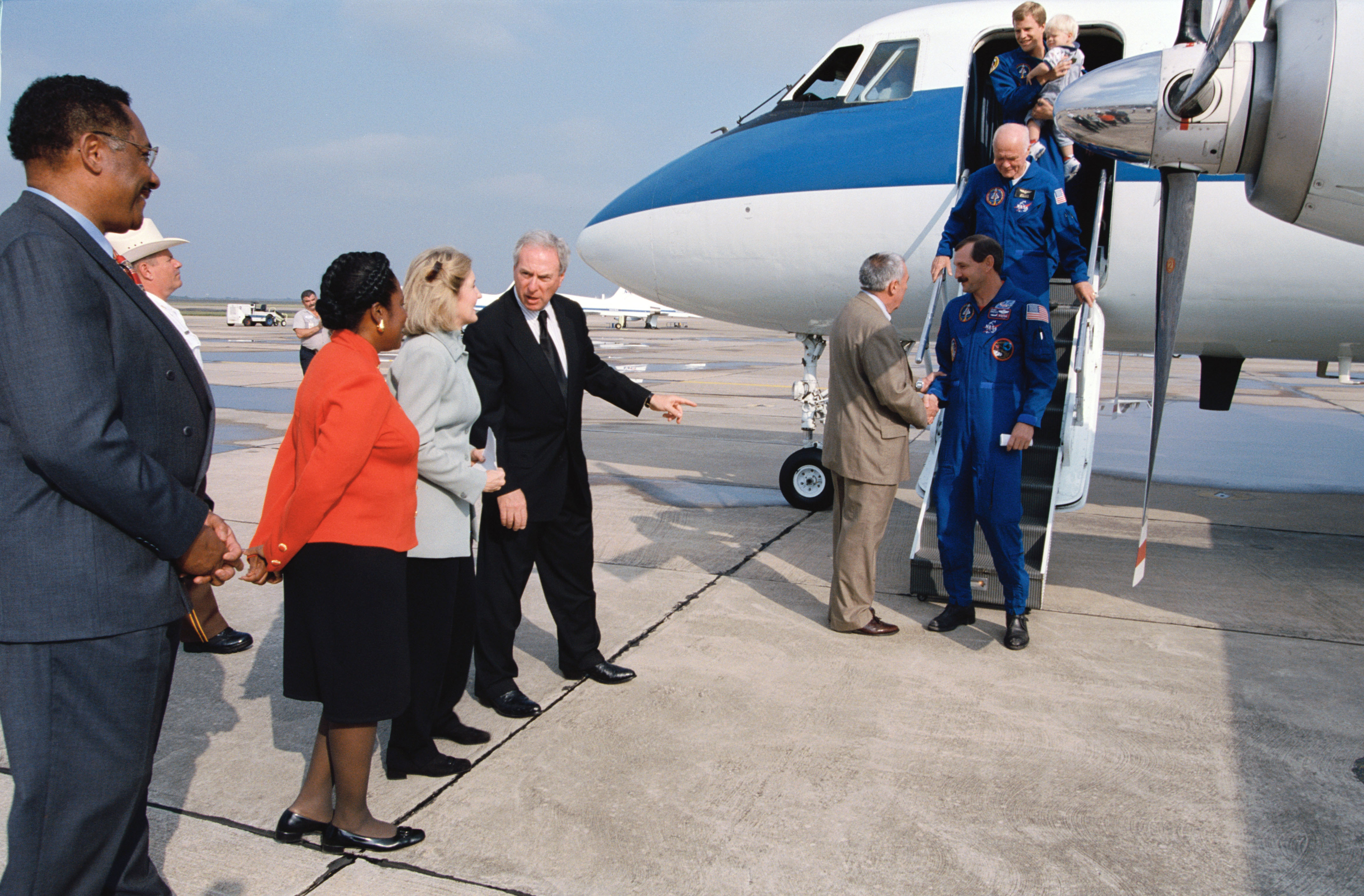



Left: Space Shuttle Discovery lands at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida to end the nine-day STS-95 mission. Middle: Dignitaries including Isao Uchida, president of Japan’s National Space Development Agency, KSC Director Roy D. Bridges, and NASA Administrator Daniel S. Goldin greet the returning STS-95 crew after their landing. Right: Dignitaries including Houston Mayor Lee P. Brown, left, U.S. Representative Sheila Jackson Lee, U.S. Senator Kay Bailey Hutchison, Administrator Goldin, and Johnson Space Center Director George W.S. Abbey greet the STS-95 crew at Ellington Field in Houston.
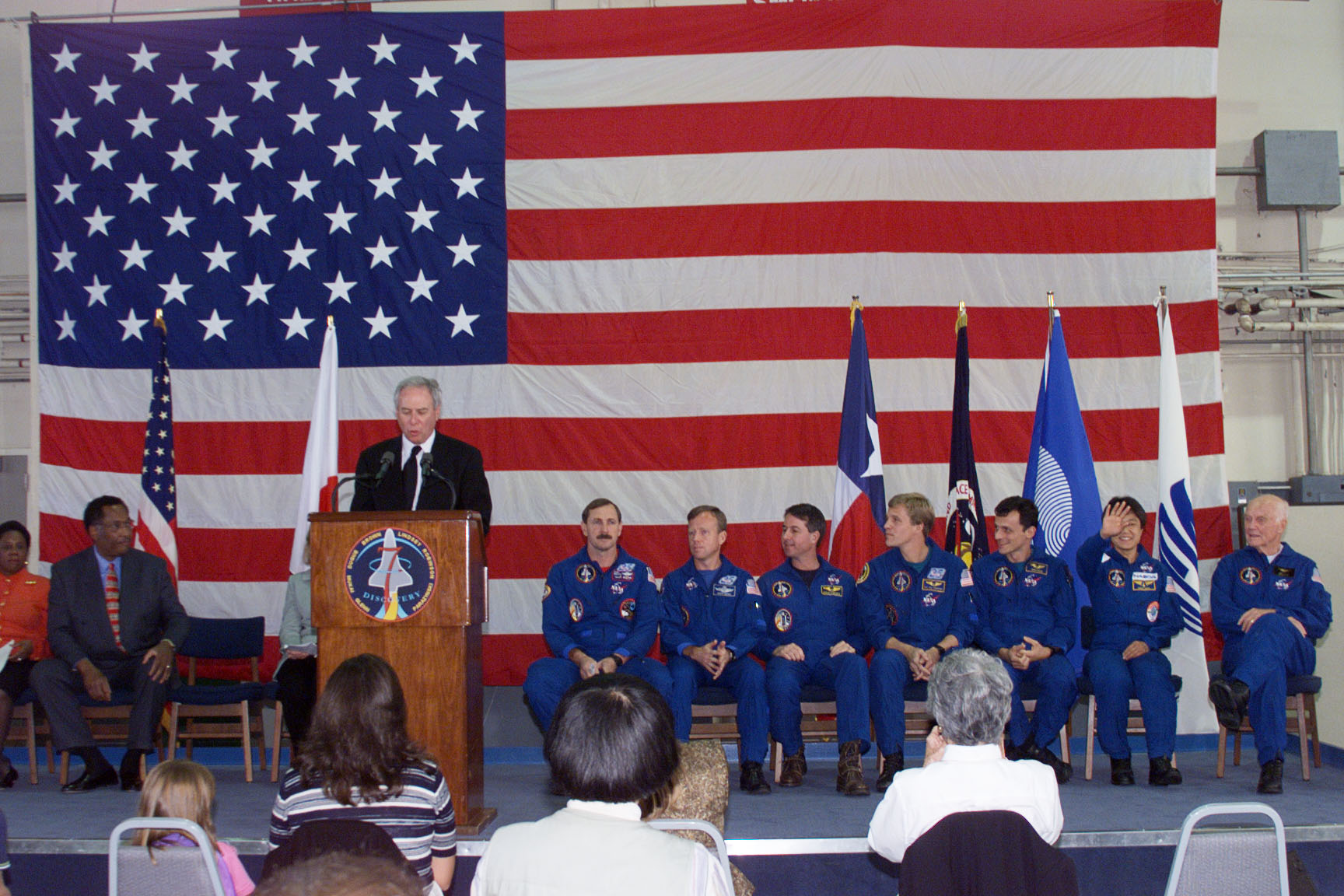


Left: U.S. Senator Kay Bailey Hutchison addresses the crowd at Ellington Field gathered to welcome the STS-95 crew back to Houston. Right: NASA Administrator Daniel S. Goldin addresses the crowd at Ellington as the STS-95 astronauts listen.
Enjoy the crew-narrated video about the STS-95 mission.
What's Your Reaction?